Related Research Articles
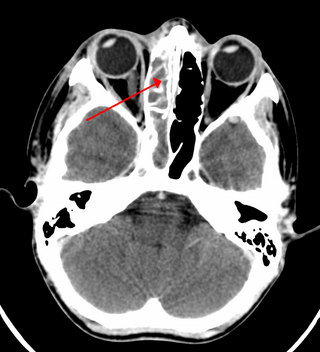
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is an inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain.

Trismus is a condition of restricted opening of the mouth. The term was initially used in the setting of tetanus. Trismus may be caused by spasm of the muscles of mastication or a variety of other causes. Temporary trismus occurs much more frequently than permanent trismus. It is known to interfere with eating, speaking, and maintaining proper oral hygiene. This interference, specifically with an inability to swallow properly, results in an increased risk of aspiration. In some instances, trismus presents with altered facial appearance. The condition may be distressing and painful. Examination and treatments requiring access to the oral cavity can be limited, or in some cases impossible, due to the nature of the condition itself.

Acute septic arthritis, infectious arthritis, suppurative arthritis, pyogenic arthritis, osteomyelitis, or joint infection is the invasion of a joint by an infectious agent resulting in joint inflammation. Generally speaking, symptoms typically include redness, heat and pain in a single joint associated with a decreased ability to move the joint. Onset is usually rapid. Other symptoms may include fever, weakness and headache. Occasionally, more than one joint may be involved, especially in neonates, younger children and immunocompromised individuals. In neonates, infants during the first year of life, and toddlers, the signs and symptoms of septic arthritis can be deceptive and mimic other infectious and non-infectious disorders.

Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the feet, spine, and hips are most commonly involved in adults.

Toothache, also known as dental pain or tooth pain, is pain in the teeth or their supporting structures, caused by dental diseases or pain referred to the teeth by non-dental diseases. When severe it may impact sleep, eating, and other daily activities.

Alveolar osteitis, also known as dry socket, is inflammation of the alveolar bone. Classically, this occurs as a postoperative complication of tooth extraction.

The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, located in the maxilla. It drains into the middle meatus of the nose through the semilunar hiatus. It is located to the side of the nasal cavity, and below the orbit.

A dental extraction is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease, or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache. Sometimes impacted wisdom teeth cause recurrent infections of the gum (pericoronitis), and may be removed when other conservative treatments have failed. In orthodontics, if the teeth are crowded, healthy teeth may be extracted to create space so the rest of the teeth can be straightened.

Pericoronitis is inflammation of the soft tissues surrounding the crown of a partially erupted tooth, including the gingiva (gums) and the dental follicle. The soft tissue covering a partially erupted tooth is known as an operculum, an area which can be difficult to access with normal oral hygiene methods. The hyponym operculitis technically refers to inflammation of the operculum alone.

A Brodie abscess is a subacute osteomyelitis, appearing as an accumulation of pus in bone, frequently with an insidious onset. Brodie's abscess is characterized by pain and swelling without fever, often resulting from diabetic wounds, fracture-related bone infection, or haematogenous osteomyelitis.
Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) is a severe bone disease (osteonecrosis) that affects the jaws. Various forms of ONJ have been described since 1861, and a number of causes have been suggested in the literature.
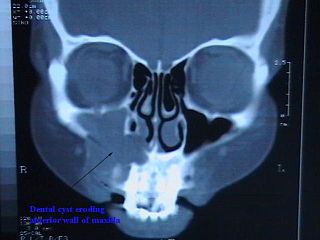
Commonly known as a dental cyst, the periapical cyst is the most common odontogenic cyst. It may develop rapidly from a periapical granuloma, as a consequence of untreated chronic periapical periodontitis.

A dental abscess is a localized collection of pus associated with a tooth. The most common type of dental abscess is a periapical abscess, and the second most common is a periodontal abscess. In a periapical abscess, usually the origin is a bacterial infection that has accumulated in the soft, often dead, pulp of the tooth. This can be caused by tooth decay, broken teeth or extensive periodontal disease. A failed root canal treatment may also create a similar abscess.
Mouth infections, also known as oral infections, are a group of infections that occur around the oral cavity. They include dental infection, dental abscess, and Ludwig's angina. Mouth infections typically originate from dental caries at the root of molars and premolars that spread to adjacent structures. In otherwise healthy patients, removing the offending tooth to allow drainage will usually resolve the infection. In cases that spread to adjacent structures or in immunocompromised patients, surgical drainage and systemic antibiotics may be required in addition to tooth extraction. Since bacteria that normally reside in the oral cavity cause mouth infections, proper dental hygiene can prevent most cases of infection. As such, mouth infections are more common in populations with poor access to dental care or populations with health-related behaviors that damage one's teeth and oral mucosa. This is a common problem, representing nearly 36% of all encounters within the emergency department related to dental conditions.
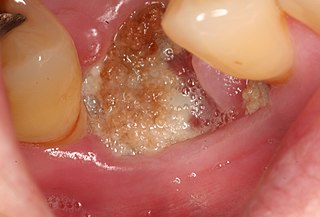
Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw is progressive death of the jawbone in a person exposed to a medication known to increase the risk of disease, in the absence of a previous radiation treatment. It may lead to surgical complication in the form of impaired wound healing following oral and maxillofacial surgery, periodontal surgery, or endodontic therapy.

Mandibular fracture, also known as fracture of the jaw, is a break through the mandibular bone. In about 60% of cases the break occurs in two places. It may result in a decreased ability to fully open the mouth. Often the teeth will not feel properly aligned or there may be bleeding of the gums. Mandibular fractures occur most commonly among males in their 30s.
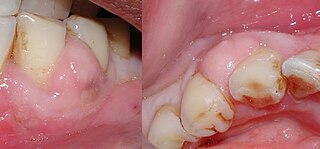
A periodontal abscess, is a localized collection of pus within the tissues of the periodontium. It is a type of dental abscess. A periodontal abscess occurs alongside a tooth, and is different from the more common periapical abscess, which represents the spread of infection from a dead tooth. To reflect this, sometimes the term "lateral (periodontal) abscess" is used. In contrast to a periapical abscess, periodontal abscesses are usually associated with a vital (living) tooth. Abscesses of the periodontium are acute bacterial infections classified primarily by location.
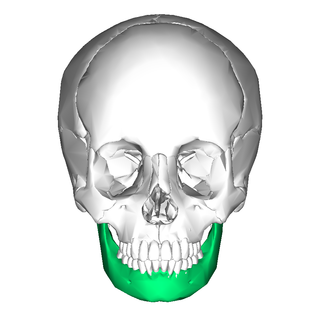
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible, lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lower – and typically more mobile – component of the mouth.
Cysts of the jaws are cysts—pathological epithelial-lined cavities filled with fluid or soft material—occurring on the bones of the jaws, the mandible and maxilla. Those are the bones with the highest prevalence of cysts in the human body, due to the abundant amount of epithelial remnants that can be left in the bones of the jaws. The enamel of teeth is formed from ectoderm, and so remnants of epithelium can be left in the bone during odontogenesis. The bones of the jaws develop from embryologic processes which fuse, and ectodermal tissue may be trapped along the lines of this fusion. This "resting" epithelium is usually dormant or undergoes atrophy, but, when stimulated, may form a cyst. The reasons why resting epithelium may proliferate and undergo cystic transformation are generally unknown, but inflammation is thought to be a major factor. The high prevalence of tooth impactions and dental infections that occur in the bones of the jaws is also significant to explain why cysts are more common at these sites.

Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) is a serious complication of radiation therapy in cancer treatment where radiated bone becomes necrotic and exposed. ORN occurs most commonly in the mouth during the treatment of head and neck cancer, and can arise over 5 years after radiation. Common signs and symptoms include pain, difficulty chewing, trismus, mouth-to-skin fistulas and non-healing ulcers.
References
- ↑ Peravali RK, Jayade B, Joshi A, Shirganvi M, Bhasker Rao C, Gopalkrishnan K (1 October 2011). "Osteomyelitis of Maxilla in Poorly Controlled Diabetics in a Rural Indian Population". Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery. 11 (1): 57–66. doi:10.1007/s12663-011-0283-0. PMC 3319832 . PMID 23449555.
- ↑ Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CA, Bouquot JE (2002). Oral & maxillofacial pathology (2nd ed.). Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders. pp. 126–132. ISBN 0721690033.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Topazian RG, Goldberg MH, Hupp JR (2002). Oral and maxillofacial infections (4th ed.). Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders. pp. 214–235. ISBN 978-0721692715.