
The salivary glands in many vertebrates including mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands, as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary glands can be classified as serous, mucous, or seromucous (mixed).

The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secretes serous saliva through the parotid duct into the mouth, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and sublingual glands. Sometimes accessory parotid glands are found close to the main parotid glands.

Adenoid cystic carcinoma is a rare type of cancer that can exist in many different body sites. This tumor most often occurs in the salivary glands, but it can also be found in many anatomic sites, including the breast, lacrimal gland, lung, brain, Bartholin gland, trachea, and the paranasal sinuses.

Invasive carcinoma of no special type, invasive breast carcinoma of no special type (IBC-NST), invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), infiltrating ductal carcinoma (IDC) or invasive ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified (NOS) is a disease. For international audiences this article will use "invasive carcinoma NST" because it is the preferred term of the World Health Organization (WHO).

A hemangiopericytoma is a type of soft-tissue sarcoma that originates in the pericytes in the walls of capillaries. When inside the nervous system, although not strictly a meningioma tumor, it is a meningeal tumor with a special aggressive behavior. It was first characterized in 1942.

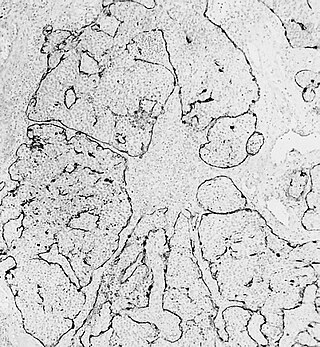
Pleomorphic adenoma is a common benign salivary gland neoplasm characterised by neoplastic proliferation of epithelial (ductal) cells along with myoepithelial components, having a malignant potentiality. It is the most common type of salivary gland tumor and the most common tumor of the parotid gland. It derives its name from the architectural Pleomorphism seen by light microscopy. It is also known as "Mixed tumor, salivary gland type", which refers to its dual origin from epithelial and myoepithelial elements as opposed to its pleomorphic appearance.

Papillary thyroid cancer is the most common type of thyroid cancer, representing 75 percent to 85 percent of all thyroid cancer cases. It occurs more frequently in women and presents in the 20–55 year age group. It is also the predominant cancer type in children with thyroid cancer, and in patients with thyroid cancer who have had previous radiation to the head and neck. It is often well-differentiated, slow-growing, and localized, although it can metastasize.

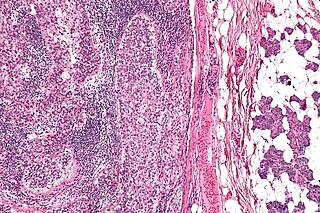
Acinic cell carcinoma is a malignant tumor representing 2% of all salivary tumors. 90% of the time found in the parotid gland, 10% intraorally on buccal mucosa or palate. The disease presents as a slow growing mass, associated with pain or tenderness in 50% of the cases. Often appears pseudoencapsulated.

CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 1 (CRTC1), previously referred to as TORC1 (Transducer Of Regulated CREB activity 1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CRTC1 gene. It is expressed in a limited number of tissues that include fetal brain and liver and adult heart, skeletal muscles, liver and salivary glands and various regions of the adult central nervous system.

Salivary gland tumours, also known as mucous gland adenomas or neoplasms, are tumours that form in the tissues of salivary glands. The salivary glands are classified as major or minor. The major salivary glands consist of the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. The minor salivary glands consist of 800 to 1000 small mucus-secreting glands located throughout the lining of the oral cavity. Patients with these types of tumours may be asymptomatic.

Mastermind-like protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MAML2 gene.
Esthesioneuroblastoma is a rare cancer of the nasal cavity. Arising from the upper nasal tract, esthesioneuroblastoma is believed to originate from sensory neuroepithelial cells, also known as neuroectodermal olfactory cells.
Sebaceous carcinoma, also known as sebaceous gland carcinoma (SGc), sebaceous cell carcinoma, and meibomian gland carcinoma is an uncommon malignant cutaneous tumor. Most are typically about 1.4 cm at presentation. SGc originates from sebaceous glands in the skin and, therefore, may originate anywhere in the body where these glands are found. SGc can be divided into 2 types: periocular and extraocular. The periocular region is rich in sebaceous glands making it a common site of origin. The cause of these lesions in the vast majority of cases is unknown. Occasional cases may be associated with Muir-Torre syndrome. SGc accounts for approximately 0.7% of all skin cancers, and the incidence of SGc is highest in Caucasian, Asian, and Indian populations. Due to the rarity of this tumor and variability in clinical and histological presentation, SGc is often misdiagnosed as an inflammatory condition or a more common neoplasm. SGc is commonly treated with wide local excision or Mohs micrographic surgery, and the relative survival rates at 5 and 10 years are 92.72 and 86.98%, respectively.

Human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal cancer, is a cancer of the throat caused by the human papillomavirus type 16 virus (HPV16). In the past, cancer of the oropharynx (throat) was associated with the use of alcohol or tobacco or both, but the majority of cases are now associated with the HPV virus, acquired by having oral contact with the genitals of a person who has a genital HPV infection. Risk factors include having a large number of sexual partners, a history of oral-genital sex or anal–oral sex, having a female partner with a history of either an abnormal Pap smear or cervical dysplasia, having chronic periodontitis, and, among men, younger age at first intercourse and a history of genital warts. HPV-positive OPC is considered a separate disease from HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancer.
Salivary gland–like carcinomas of the lung generally refers a class of rare cancers that arise from the uncontrolled cell division (mitosis) of mutated cancer stem cells in lung tissue. They take their name partly from the appearance of their abnormal cells, whose structure and features closely resemble those of cancers that form in the major salivary glands of the head and neck. Carcinoma is a term for malignant neoplasms derived from cells of epithelial lineage, and/or that exhibit cytological or tissue architectural features characteristically found in epithelial cells.

Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma (HCCC) is a rare malignant salivary gland tumour, with a good prognosis, that is usually found on the tongue or palate.
Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis is a chronic (long-lasting) inflammatory condition affecting the salivary gland. Relatively rare in occurrence, this condition is benign, but presents as hard, indurated and enlarged masses that are clinically indistinguishable from salivary gland neoplasms or tumors. It is now regarded as a manifestation of IgG4-related disease.
Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma (MASC), also termed MASCSG, is a salivary gland neoplasm. It is a secretory carcinoma which shares the microscopic pathologic features with other types of secretory carcinomas including mammary secretory carcinoma, secretory carcinoma of the skin, and salivary gland–type carcinoma of the thyroid. MASCSG was first described by Skálová et al. in 2010. The authors of this report found a chromosome translocation in certain salivary gland tumors, i.e. a (12;15)(p13;q25) fusion gene mutation. The other secretory carcinoma types carry this fusion gene.
Mammary secretory carcinoma (MSC), also termed secretory carcinoma of the breast, is a rare form of the breast cancers. MSC usually affects women but in a significant percentage of cases also occurs in men and children. Indeed, McDvitt and Stewart first described MSC in 1966 and termed it juvenile breast carcinoma because an increased number of cases were at that time diagnosed in juvenile females. MSC is the most common form of breast cancer in children, representing 80% of childhood breast cancers, although it accounts for less than 0.15% of all breast cancers.

Invasive cribriform carcinoma of the breast (ICCB), also termed invasive cribriform carcinoma, is a rare type of breast cancer that accounts for 0.3% to 0.6% of all carcinomas in the breast. It originates in a lactiferous duct as opposed to the lobules that form the alveoli in the breasts' mammary glands. ICCB was first described by Dixon and colleagues in 1983 as a tumor that on microscopic histopathological inspection had a cribriform pattern, i.e. a tissue pattern consisting of numerous "Swiss cheese"-like open spaces and/or sieve-like small holes. The latest edition (2019) of the World Health Organization (2019) termed these lesions invasive cribriform carcinomas indicating that by definition they must have a component that invades out of their ducts of origin into adjacent tissues. In situ ductal cancers that have a cribriform histopathology are regarded as belonging to the group of ductal carcinoma in situ tumors.





















