Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any type of Candida. When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth and throat. Other symptoms may include soreness and problems swallowing. When it affects the vagina, it may be referred to as a yeast infection or thrush. Signs and symptoms include genital itching, burning, and sometimes a white "cottage cheese-like" discharge from the vagina. Yeast infections of the penis are less common and typically present with an itchy rash. Very rarely, yeast infections may become invasive, spreading to other parts of the body. This may result in fevers along with other symptoms depending on the parts involved.

Oral candidiasis, also known as oral thrush among other names, is candidiasis that occurs in the mouth. That is, oral candidiasis is a mycosis of Candida species on the mucous membranes of the mouth.

Oral leukoplakia is a potentially malignant disorder affecting the oral mucosa. It is defined as "essentially an oral mucosal white lesion that cannot be considered as any other definable lesion." Oral leukoplakia is a white patch or plaque that develops in the oral cavity and is strongly associated with smoking. Leukoplakia is a firmly attached white patch on a mucous membrane which is associated with increased risk of cancer. The edges of the lesion are typically abrupt and the lesion changes with time. Advanced forms may develop red patches. There are generally no other symptoms. It usually occurs within the mouth, although sometimes mucosa in other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, or genitals may be affected.
Hairy leukoplakia is a white patch on the side of the tongue with a corrugated or hairy appearance. It is caused by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and occurs usually in persons who are immunocompromised, especially those with human immunodeficiency virus infection/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS). The white lesion, which cannot be scraped off, is benign and does not require any treatment, although its appearance may have diagnostic and prognostic implications for the underlying condition.

Stomatitis is inflammation of the mouth and lips. It refers to any inflammatory process affecting the mucous membranes of the mouth and lips, with or without oral ulceration.

Glossitis can mean soreness of the tongue, or more usually inflammation with depapillation of the dorsal surface of the tongue, leaving a smooth and erythematous (reddened) surface,. In a wider sense, glossitis can mean inflammation of the tongue generally. Glossitis is often caused by nutritional deficiencies and may be painless or cause discomfort. Glossitis usually responds well to treatment if the cause is identified and corrected. Tongue soreness caused by glossitis is differentiated from burning mouth syndrome, where there is no identifiable change in the appearance of the tongue, and there are no identifiable causes.
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed lamina propria. The oral cavity has sometimes been described as a mirror that reflects the health of the individual. Changes indicative of disease are seen as alterations in the oral mucosa lining the mouth, which can reveal systemic conditions, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiency, or the local effects of chronic tobacco or alcohol use. The oral mucosa tends to heal faster and with less scar formation compared to the skin. The underlying mechanism remains unknown, but research suggests that extracellular vesicles might be involved.

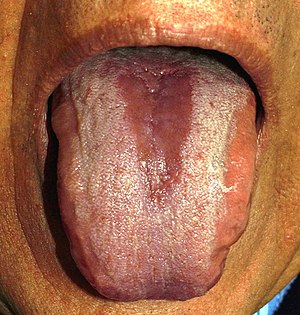
Geographic tongue, also known by several other terms, is a condition of the mucous membrane of the tongue, usually on the dorsal surface. It is a common condition, affecting approximately 2–3% of the general population. It is characterized by areas of smooth, red depapillation which migrate over time. The name comes from the map-like appearance of the tongue, with the patches resembling the islands of an archipelago. The cause is unknown, but the condition is entirely benign, and there is no curative treatment. Uncommonly, geographic tongue may cause a burning sensation on the tongue, for which various treatments have been described with little formal evidence of efficacy.
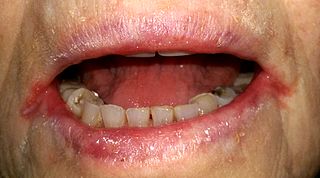
Angular cheilitis (AC) is inflammation of one or both corners of the mouth. Often the corners are red with skin breakdown and crusting. It can also be itchy or painful. The condition can last for days to years. Angular cheilitis is a type of cheilitis.
Epulis fissuratum is a benign hyperplasia of fibrous connective tissue which develops as a reactive lesion to chronic mechanical irritation produced by the flange of a poorly fitting denture. More simply, epulis fissuratum is where excess folds of firm tissue form inside the mouth, as a result of rubbing on the edge of dentures that do not fit well. It is a harmless condition and does not represent oral cancer. Treatment is by simple surgical removal of the lesion, and also by adjustment of the denture or provision of a new denture.
Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia (IPH) is a benign lesion of the oral mucosa which is characterized by the growth of one or more nodular lesions, measuring about 2mm or less. The lesion almost exclusively involves the hard palate, and in rare instances, it also has been seen on the mandible. The lesion is mostly asymptomatic and color of the mucosa may vary from pink to red.
Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a burning, tingling or scalding sensation in the mouth, lasting for at least four to six months, with no underlying known dental or medical cause. No related signs of disease are found in the mouth. People with burning mouth syndrome may also have a subjective xerostomia, paraesthesia, or an altered sense of taste or smell.
Stomatitis nicotina is a diffuse white patch on the hard palate, usually caused by tobacco smoking, usually pipe or cigar smoking. It is painless, and it is caused by a response of the palatal oral mucosa to chronic heat. A more pronounced appearance can occur with reverse smoking, sometimes distinguished from stomatitis nicotina by the term reverse smoker's stomatitis. While stomatitis nicotina that is caused by heat is not a premalignant condition, the condition that is caused by reverse smoking is premalignant.
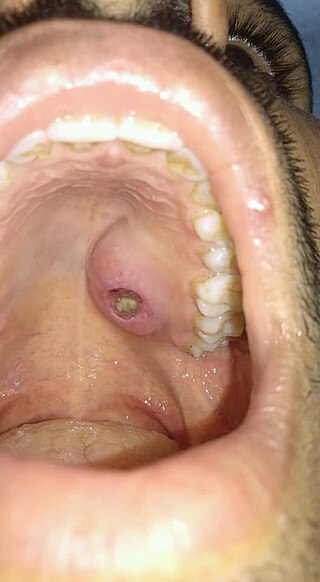
Necrotizing sialometaplasia (NS) is a benign, ulcerative lesion, usually located towards the back of the hard palate. It is thought to be caused by ischemic necrosis of minor salivary glands in response to trauma. Often painless, the condition is self-limiting and should heal in 6–10 weeks.
Leukoedema is a blue, grey or white appearance of mucosae, particularly the buccal mucosa ; it may also occur on the mucosa of the larynx or vagina. It is a harmless and very common condition. Because it is so common, it has been argued that it may in fact represent a variation of the normal appearance rather than a disease, but empirical evidence suggests that leukoedema is an acquired condition caused by local irritation. It is found more commonly in black skinned people and tobacco users. The term is derived from the Greek words λευκός leukós, "white" and οἴδημα oídēma, "swelling".
Oral and maxillofacial pathology refers to the diseases of the mouth, jaws and related structures such as salivary glands, temporomandibular joints, facial muscles and perioral skin. The mouth is an important organ with many different functions. It is also prone to a variety of medical and dental disorders.

Tongue diseases can be congenital or acquired, and are multiple in number. Considered according to a surgical sieve, some example conditions which can involve the tongue are discussed below. Glossitis is a general term for tongue inflammation, which can have various etiologies, e.g. infection.

Plasma cell gingivitis is a rare condition, appearing as generalized erythema (redness) and edema (swelling) of the attached gingiva, occasionally accompanied by cheilitis or glossitis. It is called plasma cell gingivitis where the gingiva (gums) are involved, plasma cell cheilitis, where the lips are involved, and other terms such as plasma cell orifacial mucositis, or plasma cell gingivostomatitis where several sites in the mouth are involved. On the lips, the condition appears as sharply outlined, infiltrated, dark red plaque with a lacquer-like glazing of the surface of the involved oral area.
Morsicatio buccarum is a condition characterized by chronic irritation or injury to the buccal mucosa, caused by repetitive chewing, biting or nibbling.
Denture-related stomatitis is a common condition where mild inflammation and redness of the oral mucous membrane occurs beneath a denture. In about 90% of cases, Candida species are involved, which are normally a harmless component of the oral microbiota in many people. Denture-related stomatitis is the most common form of oral candidiasis. It is more common in elderly people, and in those who wear a complete upper denture. Denture-related stomatitis is more likely to develop when the denture is left constantly in the mouth, rather than removing it during sleep, and when the denture is not cleaned regularly.