| Craniofacial abnormality | |
|---|---|
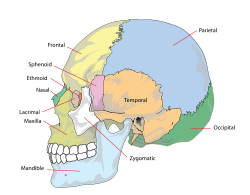 | |
| Human skull | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Craniofacial abnormalities are congenital musculoskeletal disorders which primarily affect the cranium and facial bones. [1]
Contents
They are associated with the development of the pharyngeal arches. [2] Approximately, 5% of the UK or USA population present with dentofacial deformities requiring Orthognathic surgery, jaw surgery, and Orthodontics, brace therapy, as a part of their definitive treatment. [3] [4] [5]