
An echinoderm is any deuterostomal animal of the phylum Echinodermata, which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as larvae, as adults echinoderms are recognisable by their usually five-pointed radial symmetry, and are found on the sea bed at every ocean depth from the intertidal zone to the abyssal zone. The phylum contains about 7,600 living species, making it the second-largest group of deuterostomes after the chordates, as well as the largest marine-only phylum. The first definitive echinoderms appeared near the start of the Cambrian.

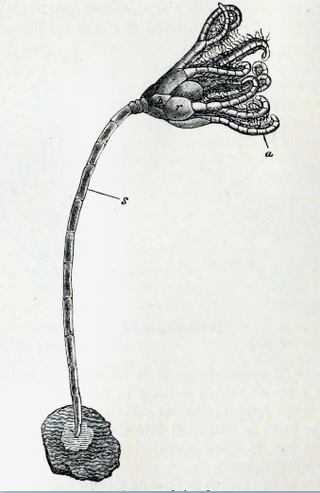
Crinoids are marine invertebrates that make up the class Crinoidea. Crinoids that remain attached to the sea floor by a stalk in their adult form are commonly called sea lilies, while the unstalked forms, called feather stars or comatulids, are members of the largest crinoid order, Comatulida. Crinoids are echinoderms in the phylum Echinodermata, which also includes the starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins and sea cucumbers. They live in both shallow water and in depths over 9,000 metres (30,000 ft).

Articulata are a subclass or superorder within the class Crinoidea, including all living crinoid species. They are commonly known as sea lilies or feather stars. The Articulata are differentiated from the extinct subclasses by their lack of an anal plate in the adult stage and the presence of an entoneural system. Articulata first appeared in the fossil record during the Triassic period although other, now extinct crinoid groups, originated in the Ordovician.
Antedon bifida is a species of crinoid in the family Antedonidae commonly known as the rosy feather star. It is found in north west Europe.

Comaster is a genus of crinoids.

Comatulida is an order of crinoids. Members of this order are known as feather stars and mostly do not have a stalk as adults. The oral surface with the mouth is facing upwards and is surrounded by five, often divided rays with feathery pinnules. Comatulids live on the seabed and on reefs in tropical and temperate waters.

Davidaster rubiginosus, the orange sea lily, is a species of crinoid in the family Comatulidae. At one time it was classified as Nemaster rubiginosa but the World Register of Marine Species has determined that the valid name is Davidaster rubiginosus. It is found on reefs in the tropical western Atlantic and the Caribbean Sea.

Davidaster discoideus, the beaded crinoid, is a species of feather star in the family Comatulidae. It was previously known as Nemaster discoidea but the World Register of Marine Species has determined that the valid name is Davidaster discoideus. It is found on reefs in the Caribbean Sea and northern coast of South America.

Metacrinus rotundus, the Japanese sea lily, is a species of stalked crinoid in the family Isselicrinidae. It is a species found off the west coast of Japan, near the edge of the continental shelf at a depth of around 100 to 150 metres deep. This is the shallowest-living species among the extant stalked crinoids.

Anneissia bennetti, the Bennett's feather star, is a species of crinoid belonging to the family Comatulidae. It is found in shallow water in the Indo-Pacific between northern Australia and southeast Asia.

Himerometra robustipinna is a species of crinoid belonging to the family Himerometridaem first described as Actinometra robustipinna by Philip Herbert Carpenter in 1881.

Comaster nobilis, the noble feather star or yellow feather star, is a crinoid in the family Comatulidae. It was previously classified as Comanthina nobilis but further research showed that it was better placed in the genus Comaster.

Antedon mediterranea is a species of stalkless crinoid in the family Antedonidae, commonly known as the Mediterranean feather star. It is found on the seabed at moderate depths in the Mediterranean Sea. It is a filter feeder and captures plankton with its long feathery arms.

Ptilometra australis, the passion flower feather star, is a species of crinoid. It is native to the coasts of southeastern Australia where it is found on reefs, in estuaries and bays at depths down to about 110 metres (360 ft).

Comatulidae is a family of comatulid crinoids. Since 2015, it replaces the family Comasteridae.

Florometra serratissima is a species of crinoid or feather star in the family Antedonidae. It is found off the Pacific coast of North America, usually in deep water.

Aporometra wilsoni is a marine invertebrate, a species of crinoid or feather star in the family Aporometridae. It is found in shallow water around the coasts of southern Australia.

Notocrinus virilis is a marine invertebrate, a species of crinoid or feather star in the family Notocrinidae. It is found in deep water in the Southern Ocean around the coasts of Antarctica and adjacent islands. A sea snail sometimes parasitizes it.

Cenometra bella is a species of crinoids belonging to the genus Cenometra. They can have up to 30 arms and can be of variable colours but are often characterised by a marked contrast between the extending free-arms and the feathery pinnules. This species clings to its support and moves around by its feet-like cirri.

Comatula solaris is a species of feather star in the family Comatulidae and the type species of the genus Comatula.




















