| Conorhynchos | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Siluriformes |
| Superfamily: | Pimelodoidea |
| Family: | incertae sedis |
| Genus: | Conorhynchos Bleeker, 1858 |
| Species: | C. conirostris |
| Binomial name | |
| Conorhynchos conirostris (Cuvier, 1829) | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
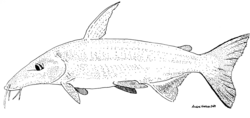
Conorhynchos conirostris is a monotypic genus of catfish (order Siluriformes).
The spelling of the generic name has been confused; it is currently valid as Conorhynchos as described by Pieter Bleeker in 1858. [2] This catfish has unknown relationships. It does not appear to be assignable to any family and is placed incertae sedis . [2] However, it has been grouped into the superfamily Pimelodoidea due to molecular evidence. [3]
Conorhynchos conirostris is endemic to the São Francisco River in Brazil and is considered a symbol of the river. [4] This fish can reach 53.5 centimetres (21.1 in) in standard length [5] and 13 kilograms (29 lb) in weight. [4] This fish is of commercial interest, [4] and is considered threatened by Brazil's Ministry of the Environment. [6]
