| Flag | County | Province | Colours | Notes |
|---|
 | Antrim | Ulster | Saffron and White | Adopted from the Seans club of West Belfast. [11] |
 | Armagh | Ulster | Orange and White | Up to 1926 Armagh wore black and amber. In 1926 they played Dublin in the All-Ireland Junior Football Championship Semi-Final and wore orange jerseys knitted by Poor Clare nuns from Omeath, County Louth. [12] |
 | Carlow | Leinster | Red, Yellow Green | Up to 1910, Carlow wore the colours of the county champions. In that year a set of green jerseys with red and yellow hoops were adopted. [13] These colours inspired Derek Ryan's song "Red, Yellow And Green." [14] |
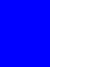 | Cavan | Ulster | Blue and White | Royal blue has been worn since 1910; it may have been borrowed from the Cavan Slashers club. [15] The white trim was added for the 1947 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship Final in New York City. |
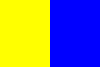 | Clare | Munster | Saffron and Blue | Colours taken from the Tulla club, the first to be formed in the county. |
 | Cork | Munster | Red and White | In 1913 Cork wore blue jerseys with a large yellow "C" in front. In a 1919 raid in by British troops on the county board rooms in Cook Street, the jerseys were taken. So, Cork used the jerseys of the St Finbarr's Total Abstinence Hall team, which were dark red/maroon, and Cork have worn red ever since. [13] An apocryphal story claims that the colours derive from Church of St Anne, Shandon, which has walls of red sandstone and white limestone. [16] |
 | Derry | Ulster | White and Red | Red was the traditional Derry colour; they wore black and white hoops in the 1930s; Derry adopted white jersey with a red hoop for the 1946–47 National Football League final and have worn them since. [17] |
 | Donegal | Ulster | Gold and Green | Origin unclear. Originally green was the dominant colour, but in the 1992 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship Donegal switched to a mostly-gold strip. [18] |
 | Down | Ulster | Red and Black | Down wore red until 1922; blue with white trim for ten years; and then changed back to a red or scarlet jersey with black collar and cuffs in 1933. Black shorts, at the time a novelty in Gaelic games when all players generally wore white, were first worn in 1962. [19] |
 | Dublin | Leinster | Sky Blue and Navy | In April 1913, Harry Boland chaired the Dublin County Board meeting at which "after some discussion, it was decided to adopt as the county colours a light blue jersey with a white shield bearing the city arms". [20] |
 | Fermanagh | Ulster | Green and White | Originally green and white hoops, the colours of country champions Teemore. Around 1934/35 a green jersey with yellow trim was used, later changed to white trim. [11] |
 | Fingal | Leinster | Purple and White | Fingal is not one of the 32 traditional counties of Ireland, but one of four local government areas in the historical area of County Dublin. Its county hurling team competed separately from Dublin from 2008 to 2016, but its management fell under the Dublin county board. [21] |
 | Galway | Connacht | Maroon and White | Originally played in the colours of the county champions. Maroon jerseys were adopted around 1936. [11] [22] [23] |
 | Kerry | Munster | Green and Gold | Adopted in the 1903 All-Ireland Football Final as the colours of the then dominant Tralee Mitchels senior team. [24] |
 | Kildare | Leinster | All White | Kildare wore the colours of the county champions originally. They played in Clane's all-white strip during the 1903 Leinster Senior Football Championship, which they won, and continued to use those colours. Clane's white jerseys were borrowed from those of Clongowes Wood College. [25] However, a separate account claims that Clane played in black and green, and that the white colour comes from a singlet worn by Joe Rafferty, a star player in 1903. [26] |
 | Kilkenny | Leinster | Black and Amber | Wore black and amber in the 1893 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final, bought from the defunct Thomas Larkins football club. They also wore black and amber in the 1905 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final replay. Arguments over county colours went on until November 1911 with the presentation of a set of jerseys by John F. Drennan. [13] |
 | Laois | Leinster | Blue and White | Laois wore black and amber hoops when they won the 1915 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship. [27] A blue jersey with white hoop was adopted in 1932. [11] |
 | Leitrim | Connacht | Green and Gold | Green with a gold hoop dates from about 1917, though white and green was sometimes worn in the 1920s. [11] |
 | Limerick | Munster | Green and White | Wore green with a white sash when winning the 1918 All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship Final but in the 1921 final wore green and white hoops. The present jersey was adopted in 1924. |
 | Longford | Leinster | Blue and Gold | Origin unclear. Jerseys belonging to Clonguish Gallowglasses (white with green hoop) used by Longford teams for a brief period in 1900's and early 1910's, after which a royal blue jersey with a gold sash was adopted. The sash disappeared around 1930 leaving royal blue jersey with gold cuffs and collar which remains the county colours today. [28] |
 | Louth | Leinster | Red and White | Louth have worn red and white since 1885. They wore all-red for a time in the 1970s. [29] |
 | Mayo | Connacht | Green and Red | Claimed to have been inspired by the Thomas Davis poem "The Green above the Red." [30] [31] Inspired the Saw Doctors song "The Green and Red of Mayo." [32] |
 | Meath | Leinster | Green and Gold | A green jersey with a gold sash was used by the Meath team from 1908. [11] |
 | Monaghan | Ulster | White and Blue | Up to 1913, the colours of the county champions were worn. The white jersey then had a blue band around 1920. Black and amber were used for a while in the 1930s but by 1937 the original white with blue trim was reintroduced. [17] |
 | Offaly | Leinster | Green, White and Gold | Many teams played in the colours of the Irish flag; supposedly Offaly earned the right to use them in Leinster aftering winning a competition. Other accounts claim it comes from green, white and gold shirts worn by the Tullamore club in 1917, and hidden during the Irish War of Independence. [33] |
 | Roscommon | Connacht | Primrose and Blue | The Roscommon jersey was either black and amber or black and white prior to 1938. Blue with a yellow band, or black with a green hoop, was also used. [17] The present colour scheme was adopted for the 1943 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship Final. |
 | Sligo | Connacht | Black and White | At one time the Sligo jersey was all black, with a white band being later added. From 1970 the county teams wore mostly white, before switching to black shirts for a famous win over Kildare in the 2001 All-Ireland Senior Football Championship; Sligo have continued to wear black shirts since. [34] [35] [36] |
 | Tipperary | Munster | Blue and Gold | Up to about 1925 Tipperary wore the colours of the county champions. In 1925 the present gold hoop on a blue jersey was introduced, taken from the Tubberadora club. [37] |
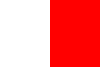 | Tyrone | Ulster | White and Red | Colours derive from the Red Hand of Ulster on a white field, the symbol of the Uí Néill dynasty, adopted around 1927 and definitely before 1931. They also wore green and gold hoops for a time in the 1930s, but soon revered to white and red. [17] [15] |
 | Waterford | Munster | White and Blue | Waterford wore the royal blue shirts of Munster with white cuffs. In 1938 the jersey was changed to white with royal blue trim. |
 | Westmeath | Leinster | Maroon and White | Up to 1912 Westmeath wore a green jersey with a white hoop. This was later changed to a maroon jersey with a saffron sash. The sash was dropped in 1936. In 1937 their kit was described as "dark red", and they have played in maroon since then. [17] |
 | Wexford | Leinster | Purple and Gold | Purple and amber was introduced in 1913. In 1937 they wore blue and saffron. [17] Since then Wexford have generally worn purple and gold, although the degree of each colour has varied. [38] |
 | Wicklow | Leinster | Blue and Gold | Bray Emmets were Wicklow county champions at the turn of the century and wearing a green jersey and gave their colours to the Wicklow team, who wore green until the early 1930s. Blue with a gold hoop was used until a changeover to the present style in 1970. [11] |


































