
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period 485.4 Ma to the start of the Silurian Period 443.8 Ma.

The Silurian is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at 443.8 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, 419.2 Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out.

Tabulata, commonly known as tabulate corals, are an order of extinct forms of coral. They are almost always colonial, forming colonies of individual hexagonal cells known as corallites defined by a skeleton of calcite, similar in appearance to a honeycomb. Adjacent cells are joined by small pores. Their distinguishing feature is their well-developed horizontal internal partitions (tabulae) within each cell, but reduced or absent vertical internal partitions. They are usually smaller than rugose corals, but vary considerably in shape, from flat to conical to spherical.
Dolerorthis is an extinct genus of hesperorthid brachiopod. The type species of this genus, D. interplicata, was described from the Silurian (Telychian) Osgood Formation. Other species belonging to this genus are known from the Ordovician and Silurian of Europe, Kazakhstan, China and Argentina. It was roughly 4 centimetres (1.6 in) across.

The Craniidae are a family of brachiopods, the only surviving members of the subphylum Craniiformea. They are the only members of the order Craniida, the monotypic suborder Craniidina, and the superfamily Cranioidea; consequently, the latter two taxa are at present redundant and rarely used.There are three living genera within Craniidae: Neoancistrocrania, Novocrania, and Valdiviathyris. As adults, craniids either live freely on the ocean floor or, more commonly, cement themselves onto a hard object with all or part of the ventral valve.

Brachiopods, phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of trochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, while the front can be opened for feeding or closed for protection. Two major categories are traditionally recognized, articulate and inarticulate brachiopods. The word "articulate" is used to describe the tooth-and-groove structures of the valve-hinge which is present in the articulate group, and absent from the inarticulate group. This is the leading diagnostic skeletal feature, by which the two main groups can be readily distinguished as fossils. Articulate brachiopods have toothed hinges and simple, vertically oriented opening and closing muscles. Conversely, inarticulate brachiopods have weak, untoothed hinges and a more complex system of vertical and oblique (diagonal) muscles used to keep the two valves aligned. In many brachiopods, a stalk-like pedicle projects from an opening near the hinge of one of the valves, known as the pedicle or ventral valve. The pedicle, when present, keeps the animal anchored to the seabed but clear of sediment which would obstruct the opening.

The Katian is the second stage of the Upper Ordovician. It is preceded by the Sandbian and succeeded by the Hirnantian Stage. The Katian began 453 million years ago and lasted for about 7.8 million years until the beginning of the Hirnantian 445.2 million years ago. During the Katian the climate cooled which started the Late Ordovician glaciation.
The Kirengellids are a group of problematic Cambrian fossil shells of marine organisms. The shells bear a number of paired muscle scars on the inner surface of the valve.
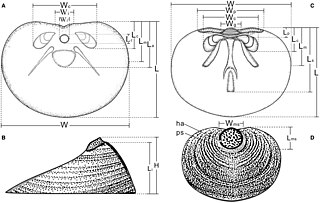
Acrotretides (Acrotretida) are an extinct order of linguliform brachiopods in the class Lingulata. Acrotretida contains 8 families within the sole superfamily Acrotretoidea. They lived from the Lower Cambrian to the Middle Devonian, rapidly diversifying during the middle Cambrian. In the upper Cambrian, linguliforms reached the apex of their diversity: acrotretides and their relatives the lingulides together comprised nearly 70% of brachiopod genera at this time. Though acrotretides continued to diversify during the Ordovician, their proportional dominance declined, as rhynchonelliforms took on a larger role in brachiopod faunas.

Lonchodomas is a genus of trilobites, that lived during the Ordovician. It was eyeless, like all raphiophorids, and had a long straight sword-like frontal spine, that gradually transforms into the relatively long glabella. Both the glabellar spine and the backward directed genal spines are subquadrate in section. Lonchodomas has five thorax segments and the pleural area of the pygidium has two narrow furrows. Lonchodomas occurred in what are today Argentina, Canada (Newfoundland), Estonia, Latvia, Norway, Sweden, the Russian Federation and the United States.

Rhynchonelliformea is a major subphylum and clade of brachiopods. It is roughly equivalent to the former class Articulata, which was used previously in brachiopod taxonomy up until the 1990s. These so-called articulated brachiopods have many anatomical differences relative to "inarticulate" brachiopods of the subphyla Linguliformea and Craniformea. Articulates have hard calcium carbonate shells with tongue-and-groove hinge articulations and separate sets of simple opening and closing muscles.

Paleontology in Oklahoma refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Oklahoma. Oklahoma has a rich fossil record spanning all three eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Oklahoma is the best source of Pennsylvanian fossils in the United States due to having an exceptionally complete geologic record of the epoch. From the Cambrian to the Devonian, all of Oklahoma was covered by a sea that would come to be home to creatures like brachiopods, bryozoans, graptolites and trilobites. During the Carboniferous, an expanse of coastal deltaic swamps formed in areas of the state where early tetrapods would leave behind footprints that would later fossilize. The sea withdrew altogether during the Permian period. Oklahoma was home a variety of insects as well as early amphibians and reptiles. Oklahoma stayed dry for most of the Mesozoic. During the Late Triassic, carnivorous dinosaurs left behind footprints that would later fossilize. During the Cretaceous, however, the state was mostly covered by the Western Interior Seaway, which was home to huge ammonites and other marine invertebrates. During the Cenozoic, Oklahoma became home to creatures like bison, camels, creodonts, and horses. During the Ice Age, the state was home to mammoths and mastodons. Local Native Americans are known to have used fossils for medicinal purposes. The Jurassic dinosaur Saurophaganax maximus is the Oklahoma state fossil.

Paterinata is an extinct class of linguliform brachiopods which lived from the lower Cambrian ("Tommotian") to the Upper Ordovician (Hirnantian). It contains the single order Paterinida and the subfamily Paterinoidea. Despite being some of the earliest brachiopods to appear in the fossil record, paterinides stayed as a relatively subdued and low-diversity group even as other brachiopods diversified later in the Cambrian and Ordovician. Paterinides are notable for their high degree of convergent evolution with rhynchonelliform (articulate) brachiopods, which have a similar set of muscles and hinge-adjacent structures.

Trimerellida is an extinct order of craniate brachiopods, containing the sole superfamily Trimerelloidea and the families Adensuidae, Trimerellidae, and Ussuniidae. Trimerellidae was a widespread family of warm-water brachiopods ranging from the Middle Ordovician to the late Silurian (Ludlow). Adensuidae and Ussuniidae are monogeneric families restricted to the Ordovician of Kazakhstan. Most individuals were free-living, though some clustered into large congregations similar to modern oyster reefs.
The Maquoketa Formation is a geologic formation in Illinois, Indiana. Iowa, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, and Wisconsin. It preserves mollusk, coral, brachiopod and graptolite fossils dating back to the Darriwilian to Hirnantian stages of the Ordovician period.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2016.

Histiodella is an extinct genus of conodonts.
Craniopsidae is an extinct family of craniiform brachiopods which lived from the mid-Cambrian to the Lower Carboniferous (Tournaisian). It is the only family in the monotypic superfamily Craniopsoidea and the monotypic order Craniopsida. If one includes the ambiguous Cambrian genus Discinopsis, craniopsids were the first craniiforms to appear, and may be ancestral to craniids and trimerellides. An even earlier Cambrian genus, Heliomedusa, has sometimes been identified as a craniopsid. More recently, Heliomedusa has been considered a stem-group brachiopod related to Mickwitzia.

Siphonotretida is an extinct order of linguliform brachiopods in the class Lingulata. The order is equivalent to the sole superfamily Siphonotretoidea, itself containing the sole family Siphonotretidae. Siphonotretoids were originally named as a superfamily of Acrotretida, before being raised to their own order.

Estlandia is a gonambonitid genus. It is one of the endemic brachiopods in the Ordovician of Baltoscandia. Currently, eight different species and subspecies of the genus have been recorded from the Aseri to Keila stages.














