
Liolaemus is a genus of iguanian lizards, containing many species, all of which are endemic to South America.

The Hyperoliidae, or sedge frogs and bush frogs, are a large family of small to medium-sized, brightly colored frogs which contains more than 250 species in 19 genera. Seventeen genera are native to sub-Saharan Africa. In addition, the monotypic genus Tachycnemis occurs on the Seychelles Islands, and the genus Heterixalus is endemic to Madagascar.

Telmatobius is a genus of frogs native to the Andean highlands in South America, where they are found in Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, northwestern Argentina and northern Chile. It is the only genus in the family Telmatobiidae. Some sources recognize Batrachophrynus as a valid genus distinct from Telmatobius.

Reef lobsters, Enoplometopus, are a genus of small lobsters that live on reefs in the Indo-Pacific, Caribbean and warmer parts of the Atlantic Ocean.

Mimallonidae Burmeister (mimallonids), sometimes known as "sack-bearer" moths for the larval case-building behavior, are a family of Lepidoptera containing over 300 named species in 43 genera. These moths are found only in the New World, with most taxa occurring in the Neotropics. Adult moths are externally similar to those belonging to some of the other Macroheterocera families Bombycoidea and Drepanoidea, and thus have been variously treated as belonging to either one of these or other superfamilies.

The shovelnose frogs are the species of frogs in the genus, Hemisus, the only genus in the family Hemisotidae. They are found in tropical and subtropical sub-Saharan Africa. The shovelnose frogs are moderate-sized frogs, reaching a length of 8 cm (3.1 in). They are round-bodied, with short legs. Their heads are small and narrow, with hard, upturned noses.

Clarias is a genus of catfishes of the family Clariidae, the airbreathing catfishes. The name is derived from the Greek chlaros, which means lively, in reference to the ability of the fish to live for a long time out of water.

Ptychadena is a genus of frogs in the grassland frog family, Ptychadenidae. They are distributed in Sub-Saharan Africa, as well as nilotic Egypt. The common names of this genus are ridged frogs and grass frogs. This type of family have many different characteristics such as the species, Ptychadena neumanni who have long hindlimbs and a large ear drum compared to the Ptychadena erlangeri, for example. They also have a unique bone structure which is a fusion between the presacral vertebrae and sacrum.
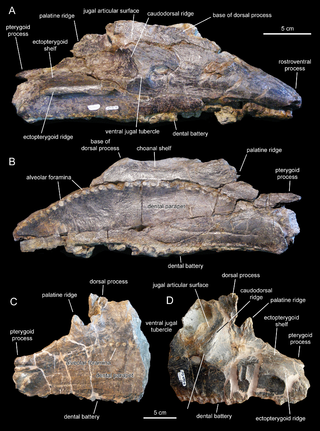
Pararhabdodon is a genus of tsintaosaurin hadrosaurid dinosaur, from the Maastrichtian-age Upper Cretaceous Tremp Group of Spain. The first remains were discovered from the Sant Romà d’Abella fossil locality and assigned to the genus Rhabdodon, and later named as the distinct species Pararhabdodon isonensis in 1993. Known material includes assorted postcranial remains, mostly vertebrae, as well as maxillae from the skull. Specimens from other sites, including remains from France, a maxilla previously considered the distinct taxon Koutalisaurus kohlerorum, an additional maxilla from another locality, the material assigned to the genera Blasisaurus and Arenysaurus, and the extensive Basturs Poble bonebed have been considered at different times to belong to the species, but all of these assignments have more recently been questioned. It was one of the last non-avian dinosaurs known from the fossil record that went extinct during the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event.

Afrixalus, commonly known as the banana frogs, spiny reed frogs, cat's eye reed frogs, or leaf-folding frogs, is a genus of frog in the family Hyperoliidae. They occur in the Subsaharan Africa. They lay their eggs in vegetation above water, often folding leaves around the eggs for protection—hence the common name "leaf-folding frogs".

Hyperolius is a large genus of frogs in the family Hyperoliidae from Sub-Saharan Africa.

Phrynobatrachus is a genus of Sub-Saharan frogs that form the monogeneric family Phrynobatrachidae. Their common name is puddle frogs, dwarf puddle frogs, African puddle frogs, or African river frogs. The common name, puddle frog, refers to the fact that many species breed in temporary waterbodies such as puddles.

Amietia is a genus of frogs, commonly known as large-mouthed frogs or river frogs, in the family Pyxicephalidae. They are endemic to central and southern Africa. Formerly, the genus was named Afrana and was placed in the family Ranidae.

Thalassina is a genus of mud lobsters found in the mangrove swamps of the Indian Ocean and western Pacific Ocean. Its nocturnal burrowing is important for the recycling of nutrients in the mangrove ecosystem, although it is sometimes considered a pest of fish and prawn farms.

Williams' mud turtle is a species of turtle in the family Pelomedusidae. The species is endemic to Africa.
Djebelemuridae is an extinct family of early strepsirrhine primates from Africa. It consists of five genera. The organisms in this family were exceptionally small, and were insectivores. This family dates to the early to late Eocene. Although they gave rise to the crown strepsirrhines, which includes today's lemurs and lorisoids, they lacked the toothcomb that identifies that group.

Afrotyphlops is a genus of snakes in the family Typhlopidae.
Canaanimico is an extinct genus of medium-sized New World monkeys from the Late Oligocene fossiliferous fluvio-lacustrine Chambira Formation of the Ucayali Basin in Amazonian Peru. The genus was described by Marivaux et al. in 2016 and the type species is C. amazonensis.
Paragiopagurus is a genus of hermit crabs in the family Parapaguridae, that contains 25 species. Members of this genus live at depths from 116 to 2,067 meters.














