This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Culasi | |
|---|---|
| Municipality | |
| Municipality of Culasi | |
Municipal Hall | |
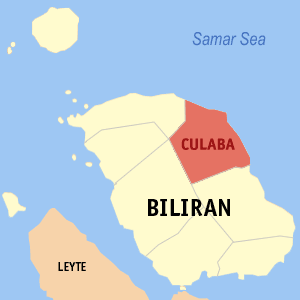
 Map of Antique with Culasi highlighted | |
Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 11°25′N122°04′E / 11.42°N 122.07°E Coordinates: 11°25′N122°04′E / 11.42°N 122.07°E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Western Visayas (Region VI) |
| Province | Antique |
| District | Lone district |
| Barangays | 44 (see Barangays) |
| Government [1] | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Jose Jeffrey Lomugdang |
| • Electorate | 23,942 voters (2016) |
| Area [2] | |
| • Total | 228.56 km2 (88.25 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation(Mount Madia-as) | 2,117 m (6,946 ft) |
| Population (2015 census) [3] | |
| • Total | 41,228 |
| • Density | 180/km2 (470/sq mi) |
| Time zone | PST (UTC+8) |
| ZIP code | 5708 |
| PSGC | 060606000 |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)36 |
| Climate type | tropical climate |
| Income class | 3rd municipal income class |
| Website | elgu |
Culasi, officially the Municipality of Culasi, (Kinaray-a : Banwa kang Culasi; Hiligaynon : Banwa sang Culasi; Filipino : Bayan ng Culasi), is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Antique, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 41,228 people. [3]

The Hiligaynon language, also often referred to by most of its speakers simply as Ilonggo, is an Austronesian regional language spoken in the Philippines by about 9.1 million people, mainly in Western Visayas and Soccsksargen, most of whom belong to the Visayan ethnic group, mainly the Hiligaynons. It is the second-most widely spoken language and a member of the so-named Visayan language family and is more distantly related to other Philippine languages.

Filipino is the national language of the Philippines. Filipino is also designated, along with English, as an official language of the country. It is a standardized variety of the Tagalog language, an Austronesian regional language that is widely spoken in the Philippines. As of 2007, Tagalog is the first language of 28 million people, or about one-third of the Philippine population, while 45 million speak Tagalog as their second language. Tagalog is among the 185 languages of the Philippines identified in the Ethnologue. Officially, Filipino is defined by the Commission on the Filipino Language as "the native dialect, spoken and written, in Metro Manila, the National Capital Region, and in other urban centers of the archipelago."

Antique is a province of the Philippines located in the region of Western Visayas. The province capital is San Jose, the most populous town in Antique. The province is situated in the western section of Panay Island and borders Aklan, Capiz and Iloilo to the east, while facing the Sulu Sea to the west.