
Wilkinson's catalyst is the common name for chloridotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I), a coordination complex of rhodium with the formula [RhCl(PPh3)3], where 'Ph' denotes a phenyl group). It is a red-brown colored solid that is soluble in hydrocarbon solvents such as benzene, and more so in tetrahydrofuran or chlorinated solvents such as dichloromethane. The compound is widely used as a catalyst for hydrogenation of alkenes. It is named after chemist and Nobel laureate Sir Geoffrey Wilkinson, who first popularized its use.

Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic solids featuring octahedral Rh(III) centres. Depending on the value of n, the material is either a dense brown solid or a soluble reddish salt. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis, notably for the industrial production of acetic acid and hydroformylation.

Iridium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula IrCl3. The anhydrous compound is relatively rare, but the related hydrate is useful for preparing other iridium compounds. The anhydrous salt is a dark green crystalline solid. More commonly encountered is the trihydrate IrCl3(H2O)3.

Crabtree's catalyst is an organoiridium compound with the formula [C8H12IrP(C6H11)3C5H5N]PF6. It is a homogeneous catalyst for hydrogenation and hydrogen-transfer reactions, developed by Robert H. Crabtree. This air stable orange solid is commercially available and known for its directed hydrogenation to give trans stereoselectivity with respective of directing group.
Cycloocta-1,5-diene is a cyclic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C8H12, specifically [−(CH2)2−CH=CH−]2.

1,2,3,4,5-Pentamethylcyclopentadiene is a cyclic diene with the formula C5Me5H (Me = CH3). 1,2,3,4,5-Pentamethylcyclopentadiene is the precursor to the ligand 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl, which is often denoted Cp* (C5Me5) and read as "C P star", the "star" signifying the five methyl groups radiating from the core of the ligand. In contrast to less-substituted cyclopentadiene derivatives, Cp*H is not prone to dimerization.

Cyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimer is the organorhodium compound with the formula Rh2Cl2(C8H12)2, commonly abbreviated [RhCl(COD)]2 or Rh2Cl2(COD)2. This yellow-orange, air-stable compound is a widely used precursor to homogeneous catalysts.
Martin Arthur Bennett FRS is an Australian inorganic chemist. He gained recognition for studies on the co-ordination chemistry of tertiary phosphines, olefins, and acetylenes, and the relationship of their behaviour to homogeneous catalysis.

Organoiridium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing an iridium-carbon chemical bond. Organoiridium compounds are relevant to many important processes including olefin hydrogenation and the industrial synthesis of acetic acid. They are also of great academic interest because of the diversity of the reactions and their relevance to the synthesis of fine chemicals.

Organorhodium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a rhodium-carbon chemical bond, and the study of rhodium and rhodium compounds as catalysts in organic reactions.
Peter Michael Maitlis, FRS was a British organometallic chemist.

Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl ruthenium dichloride is an organoruthenium chemistry with the formula [(C5(CH3)5)RuCl2]2, commonly abbreviated [Cp*RuCl2]2. This brown paramagnetic solid is a reagent in organometallic chemistry. It is an unusual example of a compound that exists as isomers that differ in the intermetallic separation, a difference that is manifested in a number of physical properties.
In organometallic chemistry, a transition metal alkene complex is a coordination compound containing one or more alkene ligands. Such compounds are intermediates in many catalytic reactions that convert alkenes to other organic products.
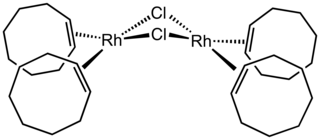
Chlorobis(cyclooctene)rhodium dimer is an organorhodium compound with the formula Rh2Cl2(C8H14)4, where C8H14 is cis-cyclooctene. Sometimes abbreviated Rh2Cl2(coe)4, it is a red-brown, air-sensitive solid that is a precursor to many other organorhodium compounds and catalysts.

Chlorobis(cyclooctene)iridium dimer is an organoiridium compound with the formula Ir2Cl2(C8H14)4, where C8H14 is cis-cyclooctene. Sometimes abbreviated Ir2Cl2(coe)4, it is a yellow, air-sensitive solid that is used as a precursor to many other organoiridium compounds and catalysts.

Chlorobis(ethylene)rhodium dimer is an organorhodium compound with the formula Rh2Cl2(C2H4)4. It is a red-orange solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. The molecule consists of two bridging chloride ligands and four ethylene ligands. The ethylene ligands are labile and readily displaced even by other alkenes. A variety of homogeneous catalysts have been prepared from this complex.

Rhodium carbonyl chloride is an organorhodium compound with the formula Rh2Cl2(CO)4. It is a red-brown volatile solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. It is a precursor to other rhodium carbonyl complexes, some of which are useful in homogeneous catalysis.
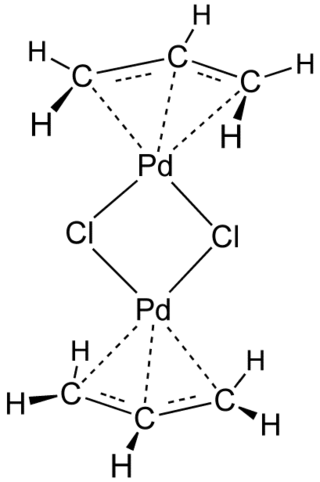
Transition-metal allyl complexes are coordination complexes with allyl and its derivatives as ligands. Allyl is the radical with the connectivity CH2CHCH2, although as a ligand it is usually viewed as an allyl anion CH2=CH−CH2−, which is usually described as two equivalent resonance structures.

Cyclooctadiene iridium methoxide dimer is an organoiridium compound with the formula Ir2(OCH3)2(C8H12)2, where C8H12 is the diene 1,5-cyclooctadiene. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents. The complex is used as a precursor to other iridium complexes, some of which are used in homogeneous catalysis.

Transition metal acyl complexes describes organometallic complexes containing one or more acyl (RCO) ligands. Such compounds occur as transient intermediates in many industrially useful reactions, especially carbonylations.


















