
The Cyrillic script, Slavonic script or simply Slavic script is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia, and used by many other minority languages.
Transliteration is a type of conversion of a text from one script to another that involves swapping letters in predictable ways, such as Greek ⟨α⟩ → ⟨a⟩, Cyrillic ⟨д⟩ → ⟨d⟩, Greek ⟨χ⟩ → the digraph ⟨ch⟩, Armenian ⟨ն⟩ → ⟨n⟩ or Latin ⟨æ⟩ → ⟨ae⟩.

The Russian alphabet is the script used to write the Russian language. It is derived from the Cyrillic script, which was modified in the 9th century to capture accurately the phonology of the first Slavic literary language, Old Slavonic. Initially an old variant of the Bulgarian alphabet, it was used in Kievan Rus' from the 10th century onward to write what would become the modern Russian language.

Cyrillization or Cyrillisation is the process of rendering words of a language that normally uses a writing system other than Cyrillic script into the Cyrillic alphabet. Although such a process has often been carried out in an ad hoc fashion, the term "cyrillization" usually refers to a consistent system applied, for example, to transcribe names of German, Chinese, or English people and places for use in Russian, Ukrainian, Serbian, Macedonian or Bulgarian newspapers and books. Cyrillization is analogous to romanization, when words from a non-Latin script-using language are rendered in the Latin alphabet for use

De is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It commonly represents the voiced dental stop, like the pronunciation of ⟨d⟩ in "door", except closer to the teeth. De is usually Romanized using the Latin letter D.

Koppa is an archaic numeral character of the Cyrillic script. Its form are derived from some forms of the Greek letter Koppa (Ϙ ϙ).

The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Greek alphabet was altered by the Etruscans, and subsequently their alphabet was altered by the Ancient Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet.

Russian cursive is a variant of the Russian alphabet used for writing by hand. It is typically referred to as (ру́сский) рукопи́сный шрифт (rússky) rukopísny shrift, "(Russian) handwritten font". It is the handwritten form of the modern Russian Cyrillic script, used instead of the block letters seen in printed material. In addition, Russian italics for lowercase letters are often based on Russian cursive. Most handwritten Russian, especially in personal letters and schoolwork, uses the cursive alphabet. In Russian schools most children are taught from first grade how to write with this script.

The Cyrillization of Korean is the transcribing and transliterating the Korean language into the Cyrillic alphabet. The main cyrillization system in use is the Kontsevich system. The Kontsevich system was created by the Soviet-Russian scholar Lev Kontsevich in the 1950s based on the earlier transliteration system designed by Aleksandr Kholodovich.

U with diaeresis is a letter of the Cyrillic script, derived from the Cyrillic letter U.
In computing, Russification involves the localization of computers and software, allowing the user interface of a computer and its software to communicate in the Russian language using Cyrillic script.
Crimean Tatar is written in both Latin and Cyrillic. Historically, the Persian script was also used.

Latinisation or latinization was a campaign in the Soviet Union to adopt the Latin script during the 1920s and 1930s. Latinisation aimed to replace Cyrillic and traditional writing systems for all languages of the Soviet Union with Latin or Latin-based systems, or introduce them for languages that did not have a writing system. Latinisation began to slow in the Soviet Union during the 1930s and a Cyrillisation campaign was launched instead. Latinization had effectively ended by the 1940s. Most of these Latin alphabets are defunct and several contain multiple letters that do not have Unicode support as of 2023.
The cyrillization of Chinese is the transcription of Chinese characters into the Cyrillic alphabet.
Cyrillization of Greek refers to the transcription or transliteration of text from the Greek alphabet to the Cyrillic script.

The spread of the Latin script has a long history, from its archaic beginnings in Latium to its rise as the dominant writing system in modernity. The ancestors of Latin letters are found in the Phoenician, Greek, and Etruscan alphabets. As the Roman Empire expanded in classical antiquity, the Latin script and language spread along with its conquests, and remained in use in Italy, Iberia, and Western Europe after the Western Roman Empire's disappearance. During the early and high Middle Ages, the script was spread by Christian missionaries and rulers, replacing the indigenous writing systems of Central Europe, Northern Europe, and the British Isles.
The cyrillization of Japanese is the process of transliterating or transcribing the Japanese language into Cyrillic script in order to represent Japanese proper names or terms in various languages that use Cyrillic, as an aid to Japanese language learning in those languages or as a potential replacement for the current Japanese writing system. This can be done in an ad hoc fashion or using one of a number of systems.
Cyrillization of German is the conversion of text written in the German Latin alphabet into the Cyrillic alphabet, according to rules based on pronunciation. Because German orthography is largely phonemic, transcription into Cyrillic follows relatively simple rules.
The Komi language, a Uralic language spoken in the north-eastern part of European Russia, has been written in several different alphabets. Currently, Komi writing uses letters from the Cyrillic script. There have been five distinct stages in the history of Komi writing:
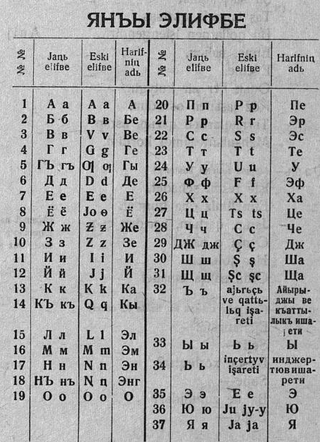
In the USSR, cyrillisation or cyrillization was the name of the campaign from the late 1930s to the 1950s which aimed to replace the writing system based on Latin script, to one based on Cyrillic.











