
Vitamin B6 is one of the B vitamins, and thus an essential nutrient. The term refers to a group of six chemically similar compounds, i.e., "vitamers", which can be interconverted in biological systems. Its active form, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate, serves as a coenzyme in more than 140 enzyme reactions in amino acid, glucose, and lipid metabolism.
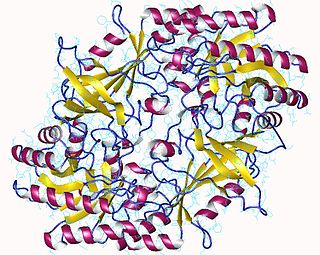
The enzyme ornithine decarboxylase catalyzes the decarboxylation of ornithine to form putrescine. This reaction is the committed step in polyamine synthesis. In humans, this protein has 461 amino acids and forms a homodimer.

Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent activities, corresponding to ~4% of all classified activities. The versatility of PLP arises from its ability to covalently bind the substrate, and then to act as an electrophilic catalyst, thereby stabilizing different types of carbanionic reaction intermediates.
Lysine 2,3-aminomutase is a radical SAM enzyme that facilitates the conversion of the amino acid lysine to beta-lysine. It accomplishes this interconversion using three cofactors and a 5'-deoxyadenosyl radical formed in a S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) activated radical reaction pathway.[1] The generalized reaction is shown below:

Pyridoxine 5′-phosphate oxidase is an enzyme, encoded by the PNPO gene, that catalyzes several reactions in the vitamin B6 metabolism pathway. Pyridoxine 5′-phosphate oxidase catalyzes the final, rate-limiting step in vitamin B6 metabolism, the biosynthesis of pyridoxal 5′-phosphate, the biologically active form of vitamin B6 which acts as an essential cofactor. Pyridoxine 5′-phosphate oxidase is a member of the enzyme class oxidases, or more specifically, oxidoreductases. These enzymes catalyze a simultaneous oxidation-reduction reaction. The substrate oxidase enzymes is hydroxlyated by one oxygen atom of molecular oxygen. Concurrently, the other oxygen atom is reduced to water. Even though molecular oxygen is the electron acceptor in these enzymes' reactions, they are unique because oxygen does not appear in the oxidized product.
In enzymology, an erythrose-4-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.72) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (R)-2-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.272) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2,4-diaminopentanoate dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.12) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an amino-acid racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an arginine racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, D-lysine 5,6-aminomutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a glutamate-1-semialdehyde 2,1-aminomutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme Glucosaminate ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.9) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2,5-diaminovalerate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an acetylornithine transaminase (EC 2.6.1.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In molecular biology, group III pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylases are a family of bacterial enzymes comprising ornithine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.17, lysine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.18 and arginine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.19.

In molecular biology, group IV pyridoxal-dependent decarboxylases are a family of enzymes comprising ornithine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.17, lysine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.18, arginine decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.19 and diaminopimelate decarboxylaseEC 4.1.1.20. It is also known as the Orn/Lys/Arg decarboxylase class-II family.
Phosphoserine transaminase is an enzyme with systematic name O-phospho-L-serine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
4,5:9,10-diseco-3-hydroxy-5,9,17-trioxoandrosta-1(10),2-diene-4-oate hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.17, tesD (gene), hsaD (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 4,5:9,10-diseco-3-hydroxy-5,9,17-trioxoandrosta-1(10),2-diene-4-oate hydrolase ( (2Z,4Z)-2-hydroxyhexa-2,4-dienoate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction







