
The Nectriaceae comprise a family of fungi in the order Hypocreales. It was circumscribed by brothers Charles and Louis René Tulasne in 1865. In 2020, an Outline of fungi was produced and listed 70 genera and about 1,336 species.

Stachybotrys is a genus of molds, hyphomycetes or asexually reproducing, filamentous fungi, now placed in the family Stachybotryaceae. The genus was erected by August Carl Joseph Corda in 1837. Historically, it was considered closely related to the genus Memnoniella, because the spores are produced in slimy heads rather than in dry chains. Recently, the synonymy of the two genera is generally accepted. Most Stachybotrys species inhabit materials rich in cellulose. The genus has a widespread distribution and contained about 50 species in 2008. There are 88 records of Stachybotrys on Species Fungorum, of which 33 species have DNA sequence data in GenBank. Species in the genus are commonly found in soil, plant litter and air and a few species have been found from damp paper, cotton, linen, cellulose-based building materials water-damaged indoor buildings, and air ducts from both aquatic and terrestrial habitats.

Herpotrichia is a genus of fungi in the family Melanommataceae.
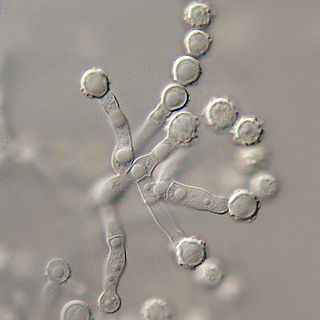
The Microascaceae are a family of fungi in the class Sordariomycetes, subclass Hypocreomycetidae. The family was published by David Malloch in 1970, an emended description based on Everet Stanley Luttrell's original 1951 publication. Family was updated in 2020.
Montagnula is a genus of fungi in the family Didymosphaeriaceae. The genus, circumscribed by mycologist Augusto Napoleone Berlese in 1896, contains an estimated 24 species in 2008, but is probably polyphyletic as currently circumscribed. It was originally placed in family Montagnulaceae, before that family was dissolved and it was later placed in family Didymosphaeriaceae, with 34 species.
Muyocopron is a genus of fungi in the Muyocopronaceae family.
Chaetosphaeria is a genus of fungi in the family Chaetosphaeriaceae.
Tubeufia is a genus in the Tubeufiaceae family of fungi.

Seiridium is a genus of plant pathogens in the family Sporocadaceae.
Trichocladium is a genus of fungi within the Chaetomiaceae family.
Stenella is a genus of anamorphic fungi in the family Mycosphaerellaceae. The widespread genus contained about 155 species in 2008.

Cordana is an ascomycete fungus genus. In 2020, it was placed within the monotypic family of Cordanaceae, and within the order Coniochaetales.
Seimatosporium is a fungus genus within the family Sporocadaceae.

The Coniochaeta are a genus of pleomorphic yeasts of the order Coniochaetales and are pathogens of trees. Some species have also been found to form endophytic associations within plants in which they live inside plant tissues but do not actually harm the organism. They can take the form of pink to brown colonies, hyphae, conidiophores or sclerotia. In 2013, the Lecythophora were merged with the Coniochaeta, following suggestions by Ziauddin Khan et al.
Gliomastix is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Bionectriaceae.

Dictyosporium is the type genus of fungi belonging to the family Dictyosporiaceae. By an estimate in 2018 it is formed by 45 species.
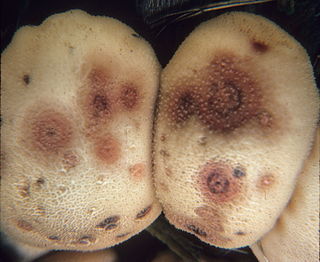
Epicoccum is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Didymellaceae.
Pseudodactylaria are a genus of fungi, within the monotypic family PseudodactylariaceaeCrous, and within the monotypic order PseudodactylarialesCrous, within the class Sordariomycetes. They are saprobic on plants in freshwater or terrestrial habitats.
Monodictys is a genus of fungi of uncertain familial and ordinal placement in the class Ascomycetes. The genus was circumscribed by Welsh-born Canadian mycologist Stanley Hughes in 1956. He assigned Monodictys putredinis as the type species.








