Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.

The Russian Far East is a region in Northeast Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asian continent; and is administered as part of the Far Eastern Federal District, which is located between Lake Baikal in eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean. The area's largest city is Khabarovsk, followed by Vladivostok. The region shares land borders with the countries of Mongolia, China, and North Korea to its south, as well as maritime boundaries with Japan to its southeast, and with the United States along the Bering Strait to its northeast.

Threatened species are any species which are vulnerable to extinction in the near future. Species that are threatened are sometimes characterised by the population dynamics measure of critical depensation, a mathematical measure of biomass related to population growth rate. This quantitative metric is one method of evaluating the degree of endangerment.

The Lesser Antillean iguana is a large arboreal lizard endemic to the Lesser Antilles. It is one of three species of lizard of the genus Iguana and is in severe decline due to habitat destruction, introduced feral predators, hunting, and hybridization with its introduced sister species, the green iguana. Successful captive breeding of this species has been limited to only two instances, as most captive-laid eggs tend to be infertile.

The conservation status of a group of organisms indicates whether the group still exists and how likely the group is to become extinct in the near future. Many factors are taken into account when assessing conservation status: not simply the number of individuals remaining, but the overall increase or decrease in the population over time, breeding success rates, and known threats. Various systems of conservation status are in use at international, multi-country, national and local levels, as well as for consumer use such as sustainable seafood advisory lists and certification. The two international systems are by the International Union for Conservation of Nature IUCN and The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES)

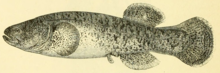
The Alaska blackfish is a species of freshwater fish in the esocid family (Esocidae) of order Esociformes. It inhabits Arctic regions of Alaska as well as Siberia and the Bering Sea islands.

Asellus aquaticus is a freshwater crustacean resembling a woodlouse. It is known by various common names including pond slater, water louse, aquatic sowbug, water hoglouse and cress bug.

A near-threatened species is a species which has been categorized as "Near Threatened" (NT) by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as that may be vulnerable to endangerment in the near future, but it does not currently qualify for the threatened status.

Yilong Lake is a large freshwater lake located in Shiping County, Honghe Prefecture, Yunnan province, southwestern China. The lake has a surface area of approximately 32 square kilometres (12 sq mi) and is particularly notable for its scenery, including the colorful lotus flowers that bloom on its surface. It is located about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) east of the county seat. The people who live in the vicinity of the lake are largely of the Yi ethnic group. As of the spring of 2013 a severe drought had resulted in substantial lowering of the water level.

The Eurasian Steppe, also simply called the Great Steppe or the steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova, Ukraine, western Russia, Siberia, Kazakhstan, Xinjiang, Mongolia and Manchuria, with one major exclave, the Pannonian steppe, located mostly in Hungary.

The Uganda mangabey is a species of Old World monkey found only in Uganda and in the Minziro Forest Reserve, just over the border in Tanzania. This crested mangabey was previously thought to just be a population of the grey-cheeked mangabey. Colin Groves upgraded the Ugandan population to the new species L. ugandae on 16 February 2007. This species is significantly smaller than the grey-cheeked mangabey, with a shorter skull and smaller face. 2008 was the most recent year in which the International Union for Conservation of Nature assessed the conservation status of L. albigena, describing it as being of least concern, and the status of L. ugandae has not been assessed separately.

The Kamchatka shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to Russia.
Abrau sprat, Clupeonella abrau, is a species of freshwater fish in the family Clupeidae. It is found landlocked in Russia in a single locality, Lake Abrau, located at 70 m above sea level near the Black Sea coast close to Novorossiysk. The lake is small and has been stocked by several alien species, whence the Abrau sprat is considered critically endangered.

The humpback whitefish, also referred to as the bottom whitefish, the Arctic whitefish or the pidschian, is a species of freshwater whitefish with a northern distribution. It is one of the members in the broader common whitefish complex, or the Coregonus clupeaformis complex. This fish lives in estuaries and brackish water near river mouths, in deltas and in slowly running rivers, in large lakes with tributaries, and floodplain lakes. It can migrate long distances upriver for spawning.

Dallia is a genus of mudminnows native to Russia and Alaska. Molecular data indicates the genus is more closely related to Esox and Novumbra than Umbra.Dallia diverged from Novumbra + Esox approximately 66 million years ago.
Limnocottus godlewskii is a species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cottidae, the typical sculpins. This fish is endemic to Lake Baikal, Russia; it is a common fish in the lake. It lives at a depth range of 2–830 metres, and inhabits the silty bottom. Males can reach a maximum total length of 19 centimetres.
Neocottus thermalis is a species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cottidae, the typical sculpins. It was described by Valentina Grigorievna Sideleva in 2002. It is a freshwater, deep water-dwelling fish which is endemic to Lake Baikal, in Russia. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 430 to 480 metres.
Procottus jeittelesii, the red sculpin or red Baikal sculpin, is a species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cottidae, the typical sculpins. This species is endemic to Lake Baikal in Russia. It is a freshwater fish that dwells under stones or in holes in the mud at a depth range of 0 to 800 m. It is often found at around 100 m (330 ft), and is most abundant during the autumn and winter. From the late winter to the spring it breeds at depths of 5 to 30 m. It can reach a maximum length of 18 cm (7.1 in), but typically is 10–12 cm (3.9–4.7 in). It has a red spotted or banded pattern on a light background. The red sculpin resembles two of its close relatives, the smaller P. gurwici and the larger P. major.
Coregonus lutokka is a putative species of whitefish in the genus Coregonus. It is native to Lake Onega and Lake Ladoga in Karelia, but it has been introduced to many other water bodies in Russia. It eats benthic larvae, molluscs and crustaceans, but in the summer it usually switches to feed on zooplankton.