
Chimaeras are cartilaginous fish in the order Chimaeriformes, known informally as ghost sharks, rat fish, spookfish, or rabbit fish; the last three names are not to be confused with rattails, Opisthoproctidae, or Siganidae, respectively.

The longsnout dogfish is a little-known deepwater dogfish, found in the Atlantic and Indian Oceans from Namibia to Mozambique and in the South Pacific off southern Australia and New Zealand.

The bareskin dogfish is a little-known, deepwater dogfish shark of the family Etmopteridae. This species is found in the western Pacific from southern Japan to western and southeastern Australia as well as in New Zealand waters.

The Australian ghostshark is a cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes) belonging to the subclass Holocephali (chimaera). Sharks, rays and skates are the other members of the cartilaginous fish group and are grouped under the subclass Elasmobranchii. Alternative names include elephant shark, makorepe, whitefish, plough-nose chimaera, or elephant fish. It is found off southern Australia, including Tasmania, and south of East Cape and Kaipara Harbour in New Zealand, at depths of 0–200 m (0–656 ft). Despite several of its names, it is not a shark, but a member of a closely related group.
The pale ghost shark is a shortnose chimaera of the family Chimaeridae. It is endemic to New Zealand waters.
The New Zealand catshark is a catshark of the family Scyliorhinidae in the order Carcharhiniformes. This species is endemic to in the deep waters around New Zealand. Its length is up to 45 centimetres (18 in). The New Zealand catshark is a small, little-known deep water bottom shark. It is dark brown around the top with a few widely spaced pale spots, and white below. It feeds on bottom-living crustaceans. It is also completely harmless to humans.
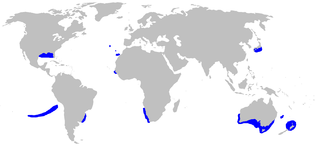
The roughskin dogfish is a sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae, found around the world on continental shelves in tropical, subtropical and temperate seas, at depths of between 100 and 1,500 m. It reaches a length of 121 cm.

The blackbelly lanternshark or lucifer shark, Etmopterus lucifer, is a shark of the family Etmopteridae, found around the world in tropical to temperate seas, at depths between 150 and 1,250 meters. Its length is up to 47 centimeters. This species consumes mesopelagic cephalopods, fishes, and crustaceans.

The sherwood dogfish or Sherwood's dogfish is a very rare sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae, found only around New Zealand. The only specimen studied was about 80 cm long.

The spotted estuary smooth-hound or rig is a houndshark of the family Triakidae, found on the continental shelves and in estuaries around New Zealand. It is closely related to the gummy shark of Australia. Males can grow up to a length of 125 cm, while females can reach a length of 151 cm.
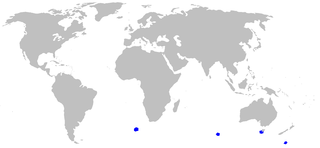
The whitetail dogfish is a very rare sleeper shark of the family Somniosidae, found from the eastern Indian Ocean round southern Australia to New Zealand, at depths of between 150 and 500 m. Its length is up to 1.1 m.

The southern lanternshark is a shark of the family Etmopteridae found in the southeast Pacific between latitudes 29°S and 59°S, at depths of between 220 and 1,460 m. This species has been found off Northland, off the Chatham Islands, on the Campbell Plateau, all in New Zealand waters. Its length is up to 60 cm. Reproduction is ovoviviparous, with 10 to 13 pups in a litter, length at birth about 18 cm. They exhibit bioluminescence.

Hydrolagus is a genus of fish in the family Chimaeridae found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.

Ogilby's ghostshark, also known as the whitefish, is a species of chimaera, native to the waters of Australia and southern Indonesia. It lives near the ocean floor on the continental shelf and continental slope 120–350 m (390–1,150 ft) deep. It reaches a maximum size of 85.0 cm (33.5 in). Reproduction is oviparous and eggs are encased in horny shells. It reaches maturity between 64–70 cm (25–28 in) in length. It is listed as a near-threatened species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) due to steep declines in population in areas affected by trawling.

The pointy-nosed blue chimaera, also known as the pointy-nosed blue ratfish, Ray Troll's chimaera or abyssal ghostshark, is a species of deep-sea fish in the family Chimaeridae.

The Chimaeridae, or short-nosed chimaeras, are a family of cartilaginous fish.
The marbled ghostshark is a chimaera species in the family Chimaeridae, which lives in waters off the eastern coast of Australia.

The whitespot ghost shark is a chimaera species in the family Chimaeridae, which lives in parts of the Galápagos Islands in the southeast Pacific Ocean. It lives in waters with steep slopes and boulders and grows to a total length of around 40–50 cm (16–20 in).
The Galápagos ghostshark is a chimaera species in the family Chimaeridae, likely endemic to the Galápagos Islands. It was discovered by John E. McCosker in 1995 and described in 2006, scientifically named in honor of McCosker. This chimaera has a brown compressed, elongate body. The holotype and paratype of the species, both juvenile females, had a total length of 38.1 centimetres (15.0 in) and 22.7 centimetres (8.9 in), respectively. It lives in rocky habitats close to the sea floor, in waters about 395–510 metres (1,296–1,673 ft) deep. It is listed as least concern on the IUCN Red List.















