Intermediate System to Intermediate System is a routing protocol designed to move information efficiently within a computer network, a group of physically connected computers or similar devices. It accomplishes this by determining the best route for data through a packet switching network.
A network switch is networking hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destination device.
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that builds a loop-free logical topology for Ethernet networks. The basic function of STP is to prevent bridge loops and the broadcast radiation that results from them. Spanning tree also allows a network design to include backup links providing fault tolerance if an active link fails.

A virtual local area network (VLAN) is any broadcast domain that is partitioned and isolated in a computer network at the data link layer. In this context, virtual refers to a physical object recreated and altered by additional logic, within the local area network. Basically, a VLAN behaves like a virtual switch or network link that can share the same physical structure with other VLANs while staying logically separate from them. Between network devices, VLANs work by applying tags to network frames and handling these tags in networking systems –creating the appearance and functionality of network traffic that is physically on a single network but acts as if it were split between separate networks. In this way, VLANs can keep network applications separate despite being connected to the same physical network, and without requiring multiple sets of cabling and networking devices to be deployed.
EtherType is a two-octet field in an Ethernet frame. It is used to indicate which protocol is encapsulated in the payload of the frame and is used at the receiving end by the data link layer to determine how the payload is processed. The same field is also used to indicate the size of some Ethernet frames.
Resilient Packet Ring (RPR), as defined by IEEE standard 802.17, is a protocol designed for the transport of data traffic over optical fiber ring networks. The standard began development in November 2000 and has undergone several amendments since its initial standard was completed in June 2004. The amended standards are 802.17a through 802.17d, the last of which was adopted in May 2011. It is designed to provide the resilience found in SONET and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy networks but, instead of setting up circuit oriented connections, provides a packet based transmission, in order to increase the efficiency of Ethernet and IP services.
The Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) and algorithm, provides both simple and full connectivity assigned to any given virtual LAN (VLAN) throughout a bridged local area network. MSTP uses bridge protocol data unit (BPDUs) to exchange information between spanning-tree compatible devices, to prevent loops in each Multiple Spanning Tree instance (MSTI) and in the common and internal spanning tree (CIST), by selecting active and blocked paths. This is done as well as in Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) without the need of manually enabling backup links and getting rid of switching loop danger.
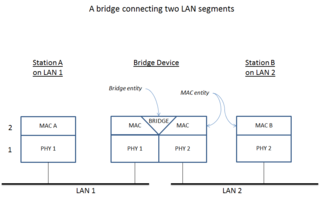
A network bridge is a computer networking device that creates a single, aggregate network from multiple communication networks or network segments. This function is called network bridging. Bridging is distinct from routing. Routing allows multiple networks to communicate independently and yet remain separate, whereas bridging connects two separate networks as if they were a single network. In the OSI model, bridging is performed in the data link layer. If one or more segments of the bridged network are wireless, the device is known as a wireless bridge.
The Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is a vendor-neutral link layer protocol used by network devices for advertising their identity, capabilities, and neighbors on a local area network based on IEEE 802 technology, principally wired Ethernet. The protocol is formally referred to by the IEEE as Station and Media Access Control Connectivity Discovery specified in IEEE 802.1AB with additional support in IEEE 802.3 section 6 clause 79.
Provider Backbone Bridge Traffic Engineering (PBB-TE) is a computer networking technology specified in IEEE 802.1Qay, an amendment to the IEEE 802.1Q standard. PBB-TE adapts Ethernet to carrier class transport networks. It is based on the layered VLAN tags and MAC-in-MAC encapsulation defined in IEEE 802.1ah, but it differs from PBB in eliminating flooding, dynamically created forwarding tables, and spanning tree protocols. Compared to PBB and its predecessors, PBB-TE behaves more predictably and its behavior can be more easily controlled by the network operator, at the expense of requiring up-front connection configuration at each bridge along a forwarding path. PBB-TE Operations, Administration, and Management (OAM) is usually based on IEEE 802.1ag. It was initially based on Nortel's Provider Backbone Transport (PBT).
IEEE 802.1ah is an amendment to the IEEE 802.1Q networking standard which adds support for Provider Backbone Bridges. It includes an architecture and a set of protocols for routing over a provider's network, allowing interconnection of multiple provider bridge networks without losing each customer's individually defined VLANs. It was initially created by Nortel before being submitted to the IEEE 802.1 committee for standardization. The final version was approved by the IEEE in June 2008 and has been integrated into IEEE 802.1Q-2011.
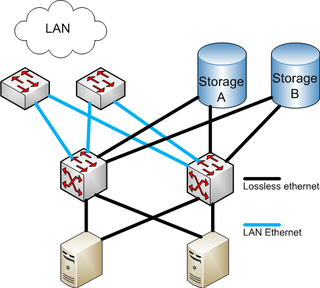
Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) is a computer network technology that encapsulates Fibre Channel frames over Ethernet networks. This allows Fibre Channel to use 10 Gigabit Ethernet networks while preserving the Fibre Channel protocol. The specification was part of the International Committee for Information Technology Standards T11 FC-BB-5 standard published in 2009. FCoE did not see widespread adoption.
IEEE 802.1aq is an amendment to the IEEE 802.1Q networking standard which adds support for Shortest Path Bridging (SPB). This technology is intended to simplify the creation and configuration of Ethernet networks while enabling multipath routing.
IEEE 802.1ad is an amendment to the IEEE 802.1Q-1998 networking standard which adds support for provider bridges. It was incorporated into the base 802.1Q standard in 2011. The technique specified by the standard is known informally as stacked VLANs or QinQ.
TRILL is a networking protocol for optimizing bandwidth and resilience in Ethernet networks, implemented by devices called TRILL switches. TRILL combines techniques from bridging and routing, and is the application of link-state routing to the VLAN-aware customer-bridging problem. Routing bridges (RBridges) are compatible with, and can incrementally replace, previous IEEE 802.1 customer bridges. TRILL Switches are also compatible with IPv4 and IPv6, routers and end systems. They are invisible to current IP routers, and like conventional routers, RBridges terminate the broadcast, unknown-unicast and multicast traffic of DIX Ethernet and the frames of IEEE 802.2 LLC including the bridge protocol data units of the Spanning Tree Protocol.
A routing bridge or RBridge, also known as a TRILL switch, is a network device that implements the TRILL protocol and should not be confused with BRouters. RBridges are compatible with previous IEEE 802.1 customer bridges as well as IPv4 and IPv6 routers and end nodes. They are invisible to current IP routers and, like routers, RBridges terminate the bridge spanning tree protocol.
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) is a set of standards under development by the Time-Sensitive Networking task group of the IEEE 802.1 working group. The TSN task group was formed in November 2012 by renaming the existing Audio Video Bridging Task Group and continuing its work. The name changed as a result of the extension of the working area of the standardization group. The standards define mechanisms for the time-sensitive transmission of data over deterministic Ethernet networks.
Deterministic Networking (DetNet) is an effort by the IETF DetNet Working Group to study implementation of deterministic data paths for real-time applications with extremely low data loss rates, packet delay variation (jitter), and bounded latency, such as audio and video streaming, industrial automation, and vehicle control.


