
Aerangis, abbreviated as Aergs in horticultural trade, is a genus of the Orchid family (Orchidaceae). The name of this genus has been derived from the Greek words 'aer' (air) and 'angos' (urn), referring to the form of the lip. It is the type genus of the subtribe Aerangidinae, which has recently been subsumed in the subtribe Angraecinae. Approximately 50 species in this genus are known mostly from tropical Africa, but also from the Comoro Islands, Madagascar and Sri Lanka.

Dendrochilum was a genus of epiphytic, lithophytic and a few terrestrial flowering plants in the orchid family (Orchidaceae). It is now considered to be a synonym of Coelogyne Lindl. The name of this genus was derived from Ancient Greek words dendron ("tree"), and either cheilos ("lip") or chilos, alluding to either the flowers' large lip or to their epiphytic growth. These orchids are popular among fans of non-traditional orchid curiosities.

Dendrobium parishii is a species of orchid native to Asia.

Dendrobium discolor, commonly known as antler orchid or golden orchid, is a species of epiphytic or lithophytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae, and are native to northern Australia, New Guinea, and part of Indonesia. It has cylindrical pseudobulbs, each with between ten and thirty five leathery leaves, and flowering stems with up to forty mostly brownish or greenish flowers with wavy and twisted sepals and petals.

Dendrobium gratiosissimum, the very graceful dendrobium, is a species of orchid. It is native to Thailand, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, Yunnan, and Assam.

Dendrobium cerinum is a species of orchid that is endemic to the island of Luzon in the Philippines. It was first formally described in 1879 by Heinrich Gustav Reichenbach in The Gardeners' Chronicle. The specific epithet cerinum is derived from the Ancient Greek word kerinos meaning "waxen", "wax-colored" or "yellowish".

Phalaenopsis parishii is a species of orchid found from the eastern Himalaya to Indochina.
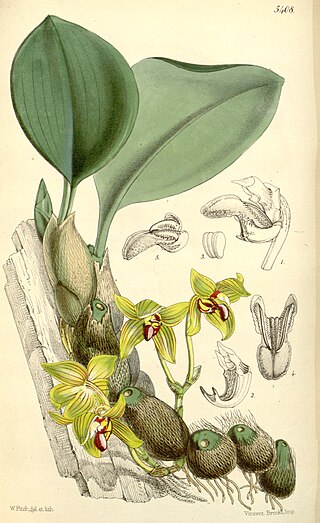
Bulbophyllum psittacoglossum is a species of orchid in the genus Bulbophyllum. It was named by Heinrich Gustav Reichenbach in 1863.

Dendrobium johannis, commonly known as the chocolate tea tree orchid, is a species of epiphytic or lithophytic orchid native to Australia and New Guinea. It has spindle-shaped pseudobulbs, between five and ten dark green leaves with purplish markings and flowering stems with up to fifteen chocolate brown flowers with a yellow labellum.

Dactylostalix is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. At the present time, there is only one known species, Dactylostalix ringens. It is native to Japan, the Kuril Islands, and Sakhalin Island.

Dendrobium striolatum, commonly known as the streaked rock orchid is a species of orchid endemic to eastern Australia. It is a small, usually lithophytic orchid with wiry stems, cylindrical leaves and flowering stems with one or two yellow, cream-coloured or greenish flowers with reddish stripes. It often grows on cliff faces in New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania.

Dipodium pictum, commonly known as brittle climbing-orchid or climbing hyacinth-orchid, is an orchid species that is native to Malesia and the Cape York Peninsula in Australia.

Dipodium paludosum is a terrestrial orchid species that is native to south-east Asia. It occurs in Cambodia, Thailand, Vietnam, the Philippines, Sumatra, Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo. The leaves up to 30 cm long and 2.5 cm wide. The axillary racemes comprise 6 to 12 fleshy flowers which are each up to 4 cm wide and are cream with purple-magenta spots.

Vanilla phaeantha, common name leafy vanilla or oblong-leaved vanilla, is a plant species known to occur in the wild only on the islands of Trinidad and Cuba, and also in Collier County, Florida. It occurs in cypress swamps and hammocks at elevations of less than 20 m.
Dendrobium macropus, commonly known as the Norfolk Island cane orchid, is a species of epiphytic or lithophytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae and is endemic to Norfolk Island. It has cylindrical pseudobulbs, thin, dark green leaves and between five and ten yellowish green flowers that do not open widely.
Dendrobium brachypus, commonly known as the dwarf cane orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae. It has crowded, yellowish green pseudobulbs, dark green leaves and two or three cream-coloured to whitish or greenish flowers which often do not open fully. It grows on trees and rocks on one mountain on Norfolk Island.

Trichoglottis atropurpurea, the dark purple trichoglottis, is a species of orchid endemic to the Philippines. This hot to warm growing epiphyte was first found growing in mangrove swamps in the islands of Biliran, Catanduanes, Mindanao and Polillo. The plant shares the same appearance with T. philippinensis except for the rich dark color of the blooms and slight variation of the perianth. This species was first described in 1877 by the German botanist Heinrich Gustav Reichenbach, an expert on the orchid family. At that time, thousands of newly discovered orchids were being sent back to Europe, and he was responsible for identifying, describing and classifying many of these new discoveries.
Dendrobium insigne, commonly known as the mangrove tartan orchid, is a species of epiphytic or lithophytic orchid native to New Guinea and Indonesia. It has crowded, cane-like stems with many leaves arranged in two vertical rows, and short-lived yellow and red flowers in groups of two or three.

Liparis condylobulbon, commonly known as the tapered sphinx orchid or 细茎羊耳蒜 is a plant in the orchid family. It is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid with crowded, glossy green, cylinder-shaped pseudobulbs, each with two linear to lance-shaped leaves and between fifteen and thirty five pale green to cream-coloured flowers with an orange labellum. This orchid usually grows on trees and rocks in rainforest from Taiwan and Indochina to the south-west Pacific.

Charles Samuel Pollock Parish (1822–1897) was an Anglo-Indian clergyman and botanist who served as chaplain to the forces of the Honourable East India Company in Burma. With his wife Eleanor he collected and painted plants, chiefly orchids, identifying and naming a number of species new to science. Several species are named in his honour.

















