
Digenea is a class of trematodes in the Platyhelminthes phylum, consisting of parasitic flatworms with a syncytial tegument and, usually, two suckers, one ventral and one oral. Adults commonly live within the digestive tract, but occur throughout the organ systems of all classes of vertebrates. Once thought to be related to the Monogenea, it is now recognised that they are closest to the Aspidogastrea and that the Monogenea are more closely allied with the Cestoda. Around 6,000 species have been described to date.

Plagiorchiida is a large order of trematodes, synonymous to Echinostomida. They belong to the Digenea, a large subclass of flukes. This order contains relatively few significant parasites of humans.

Zoogonidae are a family of trematodes in the order Plagiorchiida.
Apororhynchus is a genus of small parasitic spiny-headed worms. It is the only genus in the family Apororhynchidae, which in turn is the only member of the order Apororhynchida. A lack of features commonly found in the phylum Acanthocephala suggests an evolutionary branching from the other three orders of class Archiacanthocephala; however no genetic analysis has been completed to determine the evolutionary relationship between species. The distinguishing features of this order among archiacanthocephalans is a highly enlarged proboscis which contain small hooks. The musculature around the proboscis is also structured differently in this order. This genus contains six species that are distributed globally, being collected sporadically in Hawaii, Europe, North America, South America, and Asia. These worms exclusively parasitize birds by attaching themselves around the cloaca using their hook-covered proboscis. The bird hosts are of different orders, including owls, waders, and passerines. Infestation by an Apororhynchus species may cause enteritis and anemia.

Opisthorchiidae is a family of digenean trematodes. Opisthorchiidae have cosmopolitan distribution.

Spirorchiidae is a family of digenetic trematodes. Infestation by these trematodes leads to the disease spirorchiidiosis. Spirorchiids are mainly parasites of turtles. It has been synonymised with Proparorchiidae Ward, 1921, Spirorchidae Stunkard, 1921, and Spirorchiidae MacCallum, 1921.

Bucephalidae is a family of trematodes that parasitize fish. They lack suckers, having instead a muscular organ called a "rhynchus" at the front end which they use to attach to their hosts. The characteristics of the rhynchus are used to help define the genera of the family. It is one of the largest digenean families, with 25 genera containing hundreds of described species. Bucephalids are cosmopolitan, having been recorded all over the world. They are parasites of fish from freshwater, marine, and brackish water habitat types.
Haploporidae is a family of trematodes in the order Plagiorchiida.

Opecoelidae is a family of trematodes. It is the largest digenean family with over 90 genera and nearly 900 species, almost solely found in marine and freshwater teleost fishes. It was considered by Bray et al. to belong in the superfamily Opecoeloidea Ozaki, 1925 or the Brachycladioidea Odhner, 1905.
Telorchiidae is a family of trematode parasites.
Cainocreadium is a genus of trematodes in the family Opecoelidae. It has been synonymised with Apopodocotyle Pritchard, 1966, Cainocreadoides Nagaty, 1956, and Emmettrema Caballero y Caballero, 1946.
Peracreadium is a genus of trematodes in the family Opecoelidae. It is very similar to the related genus Cainocreadium Nicoll, 1909, and has been synonymised with the genera Anabathycreadium Salman & Srivastava, 1990, Indocreadium Salman & Srivastava, 1990, and Lebouria Nicoll, 1909.

Echinostomatidae is a family of trematodes in the order Plagiorchiida, first described in 1899.
Gorgoderidae is a family of trematodes in the order Plagiorchiida.
Aephnidiogenidae is a family of trematodes in the order Plagiorchiida.
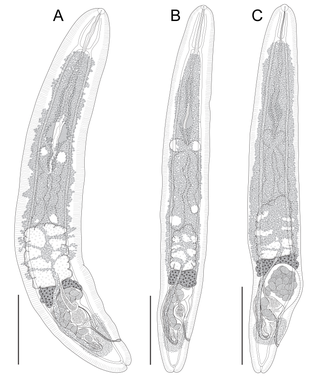
Aporocotylidae is a family of trematodes within the order Diplostomida, which contains species commonly known as fish blood flukes. It contains more than 40 genera, the largest being Cardicola. Species in this family parasite fish in both fresh and marine water.
Cryptogonimidae is a family of trematodes belonging to the order Plagiorchiida.

Clinostomum is a genus of trematodes in the order Diplostomida.
Halipeginae is a subfamily of trematode in the family Derogenidae.









