
Brayley is a lunar impact crater located in the southwest part of the Mare Imbrium. It was named after British geographer Edward W. Brayley in 1935. It has a circular rim and a low rise in the center. There are no notable craters overlapping the rim or interior. The sinuous rille Rima Brayley passes to the north of Brayley.

Caventou is a tiny lunar impact crater located in the western part of the Mare Imbrium. It is a circular, cup-shaped formation surrounded by the lunar mare. It was named after French chemist Joseph B. Caventou in 1976. Prior to that, it had the designation La Hire D, being associated with the mountain Mons La Hire to the southeast.

Bobillier is a tiny, cup-shaped lunar impact crater in the southwest part of Mare Serenitatis. It was named after French geometer Étienne Bobillier in 1976. It lies to the north-northwest of the crater Bessel. To the south and west is a wrinkle ridge designated Dorsum Buckland. Bobillier was previously identified as Bessel E.
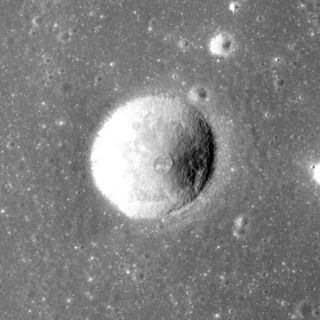
Borel is a tiny lunar impact crater located in the southeast part of Mare Serenitatis. It was named after French mathematician Émile Borel. To the northeast is the crater Le Monnier and to the southeast is the crater Abetti. Borel was previously identified as Le Monnier C.

Finsch is a relatively small lunar impact crater in the mid-part of Mare Serenitatis that has been almost completely covered by the mare, forming a ghost crater in the lava plain. It was named after German zoologist Otto Finsch. It is located to the south-southeast of the crater Sarabhai and northeast of Bessel.

Anderson is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It is located to the northwest of the crater Sharonov, and the satellite crater Sharanov X is attached to the southeast rim of Anderson. To the northeast is the peculiar formation Buys-Ballot, and to the east-southeast lies the larger crater Spencer Jones.

Asada is a small lunar impact crater located at the northern edge of Mare Fecunditatis, to the northeast of the crater Taruntius. It is a circular crater formation with inner walls that slope down toward a small central floor at the midpoint. Asada was designated Taruntius A prior to being named by the IAU.

Curtis is a very small lunar impact crater that lies in the western Mare Crisium, to the east of the crater Picard. It is a circular, cup-shaped formation that is otherwise undistinguished. It was named after American astronomer Heber D. Curtis in 1973. In the past it was designated Picard Z.
Aloha is a tiny impact crater on the Moon, that lies to the northwest of the Montes Agricola ridge, on the Oceanus Procellarum. It is located near the faint terminus of a ray that crosses the mare from the southeast, originating at the crater Glushko.

Burckhardt is a lunar impact crater that is located in the northeast part of the Moon. It lies between the craters Geminus just to the north and Cleomedes to the south.

Babakin is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the southern part of the walled basin Fermi on the far side of the Moon. The crater rim is symmetrical, circular and sharp-edged, with only some minor erosion and a slight depression along the northern edge. The interior walls slope downward gently toward the center.

Boss is a lunar impact crater that is located along the northeast rim of the Moon's near side. Due to its location, the crater is viewed from the side by observers on the Earth, and its visibility is subject to libration effects. It was named by the IAU in 1964 for astronomer Lewis Boss.

Bellot is a small lunar impact crater that is located on the southwest edge of Mare Fecunditatis. It lies between the craters Goclenius to the northwest and Crozier to the southeast. To the southwest is Colombo, and to the west is Magelhaens.

Buisson is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It is named after the French physicist Henri Buisson. Nearly attached to the southeast rim is the crater Vesalius. To the southwest is Einthoven. The rim of this crater is somewhat worn, and is lowest in the north. There is a low central ridge across the midpoint.

Belopolʹskiy is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It lies to the west of the crater Houzeau, and northeast of Strömgren. Just to the northwest of Belopolʹskiy is the crater Ioffe.

Chaucer is a lunar impact crater that is located to the west of the walled plain Hertzsprung, on the far side of the Moon. It lies to the northwest of the crater Vavilov and east of the Tsander–Kibal'chich crater pair. This is a circular crater with a slightly eroded outer rim. The interior floor is nearly featureless, with only a few tiny craterlets marking the surface. It is named after the writer Geoffrey Chaucer.

Diderot is a small lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It lies within the southwestern interior floor of the huge walled plain Fermi, about midway between the basin midpoint and the southwest rim. The crater is saucer-shaped, with smaller craters located just to the northwest and the north. The inner wall is narrower along the eastern side, and has a pair of ridges along the southern face. This crater is otherwise unremarkable.

Florensky is a lunar impact crater that is attached to the northeastern rim of the larger crater Vernadskiy. It is located on the far side of the Moon and cannot be directly seen from the Earth. The rim of this crater has been heavily eroded and it forms an irregular ring about the uneven interior. This crater was previously identified as Vernadskiy B before being assigned a name by the IAU in 1985.

Fox is a small lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is named after the American astronomer Philip Fox. It lies near the northern rim of the crater Wyld, and to the southeast of Babcock. This crater is bowl-shaped, with a roughly circular rim, simple sloping walls and a relatively level, featureless interior. There is some talus along the northern inner wall.

Aepinus is a small lunar impact crater located along the northern lunar limb, close to the north pole of the Moon. To the south east is the prominent crater Hermite.























