
Beaumont is a lava-flooded crater located on the southwestern shore of the Mare Nectaris on Earth's Moon. It lies to the northwest of the similarly flooded crater remnant Fracastorius. To the west is the prominent crater Catharina. The crater is named after French geologist Léonce Élie de Beaumont.

Artemis is a tiny lunar impact crater located in the Mare Imbrium. Craters of this dimension typically form cup-shaped excavations on the surface of the Moon. It lies near the midpoint between the craters Euler to the west and Lambert to the east. Just a few kilometers to the southeast is the even smaller Verne.

Artsimovich is a small lunar impact crater located in the western Mare Imbrium of the Earth's Moon. This is a circular crater forming a cup-shaped excavation in the surface of the lunar mare. It is named after Soviet physicist Lev A. Artsimovich. To the east is the crater Diophantus and to the northeast lies Delisle. Less than 20 kilometers to the north-northeast is the tiny Fedorov. This crater was identified as Diophantus A before being named by the International Astronomical Union.

Beer is a relatively small lunar impact crater located on the Mare Imbrium, to the east of the crater Timocharis. It was named after German astronomer Wilhelm W. Beer. Just to the northwest is the matching twin Feuillée.

Carlini is a small lunar impact crater located in the Mare Imbrium. It was named after Italian astronomer Francesco Carlini. The crater is bowl-shaped with a small central floor. It has a higher albedo than the surrounding mare, making it prominent due to its isolated location. To the south is a wrinkle ridge named Dorsum Zirkel, and farther south lies the peak Mons La Hire.
Abetti is a lunar impact crater that has been completely submerged by mare lavas. It forms a 'ghost crater' in the surface, showing only a curved rise where the rim is located. Abetti is located near the southeast edge of Mare Serenitatis, to the west of the Mons Argaeus. This crater is generally visible only at low angles of illumination. It is named after two Italian astronomers, Antonio Abetti and his son Giorgio.

Fahrenheit is a tiny lunar impact crater located in the southeast part of the Mare Crisium. This area of the surface is nearly devoid of impact features of interest. To the east are the Dorsa Harker wrinkle ridges, and beyond them is Promontorium Agarum at the edge of the mare. The landing site of the Soviet Luna 24 probe is located about 15 kilometers to the southeast.

Amontons is a tiny lunar impact crater in the western half of the Mare Fecunditatis. It is a circular, cup-shaped formation that has been excavated out of the level surface by the impact, and is the same dark hue as the surrounding mare. When the sun is at a low angle, multiple ghost-craters are visible in the mare surface to the south-southeast and north of it.

Asada is a small lunar impact crater located at the northern edge of Mare Fecunditatis, to the northeast of the crater Taruntius. It is a circular crater formation with inner walls that slope down toward a small central floor at the midpoint. Asada was designated Taruntius A prior to being named by the IAU.

Bowen is a small lunar impact crater that is located to the southwest of the Montes Haemus, on the edge of a small lunar mare named the Lacus Doloris. It was named after American astronomer Ira S. Bowen. It is distinguished only by having a relatively flat floor, rather than being bowl-shaped like most small craters. Bowen was previously designated Manilius A. The crater Manilius is located to the south, at the opposite shore of the Lacus.

Crile is a tiny lunar impact crater. It is roughly circular and cup-shaped, with interior walls that slope down to the midpoint. The crater lies in the Palus Somni, between the Mare Crisium to the east and Mare Tranquillitatis to the west.
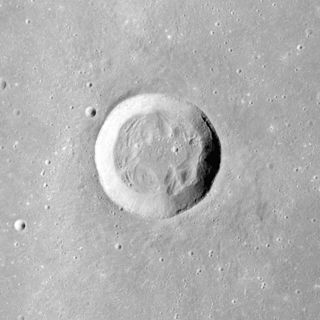
Bessel is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the southern half of the Mare Serenitatis. The crater was named after the German astronomer Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel in 1935. Despite its small size, this is the largest crater to lie entirely within the mare. It lies to the north-northeast of the crater Menelaus.

Alhazen is a lunar impact crater that lies near the eastern limb of the Moon's near side. Just to the south-southeast is the crater Hansen, and to the west is the Mare Crisium. The rim of Alhazen is nearly circular, but appears highly oblong when viewed from the Earth due to foreshortening. The inner walls and the crater floor are rugged and irregular. A low ridge joins the south rim of Alhazen with the nearby Hansen. The crater is named after the Arab Muslim scientist, Ibn al-Haytham.

Clausius is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southwest part of the Moon, in the small lunar mare designated Lacus Excellentiae. It is completely enclosed by mare material, although the tiny satellite crater Clausius A lies just to the north. The rim of Clausius is low and sharp, with a slightly oval shape that is longer in the north-south direction. The interior floor has been flooded by basaltic lava, and appears level and featureless with a darker surface that matches the mare surface that surrounds the crater exterior.

Bouguer is a lunar impact crater that lies along the southern edge of the Mare Frigoris, to the north of the crater Bianchini. To the west-southwest of Bouguer, along the same shore of the mare, is the crater Foucault. Nearly due west is the more prominent Harpalus, and to the west is La Condamine.

Brunner is a lunar impact crater that is located along the eastern limb of the Moon, to the southeast of the Mare Smythii. At this location the crater is viewed from the edge, and so it is not possible to see much detail from the Earth. The visibility of this formation is also affected by libration. The crater lies to the southwest of the walled plain Hirayama, and to the east of the elongated crater Houtermans.

Capuanus is a lunar impact crater that lies along the southern edge of the Palus Epidemiarum. It was named after Italian astronomer F. Capuano di Manfredonia. The outer rim is eroded and indented by lesser crater impacts, with notches in the north, west, and southern parts of the rim. The interior floor has been resurfaced by basaltic lava, which is connected to the surrounding lunar mare by a narrow, crater-formed gap in the northern rim. The floor is particularly notable for the hosting a number of domes, which are believed to have formed through volcanic activity.

Elmer is a small lunar impact crater that is located to the south of Mare Smythii, near the eastern limb of the Moon. This crater is seen at a highly oblique angle from Earth, and the visibility is affected by libration. Elmer lies southwest of the crater Kreiken, and east-southeast of the larger Dale. This is a circular, bowl-shaped crater with an interior floor that occupies about half the total diameter.

Courtney is a tiny lunar impact crater on the Mare Imbrium, a lunar mare in the northwest quadrant of the Moon. It lies about two crater diameters to the northwest of Euler, in an otherwise isolated stretch of the mare. The dark surface in this region is marked by Euler's ray material. The name is an English male name.

Chalonge is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It lies to the southwest of the larger crater Lewis, in the outer skirt of ejecta that surrounds the Mare Orientale impact basin. To the southeast are the Montes Cordillera, a ring of mountains that encircle the Mare Orientale formation.




















