
Humason is a tiny lunar impact crater located in the Oceanus Procellarum. This is a cup-shaped crater with an outer rim that rises slightly above the surrounding lunar mare. To the west is a low system of mare wrinkle ridges named the Dorsa Whiston that wind southwards towards Montes Agricola.

Wallach is a tiny lunar impact crater located in the eastern Mare Tranquillitatis. It was named after German chemist and Nobel laureate Otto Wallach. It is a circular, bowl-shaped feature with a negligible interior floor; the inner walls just slope down to the midpoint of the crater. Wallach is located to the northeast of the crater Maskelyne, near some low ridges in the lunar mare. It was previously identified as Maskelyne H before being given a name by the IAU.
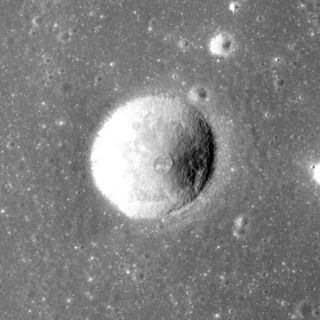
Borel is a tiny lunar impact crater located in the southeast part of Mare Serenitatis. It was named after French mathematician Émile Borel. To the northeast is the crater Le Monnier and to the southeast is the crater Abetti. Borel was previously identified as Le Monnier C.

Biot is a small, bowl-shaped lunar impact crater located in the southern reaches of the Mare Fecunditatis. It is named after French astronomer Jean-Baptiste Biot."Biot (crater)". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program. It is a circular formation with a sharp-edged rim that has not been significantly worn. The inner walls slope down to a relatively small interior floor. The albedo of the wide inner walls is higher than the surrounding lunar mare, giving it a light hue. To the southeast is the crater Wrottesley.

Grimaldi is a large basin located near the western limb of the Moon. It lies to the southwest of the Oceanus Procellarum, and southeast of the crater Riccioli. Between Oceanus Procellarum is Damoiseau, and to the north is Lohrmann.

Abbot is a small lunar impact crater that lies on the rugged ground between the Mare Fecunditatis in the south and west, and the Mare Crisium to the north. It is a circular crater with a cup-shaped interior. The inner walls slope downward to the midpoint, and no impacts of significant mark the interior or the rim.
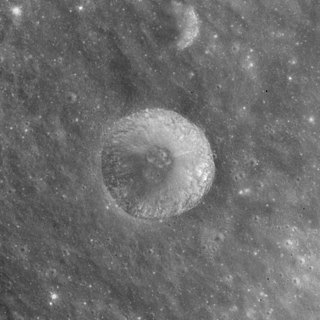
Acosta is a small lunar impact crater located just to the north of the prominent crater Langrenus, near the east edge of Mare Fecunditatis. To the west are the trio of Atwood, Naonobu, and Bilharz. Acosta is named after the Portuguese naturalist Cristóvão da Costa.

Asada is a small lunar impact crater located at the northern edge of Mare Fecunditatis, to the northeast of the crater Taruntius. It is a circular crater formation with inner walls that slope down toward a small central floor at the midpoint. Asada was designated Taruntius A prior to being named by the IAU.
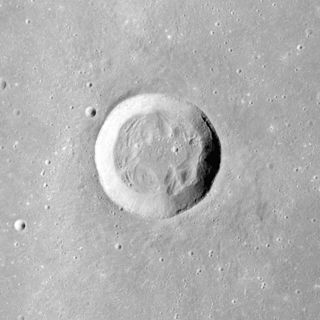
Bessel is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the southern half of the Mare Serenitatis. The crater was named after the German astronomer Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel in 1935. Despite its small size, this is the largest crater to lie entirely within the mare. It lies to the north-northeast of the crater Menelaus.

Bohnenberger is a lunar impact crater that lies near the east edge of the Mare Nectaris, in the foothills of the Montes Pyrenaeus mountain range that forms the perimeter of the mare. To the east beyond the mountains is the larger crater Colombo. The crater has a low rim along the north wall, and the floor is somewhat irregular with a ridge crossing the floor. There is a small crater along the western inner wall.

Hohmann is a lunar impact crater that lies within the central basin of the Mare Orientale formation, on the farside of the Moon. It is located to the south of the crater Maunder, and to the west of Kopff crater. Due to its proximity to the western lunar limb, this area of the surface is occasionally visible during favorable librations. However the basin is viewed from the side, restricting the amount of detail that can be observed from Earth.

Alhazen is a lunar impact crater that lies near the eastern limb of the Moon's near side. Just to the south-southeast is the crater Hansen, and to the west is the Mare Crisium. The rim of Alhazen is nearly circular, but appears highly oblong when viewed from the Earth due to foreshortening. The inner walls and the crater floor are rugged and irregular. A low ridge joins the south rim of Alhazen with the nearby Hansen. The crater is named after the Arab Muslim scientist, Ibn al-Haytham.
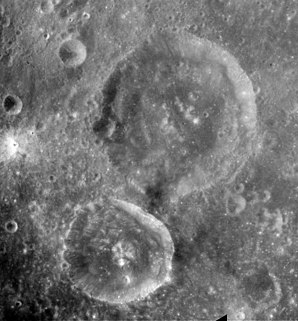
Back is a small lunar impact crater that is located near the eastern limb of the Moon. It lies on the northwest edge of the Mare Smythii, and the northeast rim is adjacent to the crater Schubert. To the west is Jenkins, and to the southwest is the Weierstrass–Van Vleck crater pair.

Bellot is a small lunar impact crater that is located on the southwest edge of Mare Fecunditatis. It lies between the craters Goclenius to the northwest and Crozier to the southeast. To the southwest is Colombo, and to the west is Magelhaens.

Drude is a lunar impact crater that lies on the far side of the Moon, in the rugged Montes Cordillera range that forms the outer ring around the Mare Orientale impact basin. It is located just behind the west-southwest limb, and this area is sometimes brought into sight from Earth during favorable librations. However, even at such times, the crater is viewed from the edge and little detail can be seen.

Leibnitz is a huge lunar impact crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. This formation is the same size as Clavius on the near side. It is located to the east-southeast of Mare Ingenii, and is joined to the northeast rim of Von Kármán. Attached to the eastern rim of Leibnitz is Davisson, and intruding into the southeast rim is Finsen. Farther to the west is the large Oppenheimer.

Bliss is small lunar impact crater that is located just to the west of the dark-floored crater Plato. It lies in a region of continental terrain between Mare Imbrium to the south and Mare Frigoris to the north. This crater is bowl-shaped, with a small interior floor at the midpoint and a somewhat eroded outer rim.

Magelhaens is a lunar impact crater that lies along the southwestern edge of the Mare Fecunditatis, in the eastern part of the Moon's near side. It was named after 16th-century Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan. It lies to the south-southwest of the crater Goclenius, about midway between Gutenberg to the northwest and Colombo to the southeast.

Eichstadt is a lunar impact crater that is located in the eastern section of the Montes Cordillera range that encircles the Mare Orientale impact basin. It lies toward the southwestern limb of the Moon, and so appears oblong when viewed from the Earth due to foreshortening. Over 200 kilometers to the east of Eichstadt are the craters Darwin and Lamarck, and to the south is Krasnov.

Chalonge is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It lies to the southwest of the larger crater Lewis, in the outer skirt of ejecta that surrounds the Mare Orientale impact basin. To the southeast are the Montes Cordillera, a ring of mountains that encircle the Mare Orientale formation.






















