
Hevelius is a low-rimmed lunar impact crater that lies at the western edge of the Oceanus Procellarum, named after the astronomer Johannes Hevelius by the IAU in 1935. The smaller but prominent crater Cavalerius is joined to the northern rim by low ridges. Due south of Hevelius is the crater Lohrmann and the dark-hued Grimaldi.

Cavalerius is a prominent lunar impact crater that lies on the western edge of the Oceanus Procellarum lunar mare on the west part of the visible Moon. It nearly joins the northern rim of Hevelius to the south.

Fechner is a lunar impact crater that lies on the far side of the Moon's southern hemisphere, attached to the western rim of the large walled plain Planck. The eastern rim of Fechner intersects the Vallis Planck, a long, wide cleft in the surface that follows a course to the north-northwest. This valley intrudes into the southeastern rim of the crater, then continues northwards from the periphery of the northeast rim.

Bragg is an ancient lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, just beyond the northwest limb. This formation has been heavily eroded and reshaped by subsequent impacts, leaving an irregular depression in the surface. The most intact portion of the rim is along the western face, while the northern and eastern rim has been nearly worn away and is overlaid by several smaller craters. The most notable of these is Bragg H, which lies across the east-southeastern rim.

Cusanus is a lunar impact crater that is located near the northeastern limb of the Moon. In this location the crater appears very foreshortened when observed from the Earth, and its visibility is affected by libration. The northern rim of Cusanus is nearly joined to the south-southeastern rim of the larger crater Petermann. To the west is Baillaud and to the southeast is Hayn.

Casatus is a lunar impact crater that is located near the southern limb of the Moon. The north-northeast rim of the crater overlies a portion of the slightly larger crater Klaproth. Along the western rim, Casatus A intrudes somewhat into the interior, producing an inward-bowing rim. To the southeast of Casatus is Newton.

Cleostratus is a lunar impact crater near the northwest limb of the Moon. It lies to the northeast of the crater Xenophanes, and west-southwest of the prominent Pythagoras. From the Earth this crater appears highly elongated due to foreshortening.

Chebyshev is a large lunar impact crater that lies in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. The somewhat smaller crater Langmuir is intruding into the east-southeastern rim of Chebyshev, forming a chain of large craters with Brouwer on Langmuir's eastern rim.

d'Alembert is a large lunar impact crater located in the northern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon, to the northeast of the somewhat smaller walled plain Campbell. Astride the southwest rim of d'Alembert is Slipher. To the north is the crater Yamamoto, and to the south-southwest lies Langevin. This walled plain has the same diameter as Clavius on the near side, making it one of the largest such formations on the Moon.

Dyson is a lunar impact crater, 63 kilometers in diameter, that lies on the far side of the Moon, past the northwest limb. It is located in the northern part of the surface, to the northwest of the crater Coulomb, and east of van't Hoff.

Delmotte is a small lunar impact crater that lies just to the east of the much larger crater Cleomedes, and to the north of the Mare Crisium, in the northeastern part of the Moon. Delmotte appears foreshortened when viewed from the Earth, although not sufficiently to obscure the interior details.

Champollion is a lunar impact crater that lies on the far side of the Moon. It is located north-northeast of the larger crater Shayn, and south-southeast of Chandler.

Euctemon is a lunar impact crater that is located in the northern part of the Moon, along the northwest rim of the crater Baillaud. To the southwest of Euctemon is the large walled plain Meton, and to the north-northeast lies the crater De Sitter. Due to its location, Euctemon appears foreshortened when viewed from the Earth.

Chandler is a lunar impact crater in the northern hemisphere, on the Moon's far side. It lies to the southeast of the large walled plain D'Alembert, and southeast of the slightly smaller Chernyshev crater.

Chaplygin is a large lunar impact crater that lies on the far side of the Moon. It is located to the southeast of the huge walled plain Mendeleev, about midway between the craters Schliemann to the northeast and Marconi to the southwest. It is about the same size as Albategnius on the near side.

Lindsay is a small lunar impact crater in the central highlands of the Moon. It was named after the Irish astronomer Eric Mervyn Lindsay. It lies in the irregular terrain to the northwest of the landing site of the Apollo 16 mission. To the south is the crater Anděl, and Taylor is to the east-northeast.
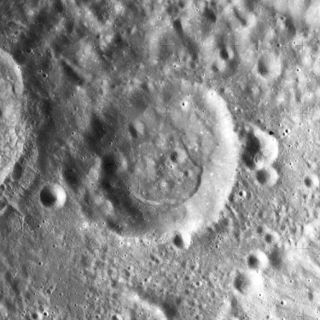
Litke is a lunar impact crater that lies within the large walled plain Fermi, near the north-northwestern inner rim. Less than one crater diameter to the west-northwest is the slightly larger Delporte. Litke is located on the far side of the Moon and cannot be viewed directly from the Earth.

Ostwald is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It lies just to the east of the crater Guyot, and near the northern border of Ibn Firnas. Recht lies along its eastern rim.

Sundman is a lunar impact crater that lies just past the western limb of the Moon. Although it lies on the far side from the Earth, this part of the surface is brought into view during periods of favorable libration and illumination. Sundman lies to the southwest of the walled plain Einstein, and to the west of the Vallis Bohr cleft. It was named after Finnish mathematician and astronomer Karl F. Sundman.

Papaleksi is an impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It lies along the northeastern outskirts of the large crater Mandel'shtam. About 20 km to the north-northeast of Papaleksi is the similar crater Spencer Jones.





















