 From Apollo 17 | |
| Coordinates | 23°18′N29°12′W / 23.3°N 29.2°W |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 28 km |
| Depth | 2.2 km |
| Colongitude | 28° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Leonhard Euler |
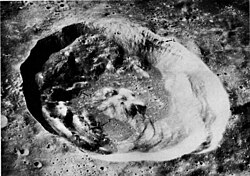
Euler is a lunar impact crater located in the southern half of the Mare Imbrium, and is named after the Swiss mathematician, physicist and astronomer Leonhard Euler. [1] The most notable nearby feature is Mons Vinogradov to the west-southwest. There is a cluster of low ridges to the southwest, and this formation includes the small crater Natasha and the tiny Jehan. About 200 kilometers to the east-northeast is the comparably sized crater Lambert.
Contents
Euler's rim is surrounded by a low rampart, and contain some slight terracing and slumped features on the irregular inner wall surface. In the middle of the small interior floor is a low central peak that formed from the rebound subsequent to the impact. The crater has a minor system of rays that extend for a distance of 200 kilometers.
Euler is a crater of Eratosthenian age. [2]


