Amazonsaurus is a genus of diplodocoid sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Period of what is now South America. It would have been a large-bodied quadrupedal herbivore with a long neck and whiplash tail. Although more derived diplodocoids were some of the longest animals ever to exist, Amazonsaurus was probably not more than 12 meters (40 ft) long. Gregory S. Paul estimated in 2010 its weight at 5000 kg.

Euhoplites is an extinct ammonoid cephalopod from the Lower Cretaceous, characterized by strongly ribbed, more or less evolute, compressed to inflated shells with flat or concave ribs, typically with a deep narrow groove running down the middle. In some, ribs seem to zigzag between umbilical tubercles and parallel ventrolateral clavi. In others the ribs are flexuous and curve forward from the umbilical shoulder and lap onto either side of the venter.

Acanthohoplites is an extinct genus of ammonites in the family Parahoplitidae that lived in the Aptian and Early Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous.
Acanthodiscus is an extinct ammonoid cephalopod genus from the order Ammonitida and included in the persphinctacean family Berriasellidae. The type species, named by Bruguière, 1792, is Acanthodiscus radiatus.
Argentiniceras is an extinct genus of cephalopod belonging to the Ammonite subclass. It belongs to the class Cephalopoda. Its fossils were found in Russia, Yemen, India, Mediterranean, Canada and South America.
Balearites is an extinct ancyloceratin genus included in the family Crioceratitidae, subclass Ammonoidea, from the Upper Hauterivian.
Frenguelliceras is an ammonite genus from the Lower Cretaceous included in the perisphinctoid family Neocomitidae named by Leanza in 1945. The type species, F. magister, is from the Valanginian,(Lower Cretaceous), of Argentina.

Arthropterygius is a widespread genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur which existed in Canada, Norway, Russia, and Argentina from the late Jurassic period to the earliest Cretaceous.

Stoycho Vassilev Breskovski was a Bulgarian paleontologist.
Curacoites is a genus of ammonites which existed during the early Barremian of what is now Argentina. It was described by Beatriz Aguirre-Urreta and Peter F. Rawson in 2012, and the type species is C. rotundus.
Sabaudiella is a genus of ammonites. It was described by Vasicek and Hoedemaeker in 2003, and the type species is S. sabaudianus, which was originally assigned to the genus Ancyloceras by Pictet and de Loriol in 1858. A new species, S. riverorum, which existed during the early Barremian of what is now Argentina, was described by Beatriz Aguirre-Urreta and Peter F. Rawson in 2012.
This list, 2012 in molluscan paleontology, is a list of new taxa of ammonites and other fossil cephalopods, as well as fossil gastropods and bivalves that have been described during the year 2012.
This list, 2013 in molluscan paleontology, is a list of new taxa of ammonites and other fossil cephalopods, as well as fossil gastropods, bivalves and other molluscs that have been described during the year 2013.

Pseudothurmannia is a genus of extinct cephalopods belonging to the subclass Ammonoidea and included in the family Crioceratitidae of the ammonitid superfamily Ancylocerataceae. These fast-moving nektonic carnivores lived in the Cretaceous period, from Hauterivian age to Barremian age.
This list, 2017 in paleomalacology, is a list of new taxa of ammonites and other fossil cephalopods, as well as fossil gastropods, bivalves and other molluscs that are scheduled to be described during the year 2017, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to molluscan paleontology that are scheduled to occur in the year 2017.

Nacientes del Biobío Formation is a geological formation that crops out near the uppermost reaches of Bío Bío River, in south-central Chile, and nearby areas of Argentina. The formation is made up of basalt and pyroclastic rocks and marine sedimentary rocks, such as sandstone and mudstone. Some less abundant sedimentary lithologies are conglomerate, volcaniclastic sedimentary rock. The formation is intruded by Grupo Plutónico Galletué which is of Late Jurassic to Late Cretaceous age. Further north in Chile the formation is similar to Nacientes del Teno Formation while in Argentina it is similar to Los Molles Formation and Lotena Formation.
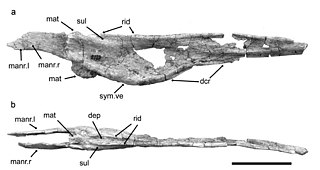
Argentinadraco is an extinct genus of azhdarchoid pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous Portezuelo Formation of Argentina. It contains a single species, A. barrealensis, named in 2017 by Alexander Kellner and Jorge Calvo. Argentinadraco is unusual for bearing a bottom jaw with a concave bottom edge, as well as a pair of ridges and depressions on the top surface. These features distinguish it from all other azhdarchoid groups, complicating its assignment, but it may belong to the Chaoyangopteridae. The ridges on the lower jaw may have been used to feed on small invertebrates in loose sediment within the system of lakes and rivers that it resided in.

Orthildaites is a genus of ammonites that lived during the lower Toarcian stage of early Jurassic, during Falciferum subzone.

The Agrio Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation that is up to 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) thick and is located in the southern Mendoza Province and northern-central Neuquén Province, in the Neuquén Basin of northwestern Patagonia, Argentina. This formation is the youngest one of the Mendoza Group, overlying the Mulichinco and Bajada Colorada Formations and overlain by the Huitrín and La Amarga Formations. It is dated to the Late Valanginian to Early Hauterivian, Late Valanginian to Early Barremian, or Hauterivian to earliest Aptian.

The Chachao Formation is a geological formation in the Mendoza Province in northern Patagonian Argentina. It is Valanginian in age and is predominantly marine, being deposited at a time of marine transgression in the Neuquén Basin, and predominantly consists of carbonate rocks.









