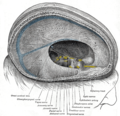
| Diaphragma sellae | |
|---|---|
 Tentorium cerebelli seen from above. (Diaphragma sellae labeled at upper left.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | diaphragma sellae |
| TA98 | A14.1.01.107 |
| TA2 | 5378 |
| FMA | 78540 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The diaphragma sellae or sellar diaphragm is a small, circular sheet of dura mater forming an (incomplete) roof over the sella turcica and covering the pituitary gland lodged therein. The diaphragma sellae forms a central opening to accommodate the passage of the pituitary stalk (infundibulum) [1] which interconnects the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus.
Contents
The diaphragma sellae is an important neurosurgical landmark. [1]