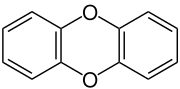
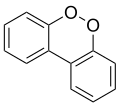
In chemistry, a structural isomer of a compound is another compound whose molecule has the same number of atoms of each element, but with logically distinct bonds between them. The term metamer was formerly used for the same concept.

In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6H5, and is often represented by the symbol Ph. The phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen, which may be replaced by some other element or compound to serve as a functional group. A phenyl group has six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the remaining carbon bonded to a substituent. Phenyl groups are commonplace in organic chemistry. Although often depicted with alternating double and single bonds, the phenyl group is chemically aromatic and has equal bond lengths between carbon atoms in the ring.
Polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs), or simply dioxins, are a group of long-lived polyhalogenated organic compounds that are primarily anthropogenic, and contribute toxic, persistent organic pollution in the environment.
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds [such as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds, resulting in "a fully conjugated cyclic dione structure". The archetypical member of the class is 1,4-benzoquinone or cyclohexadienedione, often called simply "quinone". Other important examples are 1,2-benzoquinone (ortho-quinone), 1,4-naphthoquinone and 9,10-anthraquinone.
In organic chemistry, dihydroxybenzenes (benzenediols) are organic compounds in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols. There are three structural isomers: 1,2-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as resorcinol, and 1,4-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as hydroquinone.
There are three distinct chemical compounds which are dichlorobenzenes:
Substances, mixtures and exposure circumstances in this list have been classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as group 3: The agent is not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans. This category is used most commonly for agents, mixtures and exposure circumstances for which the evidence of carcinogenicity is inadequate in humans and inadequate or limited in experimental animals. Exceptionally, agents (mixtures) for which the evidence of carcinogenicity is inadequate in humans but sufficient in experimental animals may be placed in this category when there is strong evidence that the mechanism of carcinogenicity in experimental animals does not operate in humans. Agents, mixtures and exposure circumstances that do not fall into any other group are also placed in this category.
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.
1,2-Benzoquinone, also called ortho-benzoquinone, is an organic compound with formula C6H4O2. It is one of the two isomers of quinone, the other being 1,4-benzoquinone. It is a red volatile solid that is soluble in water and ethyl ether. It is rarely encountered because of its instability, but it is of fundamental interest as the parent compound of many derivatives which are known.
In organic chemistry, umpolung or polarity inversion is the chemical modification of a functional group with the aim of the reversal of polarity of that group. This modification allows secondary reactions of this functional group that would otherwise not be possible. The concept was introduced by D. Seebach and E.J. Corey. Polarity analysis during retrosynthetic analysis tells a chemist when umpolung tactics are required to synthesize a target molecule.

The Dakin oxidation (or Dakin reaction) is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho- or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde or 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde) or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate. Overall, the carbonyl group is oxidised, whereas the H2O2 is reduced.

Divinylbenzene (DVB) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H4(CH=CH2)2 and structure H2C=CH−C6H4−HC=CH2. It is related to styrene by the addition of a second vinyl group. It is a colorless liquid manufactured by the thermal dehydrogenation of isomeric diethylbenzenes. Under synthesis conditions, o-divinylbenzene converts to naphthalene and thus is not a component of the usual mixtures of DVB.

1,4-Dioxin (also referred as dioxin or p-dioxin) is a heterocyclic, organic, non-aromatic compound with the chemical formula C4H4O2. There is an isomeric form of 1,4-dioxin, 1,2-dioxin (or o-dioxin). 1,2-Dioxin is very unstable due to its peroxide-like characteristics.

1,2-Dioxin is a heterocyclic, organic, antiaromatic compound with the chemical formula C4H4O2. It is an isomeric form of 1,4-dioxin (or p-dioxin).

Polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs) are a family of organic compounds with one or several of the hydrogens in the dibenzofuran structure replaced by chlorines. For example, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran (TCDF) has chlorine atoms substituted for each of the hydrogens on the number 2, 3, 7, and 8 carbons. Polychlorinated dibenzofurans with chlorines at least in positions 2,3,7 and 8 are much more toxic than the parent compound dibenzofurane, with properties and chemical structures similar to polychlorinated dibenzodioxins. These groups together are often inaccurately called dioxins. They are known developmental toxicants, and suspected human carcinogens. PCDFs tend to co-occur with polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs). PCDFs can be formed by pyrolysis or incineration at temperatures below 1200 °C of chlorine containing products, such as PVC, PCBs, and other organochlorides, or of non-chlorine containing products in the presence of chlorine donors. Dibenzofurans are known persistent organic pollutants (POP), classified among the dirty dozen in the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants.

Octachlorodibenzodioxin is one of polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs).

Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds (DLCs) are a group of chemical compounds that are persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the environment. They are mostly by-products of burning or various industrial processes or, in the case of dioxin-like PCBs and PBBs, unwanted minor components of intentionally produced mixtures.
A hydroxynaphthoquinone is any of several organic compounds that can be viewed as derivatives of a naphthoquinone through replacement of one hydrogen atom (H) by a hydroxyl group (-OH).

1,2,3,4,6,7,8-Heptachlorodibenzo-para-dioxin (often referred to as 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpCDD) is a polychlorinated derivative of dibenzo-p-dioxin and can therefore be categorized as polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin (PCDD), a subclass of dioxins which includes 75 congeners. HpCDD is the dibenzo-p-dioxin which is chlorinated at positions 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, and 8. It is a polycyclic heterocyclic organic compound, since HpCDD contains multiple cyclic structures (two benzene rings connected by a 1,4-dioxin ring) in which two different elements (carbon and oxygen) are members of its rings. HpCDD has molecular formula C12HCl7O2 and is an off-white powder, which is insoluble in water.