
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber.

Indigo is a deep color close to the color wheel blue, as well as to some variants of ultramarine, based on the ancient dye of the same name. The word "indigo" comes from the Latin word indicum, meaning "Indian", as the dye was originally exported to Europe from India.

Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing and painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model used to project colors onto television screens and computer monitors, brown combines red and green.

A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compounds. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli.

Indigo dye is an organic compound with a distinctive blue color. Historically, indigo was a natural dye extracted from the leaves of some plants of the Indigofera genus, in particular Indigofera tinctoria; dye-bearing Indigofera plants were commonly grown and used throughout the world, in Asia in particular, as an important crop, with the production of indigo dyestuff economically important due to the previous rarity of some blue dyestuffs historically.

Orange is the colour between yellow and red on the spectrum of visible light. Human eyes perceive orange when observing light with a dominant wavelength between roughly 585 and 620 nanometres. In traditional colour theory, it is a secondary colour of pigments, produced by mixing yellow and red. In the RGB colour model, it is a tertiary colour. It is named after the fruit of the same name.
Tyrian purple, also known as Phoenician red, Phoenician purple, royal purple, imperial purple, or imperial dye, is a reddish-purple natural dye. The name Tyrian refers to Tyre, Lebanon. It is secreted by several species of predatory sea snails in the family Muricidae, rock snails originally known by the name 'Murex'. In ancient times, extracting this dye involved tens of thousands of snails and substantial labor, and as a result, the dye was highly valued. The colored compound is 6,6′-dibromoindigo.

Cadmium pigments are a class of pigments that contain cadmium. Most of the cadmium produced worldwide has been for use in rechargeable nickel–cadmium batteries, which have been replaced by other rechargeable nickel-chemistry cell varieties such as NiMH cells, but about half of the remaining consumption of cadmium, which is approximately 2,000 tonnes annually, is used to produce colored cadmium pigments. The principal pigments are a family of yellow, orange and red cadmium sulfides and sulfoselenides, as well as compounds with other metals.

Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl.
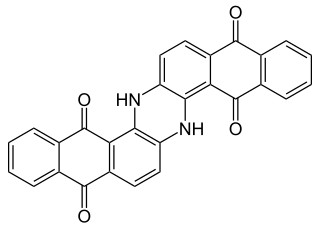
Indanthrone blue, also called indanthrene, is an organic compound with the formula (C14H6O2NH)2. It is a dark blue solid that is a common dye as well as a precursor to other dyes.

Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C-N=N-C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group, but some dyes called "disazo dyes" contain two azo groups, some dyes called "trisazo dyes" contain three azo groups and are or more. Azo dyes comprise 60-70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents.
In organic chemistry, an azo coupling is an organic reaction between a diazonium compound and another aromatic compound that produces an azo compound. In this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the aryldiazonium cation is the electrophile and the activated arene is a nucleophile. In most cases, including the examples below, the diazonium compound is also aromatic.
Vat dyes are a class of dyes that are classified as such because of the method by which they are applied. Vat dyeing is a process that refers to dyeing that takes place in a bucket or vat. The original vat dye is indigo, once obtained only from plants but now often produced synthetically.

Colored smoke is a kind of smoke created by an aerosol of small particles of a suitable pigment or dye.

Orange wine, also known as skin-contact white wine, skin-fermented white wine, or amber wine, is a type of wine made from white wine grapes where the grape skins are not removed, as in typical white wine production, and stay in contact with the juice for days or even months. This contrasts with conventional white wine production, which involves crushing the grapes and quickly moving the juice off the skins into the fermentation vessel. The skins contain color pigment, phenols and tannins that would normally be considered undesirable for white wines, while for red wines skin contact and maceration is a vital part of the winemaking process that gives red wine its color, flavor, and texture.

Anthraquinone dyes are an abundant group of dyes comprising a anthraquinone unit as the shared structural element. Anthraquinone itself is colourless, but red to blue dyes are obtained by introducing electron donor groups such as hydroxy or amino groups in the 1-, 4-, 5- or 8-position. Anthraquinone dyestuffs are structurally related to indigo dyestuffs and are classified together with these in the group of carbonyl dyes.

Pigment Violet 29 is an organic compound that is used as a pigment and vat dye. Its colour is dark red purple, or bordeaux.

Violanthrone, also known as dibenzanthrone, is an organic compound that serves as a vat dye and a precursor to other vat dyes. X-ray crystallography confirms that the molecule is planar with C2v symmetry. Isomeric with violanthrone is isoviolanthrone, which has a centrosymmetric structure.

Perinone is a class of organic compounds. The parent compound has two isomers, each of which are useful pigments.
Pigment Red 190, also called Vat Red 29, is a synthetic organic compound that is used both as a pigment and as a vat dye. Although structurally a derivative of perylene, it is produced from acenaphthene.















