Agent Orange is a chemical herbicide and defoliant, one of the "tactical use" Rainbow Herbicides. It was used by the U.S. military as part of its herbicidal warfare program, Operation Ranch Hand, during the Vietnam War from 1961 to 1971. It is a mixture of equal parts of two herbicides, 2,4,5-T and 2,4-D. In addition to its damaging environmental effects, traces of dioxin found in the mixture have caused major health problems for many individuals who were exposed, and their offspring.
Internalism and externalism are two opposite ways of integration of explaining various subjects in several areas of philosophy. These include human motivation, knowledge, justification, meaning, and truth. The distinction arises in many areas of debate with similar but distinct meanings. Internal–external distinction is a distinction used in philosophy to divide an ontology into two parts: an internal part concerning observation related to philosophy, and an external part concerning question related to philosophy.

Neon is a chemical element with the symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is a noble gas. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with about two-thirds the density of air. It was discovered in 1898 as one of the three residual rare inert elements remaining in dry air, after nitrogen, oxygen, argon and carbon dioxide were removed. Neon was the second of these three rare gases to be discovered and was immediately recognized as a new element from its bright red emission spectrum. The name neon is derived from the Greek word, νέον, neuter singular form of νέος, meaning 'new'. Neon is chemically inert, and no uncharged neon compounds are known. The compounds of neon currently known include ionic molecules, molecules held together by van der Waals forces and clathrates.

Chemical warfare (CW) involves using the toxic properties of chemical substances as weapons. This type of warfare is distinct from nuclear warfare, biological warfare and radiological warfare, which together make up CBRN, the military acronym for chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear, all of which are considered "weapons of mass destruction" (WMDs), a term that contrasts with conventional weapons.

Indigo dye is an organic compound with a distinctive blue color. Historically, indigo was a natural dye extracted from the leaves of some plants of the Indigofera genus, in particular Indigofera tinctoria; dye-bearing Indigofera plants were commonly grown and used throughout the world, in Asia in particular, as an important crop, with the production of indigo dyestuff economically important due to the previous rarity of some blue dyestuffs historically.

Operation Ranch Hand was a U.S. military operation during the Vietnam War, lasting from 1962 until 1971. Largely inspired by the British use of 2,4,5-T and 2,4-D during the Malayan Emergency in the 1950s, it was part of the overall herbicidal warfare program during the war called "Operation Trail Dust". Ranch Hand involved spraying an estimated 19 million U.S. gallons (72,000 m3) of defoliants and herbicides over rural areas of South Vietnam in an attempt to deprive the Viet Cong of food and vegetation cover. Areas of Laos and Cambodia were also sprayed to a lesser extent. Nearly 20,000 sorties were flown between 1961 and 1971.
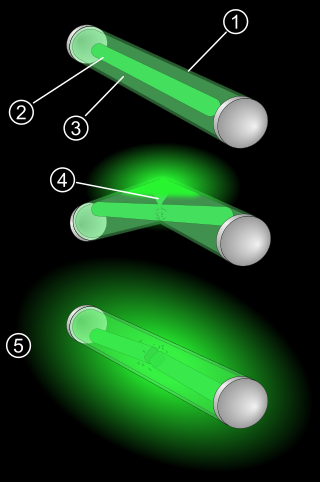
A glow stick, also known as a light stick, chem light, light wand, light rod, and rave light, is a self-contained, short-term light-source. It consists of a translucent plastic tube containing isolated substances that, when combined, make light through chemiluminescence. The light cannot be turned off and can be used only once. The used tube is then thrown away. Glow sticks are often used for recreation, such as for events, camping, outdoor exploration, and concerts. Glow sticks are also used for light in military and emergency services applications. Industrial uses include marine, transportation, and mining.

Tie-dye is a term used to describe a number of resist dyeing techniques and the resulting dyed products of these processes. The process of tie-dye typically consists of folding, twisting, pleating, or crumpling fabric or a garment, before binding with string or rubber bands, followed by the application of dye or dyes. The manipulations of the fabric before the application of dye are called resists, as they partially or completely prevent ('resist') the applied dye from coloring the fabric. More sophisticated tie-dye may involve additional steps, including an initial application of dye before the resist, multiple sequential dyeing and resist steps, and the use of other types of resists and discharge.

"NFPA 704: Standard System for the Identification of the Hazards of Materials for Emergency Response" is a standard maintained by the U.S.-based National Fire Protection Association. First "tentatively adopted as a guide" in 1960, and revised several times since then, it defines the colloquial "Safety Square" or "Fire Diamond" which is used by emergency personnel to quickly and easily identify the risks posed by hazardous materials. This helps determine what, if any, special equipment should be used, procedures followed, or precautions taken during the initial stages of an emergency response. It is an internationally accepted safety standard, and is crucial while transporting chemicals.

Jaffa Cakes are a cake introduced by McVitie and Price in the UK in 1927 and named after Jaffa oranges. The most common form of Jaffa cakes are circular, 2+1⁄8 inches (54 mm) in diameter and have three layers: a Genoise sponge base, a layer of orange flavoured jam and a coating of chocolate. Each cake is 46 calories. Jaffa Cakes are also available as bars or in small packs, and in larger and smaller sizes. The original Jaffa Cakes now come in packs of 10, 20, 30, or 40, having been downsized in 2017 from 12 or 24 per pack.

In modern English, the nouns vates and ovate (, ), are used as technical terms for ancient Celtic bards, prophets and philosophers. The terms correspond to a Proto-Celtic word which can be reconstructed as *wātis. They are sometimes also used as English equivalents to later Celtic terms such as Irish fáith "prophet, seer".

Herbicidal warfare is the use of substances primarily designed to destroy the plant-based ecosystem of an area. Although herbicidal warfare use chemical substances, its main purpose is to disrupt agricultural food production and/or to destroy plants which provide cover or concealment to the enemy, not to asphyxiate or poison humans and/or destroy human-made structures. Herbicidal warfare has been forbidden by the Environmental Modification Convention since 1978, which bans "any technique for changing the composition or structure of the Earth's biota".
Vat dyes are a class of dyes that are classified as such because of the method by which they are applied. Vat dyeing is a process that refers to dyeing that takes place in a bucket or vat. The original vat dye is indigo, once obtained only from plants but now often produced synthetically.

Colored smoke is a kind of smoke created by an aerosol of small particles of a suitable pigment or dye.
In metallurgical processes tank leaching is a hydrometallurgical method of extracting valuable material from ore.

Aleppo soap is a handmade, hard bar soap associated with the city of Aleppo, Syria. Aleppo soap is classified as a Castile soap as it is a hard soap made from olive oil and lye, from which it is distinguished by the inclusion of laurel oil.

The Areni-1 winery is an ancient winery that was discovered in 2007 in the Areni-1 cave complex in the village of Areni in the Vayots Dzor province of Armenia by a team of Armenian and Irish archaeologists. The excavations were carried out by Boris Gasparyan of the Institute of Archaeology and Ethnography of the National Academy of Sciences of Armenia and Ron Pinhasi from University College Cork (Ireland), and were sponsored by the Gfoeller Foundation (USA) and University College Cork. In 2008 the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) also joined the project with Gregory Areshian as co-director of the Areni Project. Since then the excavations have been sponsored by UCLA and the National Geographic Society as well. The excavations of the winery were completed in 2010.
The United Arab Emirates is a federation of seven Emirates, with autonomous federal and local governments. An income tax decree has been enacted by each Emirate, but in practice, the enforcement of these decrees is restricted to foreign banks and oil companies.

Lumi is a Los Angeles-based company founded by Jesse Genet and Stephan Ango that offers packaging and supply chain management software. The company got its start developing Inkodye, a photo-reactive vat dye that develops its color through exposure to UV or sunlight.

A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the end consumer. If the ultimate consumer is a business that collects and pays to the government VAT on its products or services, it can reclaim the tax paid. It is similar to, and is often compared with, a sales tax. VAT is an indirect tax because the person who ultimately bears the burden of the tax is not necessarily the same person as the one who pays the tax to the tax authorities.