
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber.

Indigo is a term used for a number of hues in the region of blue. The word comes from the ancient dye of the same name. The term "indigo" can refer to the color of the dye, various colors of fabric dyed with indigo dye, a spectral color, one of the seven colors of the rainbow as described by Newton, or a region on the color wheel, and can include various shades of blue, ultramarine, and green-blue. Since the web era, the term has also been used for various purple and violet hues identified as "indigo", based on use of the term "indigo" in HTML web page specifications.

Indigo dye is an organic compound with a distinctive blue color. Indigo is a natural dye extracted from the leaves of some plants of the Indigofera genus, in particular Indigofera tinctoria. Dye-bearing Indigofera plants were commonly grown and used throughout the world, particularly in Asia, with the production of indigo dyestuff economically important due to the historical rarity of other blue dyestuffs.

Denim is a sturdy cotton warp-faced textile in which the weft passes under two or more warp threads. This twill weave produces a diagonal ribbing that distinguishes it from cotton duck. Denim, as it is recognized today, was first produced in Nîmes, France.

Tyrian purple, also known as royal purple, imperial purple, or imperial dye, is a reddish-purple natural dye. The name Tyrian refers to Tyre, Lebanon, once Phoenicia. It is secreted by several species of predatory sea snails in the family Muricidae, rock snails originally known by the name Murex. In ancient times, extracting this dye involved tens of thousands of snails and substantial labour, and as a result, the dye was highly valued. The colored compound is 6,6'-dibromoindigo.

Isatis tinctoria, also called woad, dyer's woad, dyer's-weed, or glastum, is a flowering plant in the family Brassicaceae with a documented history of use as a blue dye and medicinal plant. Its genus name, Isatis, derives from the ancient Greek word for the plant, ἰσάτις. It is occasionally known as Asp of Jerusalem. Woad is also the name of a blue dye produced from the leaves of the plant. Woad is native to the steppe and desert zones of the Caucasus, Central Asia to Eastern Siberia and Western Asia but is now also found in South-Eastern and Central Europe and western North America.

Tie-dye is a term used to describe a number of resist dyeing techniques and the resulting dyed products of these processes. The process of tie-dye typically consists of folding, twisting, pleating, or crumpling fabric or a garment, before binding with string or rubber bands, followed by the application of dye or dyes. The manipulations of the fabric before the application of dye are called resists, as they partially or completely prevent ('resist') the applied dye from coloring the fabric. More sophisticated tie-dye may involve additional steps, including an initial application of dye before the resist, multiple sequential dyeing and resist steps, and the use of other types of resists and discharge.

Dyeing is the application of dyes or pigments on textile materials such as fibers, yarns, and fabrics with the goal of achieving color with desired color fastness. Dyeing is normally done in a special solution containing dyes and particular chemical material. Dye molecules are fixed to the fiber by absorption, diffusion, or bonding with temperature and time being key controlling factors. The bond between the dye molecule and fiber may be strong or weak, depending on the dye used. Dyeing and printing are different applications; in printing, color is applied to a localized area with desired patterns. In dyeing, it is applied to the entire textile.
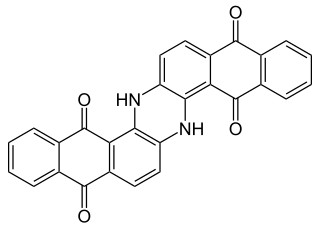
Indanthrone blue, also called indanthrene, is an organic compound with the formula (C14H6O2NH)2. It is a dark blue solid that is a common dye as well as a precursor to other dyes.

Sun printing may refer to various printing techniques which use sunlight as a developing or fixative agent.
Vat dyes are a class of dyes that are classified as such because of the method by which they are applied. Vat dyeing is a process that refers to dyeing that takes place in a bucket or vat. The original vat dye is indigo, once obtained only from plants but now often produced synthetically.

Colored smoke is a kind of smoke created by an aerosol of small particles of a suitable pigment or dye.

Old Monk Rum is a vatted Indian dark rum, launched in 1855. It is a dark rum with a distinct vanilla flavour, with an alcohol content of 42.8%. It is produced in Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh and has registered office in Solan, Himachal Pradesh.

Natural dyes are dyes or colorants derived from plants, invertebrates, or minerals. The majority of natural dyes are vegetable dyes from plant sources—roots, berries, bark, leaves, and wood—and other biological sources such as fungi.
The Clayton Aniline Company Ltd. was a British manufacturer of dyestuffs, founded in 1876 by Charles Dreyfus in Clayton, Manchester.

Vat Green 1 is an organic compound that is used as a vat dye. It is a derivative of benzanthrone. It is a dark green solid. Vat Green 1 can dye viscose, silk, wool, paper, and soap.

Violanthrone, also known as dibenzanthrone, is an organic compound that serves as a vat dye and a precursor to other vat dyes. X-ray crystallography confirms that the molecule is planar with C2v symmetry. Isomeric with violanthrone is isoviolanthrone, which has a centrosymmetric structure.

Genisteae is a tribe of trees, shrubs and herbaceous plants in the subfamily Faboideae of the family Fabaceae. It includes a number of well-known plants including broom, lupine (lupin), gorse and laburnum.

A value-added tax (VAT or goods and services tax (GST), general consumption tax (GCT)), is a consumption tax that is levied on the value added at each stage of a product's production and distribution. VAT is similar to, and is often compared with, a sales tax. VAT is an indirect tax because the consumer who ultimately bears the burden of the tax is not the entity that pays it. Specific goods and services are typically exempted in various jurisdictions.
Batch dyeing is a method of dyeing a textile material. The method involves the gradual transfer of dye from a dye bath to the textile material in the same piece of equipment. The various methods of batch dyeing result from the type of machine used in the dyeing process. Common machinery used in the batch dyeing process include the jigger dyeing machine, winch dyeing machine, jet dyeing machine and beam dyeing machine.

















