
The Controlled Drugs and Substances Act is Canada's federal drug control statute. Passed in 1996 under Prime Minister Jean Chrétien's government, it repeals the Narcotic Control Act and Parts III and IV of the Food and Drugs Act, and establishes eight Schedules of controlled substances and two Classes of precursors. It provides that "The Governor in Council may, by order, amend any of Schedules I to VIII by adding to them or deleting from them any item or portion of an item, where the Governor in Council deems the amendment to be necessary in the public interest."

The enzyme argininosuccinate lyase (EC 4.3.2.1, ASL, argininosuccinase; systematic name 2-(N ω-L-arginino)succinate arginine-lyase (fumarate-forming)) catalyzes the reversible breakdown of argininosuccinate:

Muconate lactonizing enzymes are involved in the breakdown of lignin-derived aromatics, catechol and protocatechuate, to citric acid cycle intermediates as a part of the β-ketoadipate pathway in soil microbes. Some bacterial species are also capable of dehalogenating chloroaromatic compounds by the action of chloromuconate lactonizing enzymes. MLEs consist of several strands which have variable reaction favorable parts therefore the configuration of the strands affect its ability to accept protons. The bacterial MLEs belong to the enolase superfamily, several structures from which are known. MLEs have an identifying structure made up of two proteins and two Magnesium ions as well as various classes depending on whether it is bacterial or eukaryotic. The reaction mechanism that MLEs undergo are the reverse of beta-elimination in which the enolate alpha-carbon is protonated. MLEs can undergo mutations caused by a deletion of catB structural genes which can cause some bacteria to lose its functions such as the ability to grow. Additional mutations to MLEs can cause its structure and function to alter and could cause the conformation to change therefore making it an inactive enzyme that is unable to bind its substrate. There is another enzyme called Mandelate Racemase that is very similar to MLEs in the structural way as well as them both being a part of the enolase superfamily. They both have the same end product even though they undergo different chemical reactions in order to reach the end product.

Phenanthrenoids are chemical compounds formed with a phenanthrene backbone. These compounds occur naturally in plants, although they can also be synthesized.

In enzymology, a protocatechuate 3,4-dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a stizolobinate synthase (EC 1.13.11.30) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate cycloisomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an α-pinene-oxide decyclase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a carboxy-cis,cis-muconate cyclase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
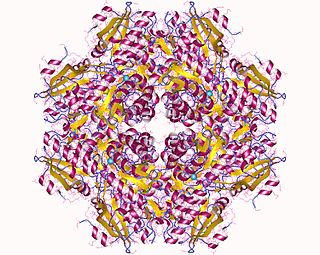
In enzymology, a chloromuconate cycloisomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cycloeucalenol cycloisomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a muconolactone Δ-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tetrahydroxypteridine cycloisomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme DDT-dehydrochlorinase catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme 4-carboxymuconolactone decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.44) catalyzes the chemical reaction
Cycloisomerase may refer to:

3-Carboxy-cis,cis-muconic acid is a metabolite of the catechin degradation by Bradyrhizobium japonicum.
Fumarate lyase belongs to the lyase class of enzymes. These proteins use fumarate as a substrate. They have been shown to share a short conserved sequence around a methionine which is probably involved in the catalytic activity of this type of enzymes.
The biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids involves a number of enzymes.







