
The wedge-tailed shearwater is a medium-large shearwater in the seabird family Procellariidae. It is one of the shearwater species that is sometimes referred to as a muttonbird, like the sooty shearwater of New Zealand and the short-tailed shearwater of Australia. It ranges throughout the tropical Pacific and Indian Oceans, roughly between latitudes 35°N and 35°S. It breeds on islands off Japan, on the Islas Revillagigedo, the Hawaiian Islands, the Seychelles, the Northern Mariana Islands, and off Eastern and Western Australia.

A true toad is any member of the family Bufonidae, in the order Anura. This is the only family of anurans in which all members are known as toads, although some may be called frogs. The bufonids now comprise more than 35 genera, Bufo being the best known.

Wedge boots, wedgies, or lifties are shoes and boots with a sole in the form of a wedge, such that one piece of material, normally rubber, serves as both the sole and the heel.
The weasel sharks are a family, the Hemigaleidae, of ground sharks found from the eastern Atlantic Ocean to the continental Indo-Pacific. They are found in shallow coastal waters to a depth of 100 m (330 ft).

Scutisorex is a genus of African shrews, mammals of the family Soricidae. Members of the genus are the only known mammal species whose vertebrae interlock, a feature which, along with the general enlargement and strengthening of the backbone and ribs, allows them to bear remarkable loads. They also have well developed muscles for flexing their spine in the sagittal plane. It is thought that these adaptations allow the shrews to wedge open spaces between the trunks of palm trees and the stems of dead leaves, as well underneath logs and rocks, allowing them to partake of a reliable source of insect larvae and earthworms that would otherwise be inaccessible.

The wedge-tailed sabrewing is a species of hummingbird in the family Trochilidae. It is found in Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, and Mexico. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest and heavily degraded former forest.

The Sikkim wedge-billed babbler or blackish-breasted babbler is a species of bird in the Old World babbler family (Timaliidae). It is named for the Indian state of Sikkim.

Bellendena montana, commonly known as mountain rocket, is a species of low-growing multi-stemmed shrub in the plant family Proteaceae. It is endemic to high-altitude subalpine and alpine regions in Tasmania, Australia. The prominent white flower spikes appear over summer, followed by small bright red or yellow fruit in late summer and autumn.
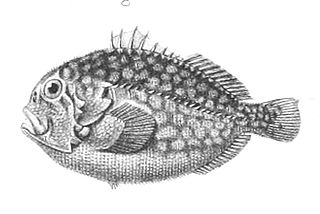
Caracanthus, the coral crouchers, or orbicular velvetfishes, are a genus of scorpaeniform fishes. They live in coral reefs of the tropical Indo-Pacific. This genus is the only member of the family Caracanthidae.

Gracile capuchin monkeys are capuchin monkeys in the genus Cebus. At one time all capuchin monkeys were included within the genus Cebus. In 2011, Jessica Lynch Alfaro et al. proposed splitting the genus between the robust capuchin monkeys, such as the tufted capuchin, and the gracile capuchins. The gracile capuchins retain the genus name Cebus, while the robust species have been transferred to Sapajus.

The wedge sole, is a flatfish of the family Soleidae. It is a bottom dwelling predatory fish inhabiting both sandy and muddy soils at depths between 10 and 450 m in the East Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea. It achieves a maximum size of 30 cm (12 in).

Achirus is a genus of American soles native to tropical and subtropical parts of the Americas. They are mainly found in coastal areas, including salt and brackish water, but some species are found in fresh water.

Trinectes is a genus of American soles native to the Americas. Most species are coastal, occurring in both salt and brackish water, but several may enter fresh water and one, T. hubbsbollinger, is restricted to rivers. They are fairly small, with the largest species only reaching 25 cm (9.8 in) in length.

Microchirus is a genus of soles native to the Eastern Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea.

Pegusa is a genus of soles native to the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea, and Black Sea.

Solea is a genus of soles from the Indo-Pacific and East Atlantic Oceans, and the Mediterranean Sea.

Zebrias is a genus of soles native to coastal waters in the Indo-Pacific and southern Australia. All species in the genus have clear dark and pale stripes, giving it a name derived from the word 'Zebra' due to the shared characteristic. At least some members of this genus are toxic.
Catalepidia is a genus of a sole described species of medium-sized trees, constituting part of the plant family Proteaceae. The species Catalepidia heyana grows naturally only in a restricted mountain region (endemic) of the wet tropics rain forests of north-eastern Queensland, Australia. Common names include Hey's nut or Hey's nut oak.
Tenacibaculum is a Gram-negative and motile bacterial genus from the family of Flavobacteriaceae.
Hemibdella soleae is a marine species of leech in the family Piscicolidae and the type taxon of its genus. Found in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, it is a parasite of flatfish such as the common sole.
















