
Takakia is a genus of two species of mosses known from western North America and central and eastern Asia. The genus is placed as a separate family, order and class among the mosses. It has had a history of uncertain placement, but the discovery of sporophytes clearly of the moss-type firmly supports placement with the mosses.
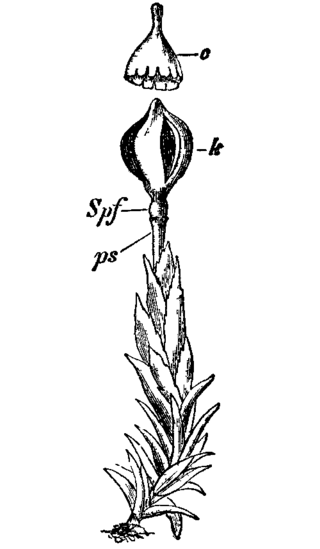
Andreaeaceae is a family of mosses which includes two genera, Andreaea, containing about 100 species, and the genus Acroschisma. The Andreaeaceae prefer rocky habitats ranging from tropical to arctic climates, on which they form tufted colonies, typically with reddish to blackish shoots. The capsules lack the peristome mechanism and dehisce longitudinally to release the spores, resulting in a paper-lantern appearance.

The Bryopsida constitute the largest class of mosses, containing 95% of all moss species. It consists of approximately 11,500 species, common throughout the whole world.

Buxbaumia is a genus of twelve species of moss (Bryophyta). It was first named in 1742 by Albrecht von Haller and later brought into modern botanical nomenclature in 1801 by Johann Hedwig to commemorate Johann Christian Buxbaum, a German physician and botanist who discovered the moss in 1712 at the mouth of the Volga River. The moss is microscopic for most of its existence, and plants are noticeable only after they begin to produce their reproductive structures. The asymmetrical spore capsule has a distinctive shape and structure, some features of which appear to be transitional from those in primitive mosses to most modern mosses.

Orthotrichaceae is the only family of mosses in the order Orthotrichales. Many species in the family are epiphytic.

Funariales is an order containing 356 species,26 genera and 7 families.

The Funariidae are a widespread group of mosses in class Bryopsida. The majority of species belong to the genera Funaria and Physcomitrium.
Gradsteinia is a genus of moss in family Amblystegiaceae.

Pottiales is an order of mosses in the subclass Dicranidae.
Merrilliobryum is a genus of moss in family Fabroniaceae. The genus is found in New Guinea and the Philippines.
Andreaeobryum, the Mossy Cowl Moss, is a genus of moss with a single species Andreaeobryum macrosporum, endemic to Alaska and western Canada. The genus is placed as a separate family, order and class among the mosses.

Oedipodium is the only genus of moss in the family Oedipodiaceae. It contains the single species Oedipodium griffithianum, the gouty-moss or Griffith's oedipodium moss. This species is distributed in cooler climates of Eurasia, as well as from Alaska, Washington state, British Columbia, Yukon, Greenland, Newfoundland, Tierra del Fuego and the Falkland Islands.

Tetraphidaceae is a family of mosses. It includes only the two genera Tetraphis and Tetrodontium, each with two species. The defining feature of the family is the 4-toothed peristome.

Bryales is an order of mosses.

The Funariaceae are a family of mosses in the order Funariales. About 303 species are included in the family, with 200 species in Funaria and another 80 classified in Physcomitrium.

Encalyptaceae is a family of mosses in order Encalyptales. It includes two genera; the genus Bryobartramia, formerly included in the family, is now placed in its own family.

Timmia is a genus of moss. It is the only genus in the family Timmiaceae and order Timmiales. The genus is named in honor of the 18th-century German botanist Joachim Christian Timm.

Bryaceae is a family of mosses.
Neosharpiella is a genus of moss containing two species in the family Bartramiaceae. The type species, Neosharpiella aztecorum, grows in alpine regions of central Mexico, while the other species, Neosharpiella turgida, has been found in Bolivia and Ecuador.

The Pottiaceae are a family of mosses. They form the most numerous moss family known, containing nearly 1500 species or more than 10% of the 10,000 to 15,000 moss species known.














