
Pseudorhabdosynochus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, included in the family Diplectanidae. The type-species of the genus is Pseudorhabdosynochus epinepheli .

The Diplectanidae are a family of monopisthocotylean monogeneans. They are all parasitic on the gills of fish. Diplectanids are small animals, generally around 1 mm in length. As parasites, they can be extremely numerous, up to several thousand on an individual fish.
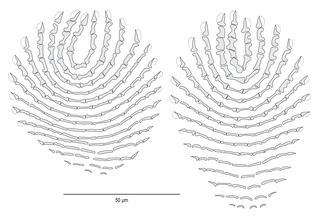
Squamodiscs are epidermal structures, which are typical of and found only in certain monogeneans of the family Diplectanidae. There are, typically, two squamodiscs, one ventral and one dorsal, located on the haptor of the monogenean. Squamodiscs are usually made up of scales embedded in the epidermis, which appear from the outside as rodlets arranged in rows.

Lagenivaginopseudobenedenia is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogenean, included in the family Capsalidae. The type-species of the genus is Lagenivaginopseudobenedenia etelisYamaguti, 1966. The genus includes only 2 species, which are both parasitic on the gills of marine fish of the family Lutjanidae.
Calydiscoides is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, included in the family Diplectanidae.
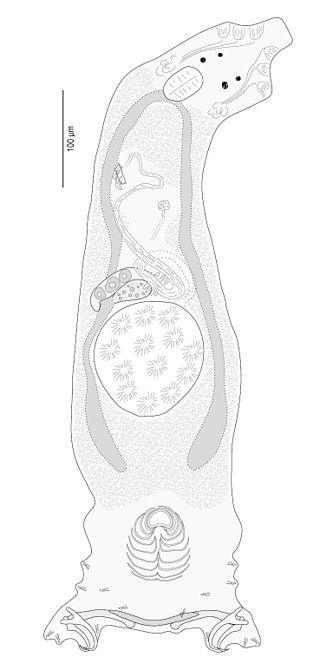
Lamellodiscus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Diplectanidae; all species of Lamellodiscus are small worms, parasitic on the gills of teleost fish.
Pseudorhabdosynochus amplidiscatus is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of groupers. It was described as Diplectanum amplidiscatum by Bravo-Hollis in 1954 and transferred to the genus Pseudorhabdosynochus by Kritsky and Beverley-Burton in 1986.
Acanthocercodes is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. All its species are parasites of the gill lamellae of marine teleosts. The type-species of the genus is Acanthocercodes bullardiKritsky & Diggles, 2015.
Latericaecum is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae.
Lobotrema is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. All its species are parasites on fish. The type-species is Lobotrema madrasiTripathi, 1959.
Monoplectanum is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. All its species are parasites on fish of the family Sillaginidae.
Murraytrema is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. Species of this genus are parasitic on the gills of marine fish of the families Sciaenidae and Sparidae.
Murraytrematoides is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Diplectanidae.
Nasobranchitrema is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. The position of Nasobranchitrema within the family Diplectanidae is a matter of controversy. Oliver considered that the absence of squamodisc and adhesive plate in the haptor and the position of the ovary made the genus closer to the Ancyrocephalidae than to the Diplectanidae.

Neodiplectanum is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. According to Mizelle & Blatz (1941), the genus Neodiplectanum "differs from DiplectanumDiesing, 1858, its closest relative, by the presence of two, instead of three, cuticular bars on the haptor". Oliver (1987) thought that the two genera were synonyms, but Neodiplectanum was resurrected later.
Oliveriplectanum is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans belonging to the family Diplectanidae. All its species are parasites on marine perciform fishes.
Pseudodiplectanum is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. Species of Pseudodiplectanum are parasites of marine teleost fish.
Rhabdosynochus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae.
Teraplectanum is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. All species of the genus are parasitic on the gills of fish in the family Teraponidae.
Protolamellodiscus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Diplectanidae. All species of Protolamellodiscus are parasites of marine perciform fishes of the families Lethrinidae, Nemipteridae, Serranidae and Sparidae.






