Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves, and blood. This may result in a low red blood cell count, inflammation around the lungs, and inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months.
Rheumatology is a branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis and management of disorders whose common feature is inflammation in the bones, muscles, joints, and internal organs. Rheumatology covers more than 100 different complex diseases, collectively known as rheumatic diseases, which includes many forms of arthritis as well as lupus and Sjögren's syndrome. Doctors who have undergone formal training in rheumatology are called rheumatologists.

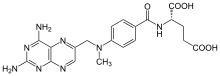
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leukemia, lung cancer, lymphoma, gestational trophoblastic disease, and osteosarcoma. Types of autoimmune diseases it is used for include psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn's disease. It can be given by mouth or by injection.

Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine, typically where the spine joins the pelvis. With AS, eye and bowel problems—as well as back pain—may occur. Joint mobility in the affected areas sometimes worsens over time. Ankylosing spondylitis is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. More than 90% of people affected in the UK have a specific human leukocyte antigen known as the HLA-B27 antigen. The underlying mechanism is believed to be autoimmune or autoinflammatory. Diagnosis is based on symptoms with support from medical imaging and blood tests. AS is a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy, meaning that tests show no presence of rheumatoid factor (RF) antibodies.

Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that occurs in people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic feature of psoriatic arthritis is swelling of entire fingers and toes with a sausage-like appearance. This often happens in association with changes to the nails such as small depressions in the nail (pitting), thickening of the nails, and detachment of the nail from the nailbed. Skin changes consistent with psoriasis frequently occur before the onset of psoriatic arthritis but psoriatic arthritis can precede the rash in 15% of affected individuals. It is classified as a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy.
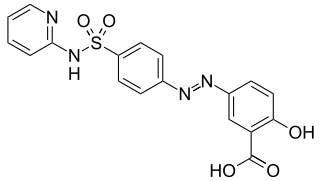
Sulfasalazine, sold under the brand name Azulfidine among others, is a medication used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn's disease. It is considered by some to be a first-line treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. It is taken by mouth or can be administered rectally.

Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, small cell lung cancer, neuroblastoma, and sarcoma. As an immune suppressor it is used in nephrotic syndrome, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and following organ transplant, among other conditions. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein.

Anakinra, sold under the brand name Kineret, is a biopharmaceutical medication used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes, familial Mediterranean fever, and Still's disease. It is a slightly modified recombinant version of the human interleukin 1 receptor antagonist protein. It is marketed by Swedish Orphan Biovitrum. Anakinra is administered by subcutaneous injection.

Leflunomide, sold under the brand name Arava among others, is an immunosuppressive disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD), used in active moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. It is a pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor that works by inhibiting dihydroorotate dehydrogenase.
Golimumab, sold under the brand name Simponi, is a human monoclonal antibody which is used as an immunosuppressive medication. Golimumab targets tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), a pro-inflammatory molecule and hence is a TNF inhibitor. Profound reduction in C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, interleukin (IL)-6, intercellaular adhesion molecules (ICAM)-1, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) demonstrates golimumab as an effective modulator of inflammatory markers and bone metabolism. Golimumab is given via subcutaneous injection.
Tocilizumab, sold under the brand name Actemra among others, is an immunosuppressive drug, used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, giant cell arteritis, cytokine release syndrome, COVID‑19, and systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD). It is a humanized monoclonal antibody against the interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R). Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is a cytokine that plays an important role in immune response and is implicated in the pathogenesis of many diseases, such as autoimmune diseases, multiple myeloma and prostate cancer. Tocilizumab was jointly developed by Osaka University and Chugai, and was licensed in 2003 by Hoffmann-La Roche.

Childhood arthritis is an umbrella term used to describe any rheumatic disease or chronic arthritis-related condition which affects individuals under the age of 16. There are several subtypes that differentiate themselves via prognosis, complications, and treatments. Most types are autoimmune disorders, where an individual's immune system may attack its own healthy tissues and cells.

14-3-3 protein eta also referred to as 14-3-3η is a protein that in humans is encoded by the YWHAH gene.
Rheumatoid lung disease is a disease of the lung associated with RA, rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid lung disease is characterized by pleural effusion, pulmonary fibrosis, lung nodules and pulmonary hypertension. Common symptoms associated with the disease include shortness of breath, cough, chest pain and fever. It is estimated that about one quarter of people with rheumatoid arthritis develop this disease, which are more likely to develop among elderly men with a history of smoking.
Sarilumab, sold under the brand name Kevzara, is a human monoclonal antibody medication against the interleukin-6 receptor. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and Sanofi developed the drug for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), for which it received US FDA approval on 22 May 2017 and European Medicines Agency approval on 23 June 2017.

Filgotinib, sold under the brand name Jyseleca, is a medication used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). It was developed by the Belgian-Dutch biotech company Galapagos NV.
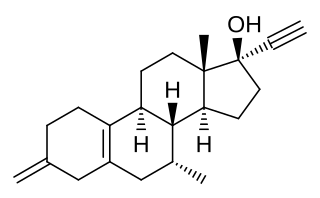
ERA-63, also known as ORG-37663, as well as 3-methylene-7α-methyl-17α-ethynylestra-5(10)-en-17β-ol, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen and a selective agonist of the ERα that was under development for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis but was never marketed. The drug produced estrogenic effects but failed to show effectiveness for rheumatoid arthritis in a phase IIa clinical study. A large clinical trial also found that prinaberel (ERB-041), a selective ERβ agonist, was ineffective in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in spite of activity in preclinical models.
Peficitinib is a pharmaceutical drug used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. It belongs to the class of drugs known as Janus kinase inhibitors.

Upadacitinib, sold under the brand name Rinvoq, is a medication used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, atopic dermatitis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, ankylosing spondylitis, and axial spondyloarthritis. Upadacitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor that works by blocking the action of enzymes called Janus kinases. These enzymes are involved in setting up processes that lead to inflammation, and blocking their effect brings inflammation in the joints under control.

An antiarthritic is any drug used to relieve or prevent arthritic symptoms, such as joint pain or joint stiffness. Depending on the antiarthritic drug class, it is used for managing pain, reducing inflammation or acting as an immunosuppressant. These drugs are typically given orally, topically or through administration by injection. The choice of antiarthritic medication is often determined by the nature of arthritis, the severity of symptoms as well as other factors, such as the tolerability of side effects.