
The Cary family is an English aristocratic family with a branch in Ireland. The earliest known ancestor of the family is Sir Adam de Kari who was living in 1198. Sir John Cary purchased the Manor of Clovelly in the 14th century and established the family's status as members of the landed gentry. Various branches of the family were ennobled in the late 16th and early 17th centuries as Baron Hunsdon and Viscount Falkland.
Sandford is a village and civil parish in the Mid Devon district, within Devon, England. Sandford is part of the electoral ward named Sandford and Creedy. The ward population at the 2011 Census was 3,429.

Sir John Northcote, 1st Baronet was an English politician who sat in the House of Commons at various times between 1640 and 1676. He supported the Parliamentarian cause in the English Civil War.
George Carew (1497/98–1583) was an English churchman who became Dean of Exeter.

Sir John Davie, 1st Baronet (1588–1654) of Creedy in the parish of Sandford, near Crediton, Devon, was a member of the Devonshire gentry and served as Member of Parliament for Tiverton in 1621-2 and as Sheriff of Devon (1629–1630). He was created a baronet in 1641.

Heanton Satchville was a historic manor in the parish of Petrockstowe, North Devon, England. With origins in the Domesday manor of Hantone, it was first recorded as belonging to the Yeo family in the mid-14th century and was then owned successively by the Rolle, Walpole and Trefusis families. The mansion house was destroyed by fire in 1795. In 1812 Lord Clinton purchased the manor and mansion of nearby Huish, renamed it Heanton Satchville, and made it his seat. The nearly-forgotten house was featured in the 2005 edition of Rosemary Lauder's "Vanished Houses of North Devon". A farmhouse now occupies the former stable block with a large tractor shed where the house once stood. The political power-base of the Rolle family of Heanton Satchville was the pocket borough seat of Callington in Cornwall, acquired in 1601 when Robert Rolle purchased the manor of Callington.

Bradfield House is a Grade I listed country house situated in the parish of Uffculme, Devon, England, 2 miles (3.2 km) south-west of the village of Uffculme.
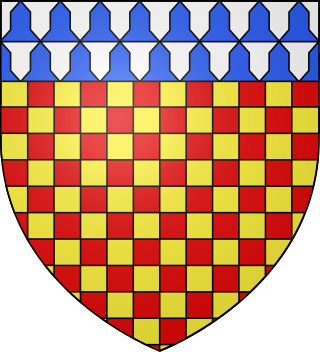
Sir John Chichester, 4th Baronet of Youlston Park in the parish of Shirwell near Barnstaple, Devon was a British landowner and Tory politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1734 to 1740.
John Northcote (1570–1632) of Uton and Hayne, Newton St Cyres, near Crediton, Devon, was a member of the Devonshire gentry, lord of the manor of Newton St Cyres, who is chiefly known to history for his artistically acclaimed effigy and monument in Newton St Cyres Church. Little or no documentary evidence concerning his career as a soldier or county administrator has survived, but either he or his identically named son was Sheriff of Devon in 1626.

Sir Robert Dennis, JP of Holcombe Burnell in Devon, was a Member of Parliament for Devon in 1555 and served as Sheriff of Devon.

Potheridge is a former Domesday Book estate in the parish of Merton, in the historic hundred of Shebbear, 3 miles south-east of Great Torrington, Devon, England. It is the site of a former grand mansion house re-built by George Monck, 1st Duke of Albemarle (1608–1670) circa 1660 on the site of the former manor house occupied by his family since at the latest 1287. It was mostly demolished in 1734 after the death of the widow of his son Christopher Monck, 2nd Duke of Albemarle.

Hudscott is a historic estate within the parish and former manor of Chittlehampton, Devon. From 1700 it became a seat of a junior branch of the influential Rolle family of Heanton Satchville, Petrockstowe and in 1779 became a secondary seat of the senior Rolle family of Stevenstone, then the largest landowner in Devon. Hudscott House, classified in 1967 a Grade II* listed building, is situated one mile south-east of the village of Chittlehampton. It was largely rebuilt in the 17th century by the Lovering family and in the late 17th century became a refuge for ejected Presbyterial ministers. In 1737 its then occupant Samuel II Rolle (1703-1747) purchased the manor of Chittlehampton and thus Hudscott House became in effect the manor house of Chittlehampton.

Little Fulford was an historic estate in the parishes of Shobrooke and Crediton, Devon. It briefly share ownership before 1700 with Great Fulford, in Dunsford, about 9 miles (14 km) to the south-west. The Elizabethan mansion house originally called Fulford House was first built by Sir William Peryam (1534-1604), a judge and Lord Chief Baron of the Exchequer. It acquired the diminutive epithet "Little" in about 1700 to distinguish it from Fulford House, Dunsford and was at some time after 1797 renamed Shobrooke House, to remove all remaining confusion between the two places. Peryam's mansion was demolished in 1815 and a new house erected on a different site away from the River Creedy. This new building was subsequently remodelled in 1850 in an Italianate style. It was destroyed by fire in 1945 and demolished, with only the stable block remaining today. The landscaped park survives, open on the south side to the public by permissive access, and crossed in parts by public rights of way, with ancient large trees and two sets of ornate entrance gates with a long decorative stone multiple-arched bridge over a large ornamental lake. The large pleasure garden survives, usually closed to the public, with walled kitchen garden and stone walls and balustrades of terraces. The park and gardens are Grade II listed in the National Register of Historic Parks and Gardens. The estate was the home successively of the families of Peryam, Tuckfield, Hippisley and lastly the Shelley baronets, in whose possession it remains today.

Creedy is an historic estate in the parish of Sandford, near Crediton in Devon. It is named from its location on the west side of the River Creedy. It was the seat of the Davie family from about 1600 until the late 20th century. The mansion house on the estate has been called at various times New House, Creedy House, and as presently, Creedy Park. It was first built in about 1600, rebuilt in 1846, burnt down in 1915 and rebuilt 1916–21. It is surrounded by a large park, the boundary of which is enclosed by a stone and brick wall several miles long.

Mohuns Ottery or Mohun's Ottery, is a house and historic manor in the parish of Luppitt, 1 mile south-east of the village of Luppitt and 4 miles north-east of Honiton in east Devon, England. From the 14th to the 16th centuries it was a seat of the Carew family. Several manorial court rolls survive at the Somerset Heritage Centre, Taunton, Somerset.

Canonteign is an historic tything in the parish of Christow, near Chudleigh, in South Devon, England and situated in the valley of the River Teign. The 'canon' in the name refers to the Augustinian canons regular, either of St Mary du Val in Normandy or of Merton Priory, which owned it for several centuries. It is best known today for the Canonteign Falls waterfall. Canonteign today contains three significant houses: the original Grade I listed 16th-century manor house, the ancient barton house situated nearby behind a granite wall, and a new mansion house built by the Pellew family in the early 19th century nearby, to which that family moved their residence thereby abandoning the old manor house.

Thomas Peyton (1418–1484) of Isleham, Cambridgeshire, was twice Sheriff of Cambridgeshire and Huntingdonshire, in 1443 and 1453. He rebuilt the church of St Andrew's in Isleham, in the chancel of which survives his monumental brass. He is depicted in a 1485 stained glass window in Long Melford Church, Suffolk, where he displays on his surcoat the Peyton arms: Sable, a cross engrailed or a mullet in the first quarter argent.

Sir Peter Carew was an English soldier who was slain at the Battle of Glenmalure in Ireland. He was a member of a prominent Devonshire gentry family. He is sometimes referred to as Sir Peter Carew the younger, to distinguish him from his first cousin Sir Peter Carew (c.1514–1575) of Mohuns Ottery, Luppitt, Devon.
Collacombe is an historic manor in the parish of Lamerton, Devon, England. The manor house survives as a grade I listed building, known as Collacombe Barton or Collacombe Manor (House).

Bagtor is an historic estate in the parish of Ilsington in Devon, England. It was the birthplace of John Ford (1586-c.1639) the playwright and poet. The Elizabethan mansion of the Ford family survives today at Bagtor as the service wing of a later house appended in about 1700.























