
74 Aquarii is a triple star system in the constellation of Aquarius. 74 Aquarii is its Flamsteed designation and it also bears the variable star designation HI Aquarii. The combined apparent visual magnitude is 5.8, although it is very slightly variable, and it is located at a distance of 590 light-years from Earth.

Omicron1 Canis Majoris is a red supergiant star in the constellation Canis Major. It is also a variable star.
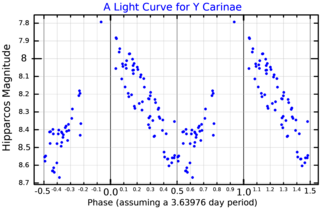
Y Carinae is a Classical Cepheid variable, a type of variable star, in the constellation Carina. Its apparent magnitude varies from 7.53 to 8.48.

1 Vulpeculae is a class B4IV star in the constellation Vulpecula. Its apparent magnitude is 4.77 and it is approximately 780 light years away based on parallax.

WR 136 is a Wolf–Rayet star located in the constellation Cygnus. It is in the center of the Crescent Nebula. Its age is estimated to be around 4.7 million years and it is nearing the end of its life. Within a few hundred thousand years, it is expected to explode as a supernova.

WR 46 is a Wolf-Rayet star in the constellation of the Southern Cross of apparent magnitude +10.8. It is located at 55 arcmin north of Theta2 Crucis. The star is a member of the distant stellar association Cru OB4, and is around 2,900 parsecs or 9,300 light years from the Solar System.

WR 24 is a Wolf-Rayet star in the constellation Carina. It is one of the most luminous stars known. At the edge of naked eye visibility it is also one of the brightest Wolf Rayet stars in the sky.

WR 148 is a spectroscopic binary in the constellation Cygnus. The primary star is a Wolf–Rayet star and one of the most luminous stars known. The secondary has been suspected of being a stellar-mass black hole but may be a class O main sequence star.

Sigma Ophiuchi, Latinized from σ Ophiuchi, is a single, orange-hued star in the equatorial constellation Ophiuchus. Its apparent visual magnitude is 4.31, which is bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye. The annual parallax shift of 3.62 mas as seen from Earth provides a distance estimate of roughly 900 light years. It is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −28 km/s.

QZ Puppis is a class B2.5V star in the constellation Puppis. Its apparent magnitude is 4.5 and it is approximately 650 light years away based on parallax.

WR 134 is a variable Wolf-Rayet star located around 6,000 light years away from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus, surrounded by a faint bubble nebula blown by the intense radiation and fast wind from the star. It is five times the radius of the sun, but due to a temperature over 63,000 K it is 400,000 times as luminous as the Sun.
EQ Pegasi is a nearby binary system of two red dwarfs. Both components are flare stars, with spectral types of M4Ve and M6Ve respectively, and a current separation between the components of 5.8 arcseconds. The system is at a distance of 20.4 light-years, and is 950 million years old. The primary star is orbited by one known exoplanet.

WR 20a is an eclipsing binary star belonging to or recently ejected from the young, massive cluster Westerlund 2. It was discovered in 2004 to be one of the most massive binary systems known, for which the masses of the components have been accurately measured.

CD Crucis, also known as HD 311884, is an eclipsing binary star system in the constellation Crux. It is around 14,000 light years away near the faint open cluster Hogg 15. The binary contains a Wolf–Rayet star and is also known as WR 47.

WR 30a is a massive spectroscopic binary in the Milky Way galaxy, in the constellation Carina. The primary is an extremely rare star on the WO oxygen sequence and the secondary a massive class O star. It appears near the Carina Nebula but is much further away.

S Cassiopeiae is a Mira variable and S-type star in the constellation Cassiopeia. It is an unusually cool star, rapidly losing mass and surrounded by dense gas and dust producing masers.
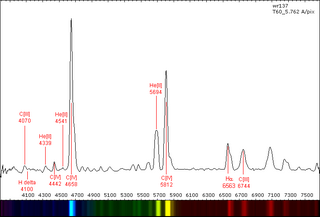
WR 137 is a variable Wolf-Rayet star located around 6,000 light years away from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus.

WR 9 is a spectroscopic binary in the constellation Puppis consisting of a Wolf-Rayet star and a class O star. It is around 12,000 light years away.

HD 151932, also known as WR 78, is a Wolf-Rayet star located in the constellation Scorpius, close to the galactic plane. Its distance is around 1,300 parsecs away from the Earth. Despite being a blue-colored Wolf-Rayet star, it is extremely reddened by interstellar extinction, so its apparent magnitude is brighter for longer-wavelength passbands. HD 151932 lies about 22′ west of the open cluster NGC 6231, the center of the OB association Scorpius OB1; it is not clear whether it is a part of the association or not. With an apparent magnitude of about 6.5, it is one of the few Wolf-Rayet stars that can be seen with the naked eye.




















