Related Research Articles
The Electoral district of City of Sydney was an electorate of the New South Wales Legislative Council.

The Electoral district of County of Bathurst was an electorate of the New South Wales Legislative Council at a time when some of its members were elected and the balance were appointed by the Governor.
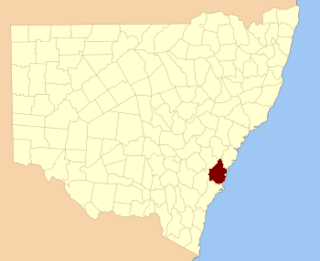
The Electoral district of County of Camden was an electorate of the New South Wales Legislative Council at a time when some of its members were elected and the balance were appointed by the Governor.

The Electoral district of Counties of Gloucester, Macquarie, and Stanley and from 1851, Gloucester and Macquarie, was an electorate of the partially elected New South Wales Legislative Council, created for the first elections for the Council in 1843. The counties of Gloucester and Macquarie were the settled coastal areas north of Northumberland County, while the County of Stanley was the area surrounding Brisbane, in what became part of Queensland after its separation in 1859. Polling took place at Raymond Terrace, Port Macquarie, Dungog, Stroud, Brisbane, Ipswich and Mr Rowley's residence on the Manning River. The County of Stanley was removed from the district with the expansion of the Council in 1851 and became the districts of County of Stanley and Stanley Boroughs.
The 1856 New South Wales colonial election was to return 54 members of Legislative Assembly composed of 34 electoral districts with 18 returning 1 member, 13 returning 2 members, two returning 3 members and one returning 4 members, all with a first past the post system. In multi-member districts, because each voter could cast more than one vote, it is not possible to total the votes to show the number of voters and voter turnout in these districts is estimated. 8 members from 6 districts were returned unopposed.
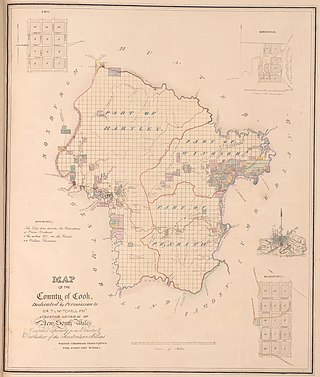
The Electoral district of Counties of Cook and Westmoreland, also known as the United Midland Counties of Cook and Westmoreland, was an electorate of the New South Wales Legislative Council at a time when some of its members were elected and the balance were appointed by the Governor.
The electoral district of Cumberland Boroughs, also known as the united towns of Windsor, Richmond, Liverpool and Campbelltown, was an electorate of the New South Wales Legislative Council at a time when two thirds were elected, one sixth were official members, that is they held a government office and the balance were appointed by the Governor.
The 1843 New South Wales colonial election, the first in the colony, was held between 15 June and 3 July 1843, to elect 24 members from 18 electoral districts. Each district returned 1 member except for Port Phillip which returned 5 members while County of Cumberland, and Town of Sydney returned 2 each.
The 1848 New South Wales colonial election was held between 29 July and 2 August. No candidates were nominated for Port Phillip as a result of the campaign for independence from New South Wales, and a fresh writ was issued for an election on 3 October.
The Electoral district of Counties of Hunter, Brisbane and Bligh and from 1851, Phillip, Brisbane and Bligh, was an electorate of the partially elected New South Wales Legislative Council, created for the first elections for the Council in 1843. The electoral district included the north western counties of Hunter, Brisbane, Bligh. Polling took place in the towns of Jerrys Plains, nearby Merton, Muswellbrook, Scone, as far north as Murrurundi, Watson's on the Macdonald River, Cassilis and as far west as Montefiores. With the expansion of the Council in 1851 Phillip, the other north west county, was added to the district, replacing Hunter which was combined with the lower Hunter county of Northumberland as Counties of Northumberland and Hunter.
The Electoral district of Counties of St Vincent and Auckland was an electorate of the partially elected New South Wales Legislative Council, created for the first elections for the Council in 1843. The electoral district consisted of the two south coast counties of St Vincent and Auckland, extending from Jervis Bay south to Eden and west to Braidwood. Polling took place at Jervis Bay, Ulladulla, Braidwood, Broulee and Eden. The district was abolished with the expansion of the Council in 1851. St Vincent was combined with Murray to the west as the Counties of Murray and St Vincent while Auckland became part of the Pastoral District of Maneroo.
The Electoral district of Counties of Murray, King and Georgiana and from 1851, Counties of King and Georgiana was an electorate of the partially elected New South Wales Legislative Council, created for the first elections for the Council in 1843. The electoral district included the south western counties of Murray, King and Georgiana. Polling took place at Queanbeyan, Yass and Wheeo, which were within the counties and the nearby towns of Braidwood, Goulburn and Bathurst. The towns of Queanbeyan and Yass were removed from the district with the expansion of the Council in 1851 and combined with Braidwood and Goulburn to form the Southern Boroughs. The rural area of the County of Murray became part of the Counties of Murray and St Vincent and leaving the district to cover the remaining rural areas of the Counties of King and Gergiana.
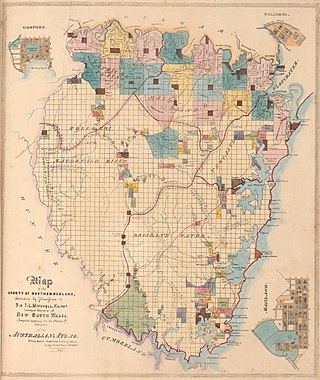
The Electoral district of County of Northumberland and from 1851, Northumberland and Hunter, was an electorate of the partially elected New South Wales Legislative Council, created for the first elections for the Council in 1843. The County of Northumberland was bounded by the part of the Hawkesbury River to the south, the Macdonald River to the south-west, and the Hunter River to the north, however the electoral district did not include the towns of East Maitland, West Maitland and Newcastle which made up the district of Northumberland Boroughs. Polling took place at Gosford, Newcastle, East Maitland, Wollombi, Singleton and Watson's on the Macdonald River. The County of Hunter was added to the district with the expansion of the Council in 1851 and elected two members.

The Electoral district of Northumberland Boroughs was an electorate of the partially elected New South Wales Legislative Council, created for the first elections for the Council in 1843. From 1843 until 1851 the electorate covered the major towns or boroughs of Northumberland County, East Maitland, West Maitland and Newcastle, and polling took place at East Maitland, West Maitland and Newcastle. Morpeth was added to the electorate from 1851 while Newcastle was removed from the electorate to form, with Raymond Terrace, the North Eastern Boroughs. The rest of Northumberland County was covered by the County of Northumberland from 1843 until 1951, and Counties of Northumberland and Hunter from 1851 until 1856.
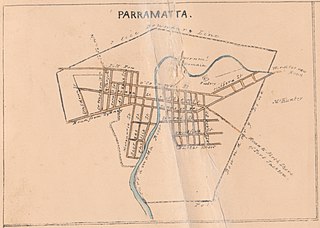
The Electoral district of Town of Parramatta was an electorate of the partially elected New South Wales Legislative Council, created for the first elections for the Council in 1843, at the time the principal residence of the Governor Sir Charles FitzRoy. Polling took place at Parramatta. In 1856, the unicameral Legislative Council was abolished and replaced with an elected Legislative Assembly and an appointed Legislative Council. The district was represented by the Legislative Assembly Parramatta, the only electorate to have existed continuously since the first Legislative Assembly election in 1856.
The 1851 New South Wales colonial election, was held between 12 and 25 September. It involved a re-distribution of electorates as a result of the separation of Victoria, which had 6 seats in the previous council, and the expansion of the council from 24 elected members to 36 elected members representing 31 electorates. The major changes were the addition of 8 pastoral districts and the separate representation for the northern regions of what would later become Queensland. These had previously been a part of the single district of Gloucester, Macquarie, and Stanley and from 1851 were covered by the separate districts of Stanley, Stanley Boroughs and the pastoral districts of Moreton, Wide Bay, Burnett, and Maranoa. The other 8 additional seats were distributed among the nineteen counties of New South Wales.
The Electoral district of Pastoral Districts of Lachlan and Lower Darling was an electorate of the New South Wales Legislative Council at a time when some of its members were elected and the balance were appointed by the Governor. It was a new electorate created in 1851 by the expansion of the Legislative Council to 54, 18 to be appointed and 36 elected. The district covered the south west of New South Wales was named after the Lachlan and Darling Rivers. On its eastern side were the districts of County of Bathurst and Counties of King and Georgiana, to the north was the Pastoral Districts of Wellington and Bligh and to the south was the Counties of Murray and St Vincent. Polling was to occur in the towns of Binalong, Wagga Wagga, Balranald, Canowindra, Gundagai and Yass.
The Electoral district of Pastoral Districts of Liverpool Plains and Gwydir was an electorate of the New South Wales Legislative Council at a time when some of its members were elected and the balance were appointed by the Governor. It was a new electorate created in 1851 by the expansion of the Legislative Council to 54, 18 to be appointed and 36 elected. The district was named after the Liverpool Plains and Gwydir River and covered what is now known as the North West Slopes region. On its eastern side was the Pastoral Districts of New England and Macleay and to the south was the Pastoral Districts of Wellington and Bligh. Polling was to occur in the towns of Murrurundi, Tamworth, Wee Waa, Warialda and the Woolshed on the Namoi River.
The Electoral district of Counties of Murray and St Vincent was an electorate of the New South Wales Legislative Council at a time when some of its members were elected and the balance were appointed by the Governor. It was a new electorate created in 1851 by the expansion of the Legislative Council to 54, 18 to be appointed and 36 elected. The district consisted of the rural areas of Murray County, which had previously been part of Counties of Murray, King and Georgiana, and St Vincent County, which had previously been part of Counties of St Vincent and Auckland. The towns of Braidwood and Queanbeyan were not part of the district, being included in Southern Boroughs.
The Electoral district of Pastoral Districts of Wellington and Bligh was an electorate of the New South Wales Legislative Council at a time when some of its members were elected and the balance were appointed by the Governor. It was a new electorate created in 1851 by the expansion of the Legislative Council to 54, 18 to be appointed and 36 elected. The district was located in the central west region of the state and covered the pastoral areas to the west of the Counties of Roxburgh and Wellington and Counties of Phillip, Brisbane and Bligh. To the north was the Pastoral Districts of Liverpool Plains and Gwydir and to the south the Pastoral Districts of Lachlan and Lower Darling. If polling had been required, it would have taken place in the towns of Molong, Wellington, Dubbo, Canowindra, Coola and Mudgee.
References
- 1 2 "An Act to provide for the division of the Colony of New South Wales into Electoral Districts and for the Election of Members to serve in the Legislative Council.". Act No. 16 of 23 February 1843 (PDF). Australasian Legal Information Institute. Retrieved 27 May 2019.
- ↑ "Polling places". The Sydney Morning Herald . 14 July 1848. p. 2. Retrieved 28 May 2019– via Trove.
- ↑ "An Act to provide for the division of the Colony of New South Wales after the separation of the District of Port Phillip therefrom into Electoral Districts and for the Election of Members to serve in the Legislative Council.". Act No. 48 of 2 May 1851 (PDF). Australasian Legal Information Institute. Retrieved 27 May 2019.
- ↑ "Mr William Henry Suttor (Senior) (1805–1877)". Former members of the Parliament of New South Wales . Retrieved 19 April 2019.
- ↑ "Sir Saul Samuel (1820-1900)". Former members of the Parliament of New South Wales . Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ "Roxburgh, Phillip and Wellington election". The Sydney Morning Herald . 28 June 1843. p. 2. Retrieved 23 May 2019– via Trove.
- ↑ "Nomination day for Roxburgh". Bathurst Advocate . 29 July 1848. p. 3. Retrieved 29 May 2019– via Trove.
- ↑ "Counties of Roxburgh and Wellington". The Sydney Morning Herald . 20 September 1851. p. 3. Retrieved 29 May 2019– via Trove.
- ↑ "Roxburgh and Wellington election - nomination day". The Sydney Morning Herald . 24 October 1854. p. 5. Retrieved 29 May 2019– via Trove.