A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds, or some combination of these effects. Chemical bonds are described as having different strengths: there are "strong bonds" or "primary bonds" such as covalent, ionic and metallic bonds, and "weak bonds" or "secondary bonds" such as dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force, and hydrogen bonding.

A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding.
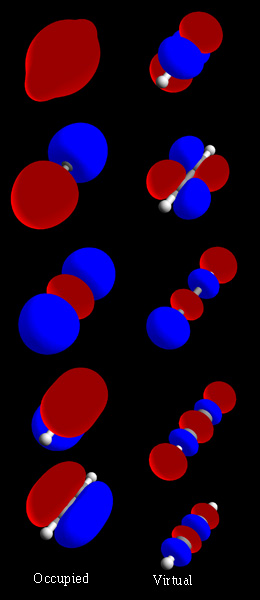
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms atomic orbital and molecular orbital were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean one-electron orbital wave functions. At an elementary level, they are used to describe the region of space in which a function has a significant amplitude.
In quantum mechanics, the Pauli exclusion principle states that two or more identical particles with half-integer spins cannot simultaneously occupy the same quantum state within a system that obeys the laws of quantum mechanics. This principle was formulated by Austrian physicist Wolfgang Pauli in 1925 for electrons, and later extended to all fermions with his spin–statistics theorem of 1940.
Quantum chemistry, also called molecular quantum mechanics, is a branch of physical chemistry focused on the application of quantum mechanics to chemical systems, particularly towards the quantum-mechanical calculation of electronic contributions to physical and chemical properties of molecules, materials, and solutions at the atomic level. These calculations include systematically applied approximations intended to make calculations computationally feasible while still capturing as much information about important contributions to the computed wave functions as well as to observable properties such as structures, spectra, and thermodynamic properties. Quantum chemistry is also concerned with the computation of quantum effects on molecular dynamics and chemical kinetics.

A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels. This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any amount of energy. The term is commonly used for the energy levels of the electrons in atoms, ions, or molecules, which are bound by the electric field of the nucleus, but can also refer to energy levels of nuclei or vibrational or rotational energy levels in molecules. The energy spectrum of a system with such discrete energy levels is said to be quantized.

In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6, meaning that the 1s, 2s, and 2p subshells are occupied by two, two, and six electrons, respectively.

A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. For example, NH3 is a Lewis base, because it can donate its lone pair of electrons. Trimethylborane () is a Lewis acid as it is capable of accepting a lone pair. In a Lewis adduct, the Lewis acid and base share an electron pair furnished by the Lewis base, forming a dative bond. In the context of a specific chemical reaction between NH3 and Me3B, a lone pair from NH3 will form a dative bond with the empty orbital of Me3B to form an adduct NH3•BMe3. The terminology refers to the contributions of Gilbert N. Lewis.

The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that reflects the theory that main-group elements tend to bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its valence shell, giving it the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The rule is especially applicable to carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and the halogens; although more generally the rule is applicable for the s-block and p-block of the periodic table. Other rules exist for other elements, such as the duplet rule for hydrogen and helium, and the 18-electron rule for transition metals.
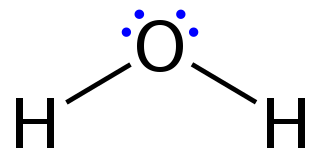
Lewis structures – also called Lewis dot formulas, Lewis dot structures, electron dot structures, or Lewis electron dot structures (LEDs) – are diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule, as well as the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule. A Lewis structure can be drawn for any covalently bonded molecule, as well as coordination compounds. The Lewis structure was named after Gilbert N. Lewis, who introduced it in his 1916 article The Atom and the Molecule. Lewis structures extend the concept of the electron dot diagram by adding lines between atoms to represent shared pairs in a chemical bond.

In quantum physics and chemistry, quantum numbers are quantities that characterize the possible states of the system. To fully specify the state of the electron in a hydrogen atom, four quantum numbers are needed. The traditional set of quantum numbers includes the principal, azimuthal, magnetic, and spin quantum numbers. To describe other systems, different quantum numbers are required. For subatomic particles, one needs to introduce new quantum numbers, such as the flavour of quarks, which have no classical correspondence.
In chemistry, valence bond (VB) theory is one of the two basic theories, along with molecular orbital (MO) theory, that were developed to use the methods of quantum mechanics to explain chemical bonding. It focuses on how the atomic orbitals of the dissociated atoms combine to give individual chemical bonds when a molecule is formed. In contrast, molecular orbital theory has orbitals that cover the whole molecule.
In physics and chemistry, the spin quantum number is a quantum number that describes the intrinsic angular momentum of an electron or other particle. It has the same value for all particles of the same type, such as s = 1/2 for all electrons. It is an integer for all bosons, such as photons, and a half-odd-integer for all fermions, such as electrons and protons.

Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a model used in chemistry to predict the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms. It is also named the Gillespie-Nyholm theory after its two main developers, Ronald Gillespie and Ronald Nyholm.

In theoretical chemistry, an antibonding orbital is a type of molecular orbital that weakens the chemical bond between two atoms and helps to raise the energy of the molecule relative to the separated atoms. Such an orbital has one or more nodes in the bonding region between the nuclei. The density of the electrons in the orbital is concentrated outside the bonding region and acts to pull one nucleus away from the other and tends to cause mutual repulsion between the two atoms. This is in contrast to a bonding molecular orbital, which has a lower energy than that of the separate atoms, and is responsible for chemical bonds.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place.
Alfred Lauck Parson was a British chemist and physicist, whose "magneton theory" of the atom contributed to the history of chemistry.
In spectroscopy and quantum chemistry, the multiplicity of an energy level is defined as 2S+1, where S is the total spin angular momentum. States with multiplicity 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 are respectively called singlets, doublets, triplets, quartets and quintets.

In chemistry, an unpaired electron is an electron that occupies an orbital of an atom singly, rather than as part of an electron pair. Each atomic orbital of an atom has a capacity to contain two electrons with opposite spins. As the formation of electron pairs is often energetically favourable, either in the form of a chemical bond or as a lone pair, unpaired electrons are relatively uncommon in chemistry, because an entity that carries an unpaired electron is usually rather reactive. In organic chemistry they typically only occur briefly during a reaction on an entity called a radical; however, they play an important role in explaining reaction pathways.

Linnett double-quartet theory (LDQ) is a method of describing the bonding in molecules which involves separating the electrons depending on their spin, placing them into separate 'spin tetrahedra' to minimise the Pauli repulsions between electrons of the same spin. Introduced by J. W. Linnett in his 1961 monograph and 1964 book, this method expands on the electron dot structures pioneered by G. N. Lewis. While the theory retains the requirement for fulfilling the octet rule, it dispenses with the need to force electrons into coincident pairs. Instead, the theory stipulates that the four electrons of a given spin should maximise the distances between each other, resulting in a net tetrahedral electronic arrangement that is the fundamental molecular building block of the theory.