Related Research Articles
In biology and biochemistry, protease inhibitors, or antiproteases, are molecules that inhibit the function of proteases. Many naturally occurring protease inhibitors are proteins.
Plasmepsins are a class of at least 10 enzymes produced by the Plasmodium falciparum parasite. There are ten different isoforms of these proteins and ten genes coding them respectively in Plasmodium. It has been suggested that the plasmepsin family is smaller in other human Plasmodium species. Expression of Plm I, II, IV, V, IX, X and HAP occurs in the erythrocytic cycle, and expression of Plm VI, VII, VIII, occurs in the exoerythrocytic cycle. Through their haemoglobin-degrading activity, they are an important cause of symptoms in malaria sufferers. Consequently, this family of enzymes is a potential target for antimalarial drugs.

Pepsin A is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Aspergillopepsin I is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
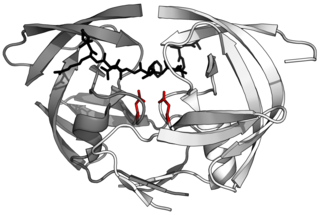
Aspartic proteases are a catalytic type of protease enzymes that use an activated water molecule bound to one or more aspartate residues for catalysis of their peptide substrates. In general, they have two highly conserved aspartates in the active site and are optimally active at acidic pH. Nearly all known aspartyl proteases are inhibited by pepstatin.

Thermolysin is a thermostable neutral metalloproteinase enzyme produced by the Gram-positive bacteria Bacillus thermoproteolyticus. It requires one zinc ion for enzyme activity and four calcium ions for structural stability. Thermolysin specifically catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds containing hydrophobic amino acids. However thermolysin is also widely used for peptide bond formation through the reverse reaction of hydrolysis. Thermolysin is the most stable member of a family of metalloproteinases produced by various Bacillus species. These enzymes are also termed 'neutral' proteinases or thermolysin -like proteinases (TLPs).

In molecular biology, Proteinase K is a broad-spectrum serine protease. The enzyme was discovered in 1974 in extracts of the fungus Parengyodontium album. Proteinase K is able to digest hair (keratin), hence, the name "Proteinase K". The predominant site of cleavage is the peptide bond adjacent to the carboxyl group of aliphatic and aromatic amino acids with blocked alpha amino groups. It is commonly used for its broad specificity. This enzyme belongs to Peptidase family S8 (subtilisin). The molecular weight of Proteinase K is 28,900 daltons.

Cathepsin D is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTSD gene. This gene encodes a lysosomal aspartyl protease composed of a protein dimer of disulfide-linked heavy and light chains, both produced from a single protein precursor. Cathepsin D is an aspartic endo-protease that is ubiquitously distributed in lysosomes. The main function of cathepsin D is to degrade proteins and activate precursors of bioactive proteins in pre-lysosomal compartments. This proteinase, which is a member of the peptidase A1 family, has a specificity similar to but narrower than that of pepsin A. Transcription of the CTSD gene is initiated from several sites, including one that is a start site for an estrogen-regulated transcript. Mutations in this gene are involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases, including breast cancer and possibly Alzheimer disease. Homozygous deletion of the CTSD gene leads to early lethality in the postnatal phase. Deficiency of CTSD gene has been reported an underlying cause of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (NCL).
Progastricsin also known as pepsinogen C or pepsinogen II is a pepsinogen precursor of the enzyme gastricsin that in humans is encoded by the PGC gene.
Nepenthesin is an aspartic protease of plant origin that has so far been identified in the pitcher secretions of Nepenthes and in the leaves of Drosera peltata. It is similar to pepsin, but differs in that it also cleaves on either side of Asp residues and at Lys┼Arg. While more pH and temperature stable than porcine pepsin A, it is considerably less stable in urea or guanidine hydrochloride. It is the only known protein with such a stability profile.

Aspergilloglutamic peptidase, also called aspergillopepsin II is a proteolytic enzyme. The enzyme was previously thought be an aspartic protease, but it was later shown to be a glutamic protease with a catalytic Glu residue at the active site, and was therefore renamed aspergilloglutamic peptidase.
Penicillopepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Rhizopuspepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Mucorpepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Acrocylindropepsin (EC 3.4.23.28, Acrocylindrium proteinase, Acrocylindrium acid proteinase) is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Scytalidopepsin A (EC 3.4.23.31, Scytalidium aspartic proteinase A, Scytalidium lignicolum aspartic proteinase, Scytalidium lignicolum aspartic proteinase A-2, Scytalidium lignicolum aspartic proteinase A-I, Scytalidium lignicolum aspartic proteinase C, Scytalidium lignicolum carboxyl proteinase, Scytalidium lignicolum acid proteinase) is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Scytalidocarboxyl peptidase B, also known as Scytalidoglutamic peptidase and Scytalidopepsin B is a proteolytic enzyme. It was previously thought to be an aspartic protease, but determination of its molecular structure showed it to belong a novel group of proteases, glutamic protease.
Phytepsin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Atrolysin C is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Glutamic proteases are a group of proteolytic enzymes containing a glutamic acid residue within the active site. This type of protease was first described in 2004 and became the sixth catalytic type of protease. Members of this group of protease had been previously assumed to be an aspartate protease, but structural determination showed it to belong to a novel protease family. The first structure of this group of protease was scytalidoglutamic peptidase, the active site of which contains a catalytic dyad, glutamic acid (E) and glutamine (Q), which give rise to the name eqolisin. This group of proteases are found primarily in pathogenic fungi affecting plant and human.
References
- ↑ Blundell TL, Jenkins JA, Sewell BT, Pearl LH, Cooper JB, Tickle IJ, Veerapandian B, Wood SP (February 1990). "X-ray analyses of aspartic proteinases. The three-dimensional structure at 2.1 A resolution of endothiapepsin". Journal of Molecular Biology. 211 (4): 919–41. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(90)90084-Y. PMID 2179568.
- ↑ Hemmings AM, Foundling SI, Sibanda BL, Wood SP, Pearl LH, Blundell T (December 1985). "Energy calculations on aspartic proteinases: human renin, endothiapepsin and its complex with an angiotensinogen fragment analogue, H-142". Biochemical Society Transactions. 13 (6): 1036–41. doi:10.1042/bst0131036. PMID 3912234.
- ↑ Whitaker, J.R. (1970). "Protease of Endothia parasitica". Protease of Endothia parasitica. Methods Enzymol. Vol. 19. pp. 436–445. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(70)19032-x. ISBN 978-0-12-181881-4.
- ↑ Williams DC, Witaker JR, Caldwell PV (March 1972). "Hydrolysis of peptide bonds of the oxidized B-chain of insulin by Endothia parasitica protease". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 149 (1): 52–61. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(72)90298-6. PMID 4552802.
- ↑ Barkholt V (September 1987). "Amino acid sequence of endothiapepsin. Complete primary structure of the aspartic protease from Endothia parasitica". European Journal of Biochemistry. 167 (2): 327–38. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13340.x. PMID 3305016.
- ↑ Cooper J, Foundling S, Hemmings A, Blundell T, Jones DM, Hallett A, Szelke M (November 1987). "The structure of a synthetic pepsin inhibitor complexed with endothiapepsin". European Journal of Biochemistry. 169 (1): 215–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13600.x . PMID 3119339.