
Branchiopoda is a class of crustaceans. It comprises fairy shrimp, clam shrimp, Diplostraca, Notostraca, the Devonian Lepidocaris and possibly the Cambrian Rehbachiella. They are mostly small, freshwater animals that feed on plankton and detritus.

Shellfish is a colloquial and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater environments, some are found in freshwater. In addition, a few species of land crabs are eaten, for example Cardisoma guanhumi in the Caribbean. Shellfish are among the most common food allergens.

Clam shrimp are a group of bivalved branchiopod crustaceans that resemble the unrelated bivalved molluscs. They are extant and also known from the fossil record, from at least the Devonian period and perhaps before. They were originally classified in the former order Conchostraca, which later proved to be paraphyletic, due to the fact that water fleas are nested within clam shrimps. Clam shrimp are now divided into three orders, Cyclestherida, Laevicaudata, and Spinicaudata, in addition to the fossil family Leaiidae.
Reef safe is a distinction used in the saltwater aquarium hobby to indicate that a fish or invertebrate is safe to add to a reef aquarium. There is no fish that is completely reef safe. Every fish that is commonly listed as reef safe are species that usually do not readily consume small fish or invertebrates. Fish listed as reef safe also do not bother fellow fish unless in some cases, for instance tangs, they do not get along with conspecifics and sometimes fish with similar color or body shape. Every fish has a personality, is different, and, in some cases, are opportunistic feeders. Tangs, which by most accounts are reef safe, may in adulthood eat some crustaceans shortly after they molt. Many larger predatory fish, for instance eels and pufferfish, will adapt very well to a reef tank and will be problem-free as long as they have sizable tank-mates and no crustaceans. Some aquarists have also had success in keeping smaller fish with predatory ones in reef tanks by adding the smaller fish at night, sometimes with newly rearranged rockwork.

Bandon Marsh National Wildlife Refuge is a U.S. National Wildlife Refuge on Oregon's coast. It is one of six National Wildlife Refuges comprising the Oregon Coast National Wildlife Refuge Complex and is renowned among bird watchers for being able to view rare shorebirds including ruff, Hudsonian godwit, and Mongolian plover. The refuge was last expanded in 1999, it now has 889 acres (3.60 km2) in two units: Bandon Marsh and Ni-les'tun.
The graceful clam shrimp is a species of clam shrimp found in Texas, northern Florida and possibly other regions in between.
A valve is each articulating part of the shell of a mollusc or another multi-shelled animal such as brachiopods and some crustaceans. Each part is known as a valve or in the case of chitons, a "plate". Members of two classes of molluscs, the Bivalvia (clams) and the Polyplacophora (chitons), have valves.
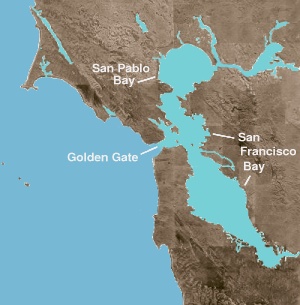
The San Francisco Estuary together with the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta represents a highly altered ecosystem. The region has been heavily re-engineered to accommodate the needs of water delivery, shipping, agriculture, and most recently, suburban development. These needs have wrought direct changes in the movement of water and the nature of the landscape, and indirect changes from the introduction of non-native species. New species have altered the architecture of the food web as surely as levees have altered the landscape of islands and channels that form the complex system known as the Delta.

Diplurus is a genus of prehistoric mawsoniid coelacanth fish which lived during the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic period in North America. The fossils of this genus are common on the eastern North American Margin, being a key taxon of the Newark Supergroup, and recovered from units such as the Bull Run Formation, Lockatong Formation, Stockton Formation, Solite Quarry, Midland Formation, East Berlin Formation, Boonton Formation and the Portland Formation. Three species are know, the type D. longicaudatus, the youngest and biggest, D. newarki, the oldest, followed then by "D. uddeni" (Eastman), also from older rocks and considered dubious. A recent work has recovered a 3rd or 4th species, D. enigmaticus, from the Late Triassic of New Jersey, representing another small-bodied form living in sympatry with the similarly sized D. newarki. This genus ranges in size from 15 cm of D. newarki and D. enigmaticus in New Jersey to the larger 60 cm specimens of Diplurus longicaudatus found in the Connecticut River Valley, which indicates a considerable growth and likely a change in the ecological position of the genus to a possible apex predatory niche.
Aquaculture in Vanuatu exists on a small scale, both commercially and privately. Several aquacultural efforts have been made in the country, including attempts to raise Pacific oyster, rabbitfish, Malaysian prawn, and tilapia. Experiments with Kappaphycus alvarezii and three species of giant clam were carried out by the Fisheries Department in 1999. The official Fisheries Department records state that $1165 US of cultured coral was exported from the country in 2000, with 275 pieces in total. The cultivation of Macrobrachium lar in taro terraces is practiced for subsistence purposes, and Macrobrachium rosenbergii has been identified by the Vanuatu government as a high-priority species.

A shrimp (pl.: shrimp or shrimps is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – typically belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchiata of the order Decapoda, although some crustaceans outside of this order are also referred to as "shrimp".
Leptestheriidae is a family of crustaceans in the order Spinicaudata. They are distinguished from the family Cyzicidae by the presence of a rostral spine. Members of Leptestheriidae are believed to graze on detritus.

Cyzicus is a genus of clam shrimps in the family Cyzicidae. Identified by Jean Victoire Audouin in 1837, the genus was reidentified as Caenestheriella by Eugen von Daday in 1910.
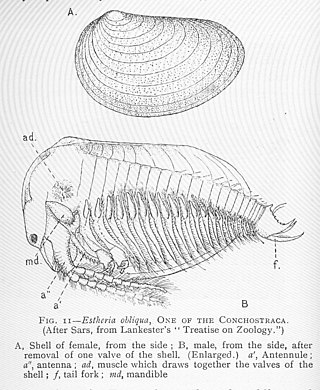
Lioestheria is an extinct genus of clam shrimp that thrived from the Carboniferous to the Cretaceous. They fed on detritus, being very small slow moving, nektonic organisms that filter fed as they floated. They have been found in both marine and freshwater environments.
Lynceidae is a family of clam shrimp in the order Laevicaudata. There are about 5 genera and more than 20 described species in Lynceidae.
Leptestheria compleximanus is a species of North American clam shrimp known by the common name playa clam shrimp or spineynose clam shrimp.







