
The Calpinae are a subfamily of moths in the family Erebidae described by Jean Baptiste Boisduval in 1840. This subfamily includes many species of moths that have a pointed and barbed proboscis adapted to piercing the skins of fruit to feed on juice, and in the case of the several Calyptra species of vampire moths, to piercing the skins of mammals to feed on blood. The subfamily contains some large moths with wingspans longer than 5 cm (2 in).

The Calpini are a tribe of fruit-piercing moths in the family Erebidae; formerly they were included in the family Noctuidae. The proboscis of the adult moths of this tribe is pointed and barbed, allowing the moth to pierce the skin of fruit to drink the juice. The vampire moths in the genus Calyptra can pierce mammal skin to drink blood.

Eudocima is a genus of moths of the family Erebidae with numerous tropical species. The genus was first categorised by Gustaf Johan Billberg in 1820, and species currently in the genus have been placed under a range of other genera in the past. Adult moths in the genus are known for puncturing and feeding on the juices of fruits, because of which they are considered as pests by horticulturists.

Eudocima materna, the dot-underwing moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae found in widespread parts of the world, mainly in tropical Asia extending to New Guinea and Australia as well as in Africa. Reports from the United States, Canada and the French Antilles are now considered to be Eudocima apta. The species can be differentiated from other Eudocima moths by the presence of small central black dot in each hindwing. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1767 12th edition of Systema Naturae.

Sarcopetalum harveyanum, known as the pearl vine, is a common plant found mostly in coastal areas of eastern Australia. It can be found in or around rainforests, and is also seen in eucalyptus forests.

Eudocima iridescens is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is found in large parts of the world, including Australia, New Zealand and Papua New Guinea.

Eudocima apta is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is found in large parts of Brazil. At times it migrates north into the United States. The wingspan is about 45 mm.
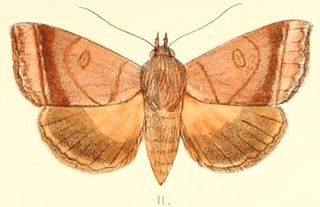
Ophiusa trapezium is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found from the Indo-Australian tropics of India, Sri Lanka to Queensland, the Bismarck Islands and New Caledonia. Adults are fruit piercers.

Eudocima phalonia, the common fruit-piercing moth, is a fruit piercing moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1763 Centuria Insectorum. It is found in large parts of the tropics, mainly in Asia, Africa and Australia but introduced into other areas such as Hawaii, New Zealand and the Society Islands. It is one of major fruit pests in the world.

Eudocima aurantia, the fruit-sucking moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Frederic Moore in 1877. It is found across south-east Asia, from Sri-Lanka to northern Queensland, Australia. It is also present on the Andamans.

Eudocima cocalus, the cocalus fruit piercing moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is found in the north-eastern part of the Himalaya, to Sundaland and east to Queensland, Australia and the Solomons.

Eudocima homaena is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Jacob Hübner in 1816. It is found in the Indian subregion, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Taiwan, the Nicobars, Peninsular Malaysia, Borneo, the Philippines and on Christmas Island. It is a major pest on orange plants.

Eudocima salaminia, the green fruit-piercing moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Pieter Cramer in 1777. It is found from India, and across south-east Asia to the Pacific Islands. In Australia it occurs in the Northern Territory, Queensland and New South Wales. The adult is a fruit piercer.

Platyja umminia is a species of moth in the family Noctuidae first described by Pieter Cramer in 1780. It is found from the Indo-Australian tropics of China, Japan, India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar to New Guinea and Queensland. It is also present on Guam. Adults have been recorded piercing fruit in Thailand and Guam.

The Erebidae are a family of moths in the superfamily Noctuoidea. The family is among the largest families of moths by species count and contains a wide variety of well-known macromoth groups. The family includes the underwings (Catocala); litter moths (Herminiinae); tiger, lichen, and wasp moths (Arctiinae); tussock moths (Lymantriinae), including the arctic woolly bear moth ; fruit-piercing moths ; micronoctuoid moths (Micronoctuini); snout moths (Hypeninae); and zales, though many of these common names can also refer to moths outside the Erebidae. Some of the erebid moths are called owlets.

Oraesia emarginata is a species of moth of the family Erebidae first described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1794. It is found in Australia, New Caledonia, Indonesia, New Guinea, Pakistan, the Philippines, India, Sri Lanka, Sulawesi, Taiwan, China, Japan, Korea and Nepal as well as Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Namibia, Nigeria, South Africa, Tanzania, the Gambia, Uganda, Oman and Yemen.

Helena "Nellie" Scott was an Australian illustrator of natural history. She was also a botanical collector who collected a number of type specimens. She and her sister Harriet Morgan (1830–1907) were the daughters of the Australian entomologist Alexander Walker Scott.

The Cocytiini are a tribe of moths in the family Erebidae. Adults of some members of the subfamily, especially in the genus Serrodes, have a proboscis capable of piercing fruit skins, allowing the moth to drink the fruit juice.

Eudocima serpentifera is a species of fruit-piercing moth in the family Erebidae first described by Francis Walker in 1858. It is found in North America.




















