A European Capital of Culture is a city designated by the European Union (EU) for a period of one calendar year during which it organises a series of cultural events with a strong pan-European dimension. Being a European Capital of Culture can be an opportunity for a city to generate considerable cultural, social, and economic benefits, and it can help foster urban regeneration, change the city's image, and raise its visibility and profile on an international scale. Multiple cities can be a European Capital of Culture simultaneously.

The Eurovision Song Contest 2002 was the 47th edition of the Eurovision Song Contest. It took place in Tallinn, Estonia, following the country's victory at the 2001 contest with the song "Everybody" by Tanel Padar, Dave Benton and 2XL. Organised by the European Broadcasting Union (EBU) and host broadcaster Eesti Televisioon (ETV), the contest was held at the Saku Suurhall on 25 May 2002. The contest was presented by Estonian opera singer Annely Peebo and actor Marko Matvere. It was the first Eurovision Song Contest held in one of the former Soviet republics.

Arboriculture is the cultivation, management, and study of individual trees, shrubs, vines, and other perennial woody plants. The science of arboriculture studies how these plants grow and respond to cultural practices and to their environment. The practice of arboriculture includes cultural techniques such as selection, planting, training, fertilization, pest and pathogen control, pruning, shaping, and removal.

An arborist, or arboriculturist, is a professional in the practice of arboriculture, which is the cultivation, management, and study of individual trees, shrubs, vines, and other perennial woody plants in dendrology and horticulture.
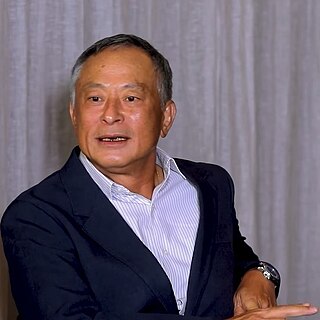
Johnnie To Kei-fung is a Hong Kong filmmaker. Popular in his native Hong Kong, To has also found acclaim overseas. Intensely prolific, To has made films in a variety of genres, though in the West he is best known for his action and crime movies, which have earned him critical respect and a cult following, which includes American filmmaker Quentin Tarantino.

The East African Community (EAC) is an intergovernmental organisation in East Africa. The EAC's membership consists of eight states: Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Federal Republic of Somalia, the Republics of Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda, South Sudan, Uganda and Tanzania. Salva Kiir Mayardit, the president of South Sudan, is the current EAC chairman. The organisation was founded in 1967, collapsed in 1977, and was revived on 7th July 2000. The main objective of the EAC is to foster regional economic integration.
The European Film Awards have been presented annually since 1988 by the European Film Academy to recognize excellence in European cinematic achievements. The awards are given in 19 categories, of which the most important is the Best Film. They are restricted to European cinema and European producers, directors and actors. The awards were officially also called the "Felix Awards" until 1997, in reference to the former award's trophy statuette, which was replaced by a feminine statuette.

Afforestation is the establishment of a forest or stand of trees in an area where there was no recent tree cover. There are three types of afforestation: Natural regeneration, agroforestry and tree plantations. Afforestation has many benefits. In the context of climate change, afforestation can be helpful for climate change mitigation through the route of carbon sequestration. Afforestation can also improve the local climate through increased rainfall and by being a barrier against high winds. The additional trees can also prevent or reduce topsoil erosion, floods and landslides. Finally, additional trees can be a habitat for wildlife, and provide employment and wood products.
The European Design Awards, also known as the ED-Awards, are annual awards presented to European designers for outstanding work in the communication design field. The ED-Awards is a joint initiative of design magazines from across Europe and endorsed by the International Council of Design. The ED-Awards are judged by a panel of representatives from fifteen European design magazines, while the winning submissions are featured in the ED-Awards Catalogue.

The East African Federation is a proposed federal sovereign state consisting of the eight member states of East African Community in the African Great Lakes region – Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Rwanda, Somalia, South Sudan, Tanzania and Uganda. The idea of this federation has existed since the early 1960s but has not yet come to fruition for several reasons. In September 2018, a committee was formed to begin the process of drafting a regional constitution, and a draft constitution for the confederation was set to be written by the end of 2021 with its implementation by 2023. However, the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted plans to draft and implement a constitution. On 9 May 2023, the drafting of the constitution resumed with a 20-day consultation with local stakeholders in Kenya.The East African Federation has not yet been established, but many steps have been taken to advance this eventual goal. Institutions and governing bodies already exist for the eventual union of these nations, with representatives from all of the related nations working together towards this common goal.
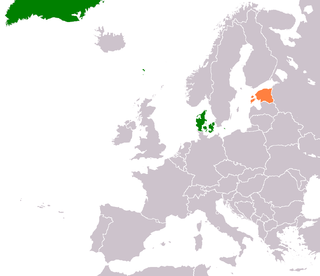
Denmark recognized and established diplomatic relations with Estonia on 5 February 1921. Relations were renewed on 24 August 1991 as Denmark has never recognized Soviet occupation of the country. Both countries are members of the European Union, NATO and the Nordic-Baltic Eight. Denmark has an embassy in Tallinn, and Estonia has an embassy in Copenhagen. Denmark has a military presence in Estonia, and Estonian Prime Minister Jüri Ratas described Denmark as a close friend in 2020.
Tallinn Black Nights Film Festival, or PÖFF, is an annual film festival held since 1997 in Tallinn, the capital city of Estonia. PÖFF is one of the largest film festivals in Northern Europe. In 2014 it was upgraded to an A-list festival by FIAPF.
Malta participated in the Eurovision Song Contest 2002 with the song "7th Wonder" written by Philip Vella and Gerard James Borg. The song was performed by Ira Losco. The Maltese entry for the 2002 contest in Tallinn, Estonia was selected through the national final Malta Song for Europe 2002, organised by the Maltese broadcaster Public Broadcasting Services (PBS). The competition consisted of a final, held on 15 and 16 February 2002, where "7th Wonder" performed by Ira Losco eventually emerged as the winning entry after scoring the most points from a five-member jury and a public televote.
The Tall Building Awards or CTBUH Awards recognizes projects and individuals who have made an extraordinary contribution to the advancement of tall buildings and urban environment, as well as achieving sustainability at the highest and broadest level. The annual awards are judged by an independent panel of experts commissioned by the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat (CTBUH), a non-profit organization headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. As of 2019, there are two individual lifetime achievement awards, The Lynn S. Beedle Lifetime Achievement Award and Fazlur Khan Lifetime Achievement Medal, and several categorical awards for projects and structures.
A business improvement district (BID) is a defined area within whichever businesses elect to pay an additional fee in order to fund projects within the district's boundaries. A BID is not a tax, as taxes fund the government. BID funds are collected and used for the exclusive benefit of the industry that pays the assessment.

The European Green Capital Award (EGCA) is an award given by the European Commission each year to a European city based on its environmental record. The award was launched on 22 May 2008, with the first award being given to Stockholm for the year 2010. The European Commission has long recognised the important role that local authorities play in improving the environment, and their high level of commitment to genuine progress. The European Green Capital Award has been conceived as an initiative to promote and reward these efforts.

The European Arboricultural Council (EAC) based in Bad Honnef, Germany is a forum where delegates from a wide range of arboricultural organizations throughout Europe meet. The goal of the EAC is to elevate the status and to raise the professional level of competence within arboriculture. This objective is carried out by liaising on matters ranging from research and education to successful tree establishment and the improvement of safe working practices.
The Holcim Foundation for Sustainable Construction is a non-profit organization dedicated to promoting sustainable practices in the fields of architecture, engineering, urban planning, and construction. Its primary aim is to identify, discuss, and democratize the latest advancements and best practices in sustainable construction worldwide.
Bjarke Ingels Group, often referred to as BIG, is a Copenhagen, New York City, London, Barcelona, Shenzhen, Oslo and Los Angeles-based group of architects and designers operating within the fields of architecture, product and landscape design, engineering and planning. The office is currently involved in a large number of projects throughout Europe, North America, Asia and the Middle East. As of 2023, the company employs 700+ people.

South Sudan became the world's newest country and Africa's 55th nation on 9 July 2011. The South Sudanese Civil War, which started in December 2013, undermined economic development achieved since independence, making humanitarian work difficult to conduct within the country. As such, South Sudan is facing economic stagnation and instability in its first 10 years after independence. Moreover, poverty is widespread throughout the country as a result of inter-communal conflict, displacement, and the negative effects of the war in Sudan on the country's oil industry.