Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. These points are usually on the surface of the Earth, and they are often used to establish maps and boundaries for ownership, locations, such as the designated positions of structural components for construction or the surface location of subsurface features, or other purposes required by government or civil law, such as property sales.

The Public Land Survey System (PLSS) is the surveying method developed and used in the United States to plat, or divide, real property for sale and settling. Also known as the Rectangular Survey System, it was created by the Land Ordinance of 1785 to survey land ceded to the United States by the Treaty of Paris in 1783, following the end of the American Revolution. Beginning with the Seven Ranges in present-day Ohio, the PLSS has been used as the primary survey method in the United States. Following the passage of the Northwest Ordinance in 1787, the Surveyor General of the Northwest Territory platted lands in the Northwest Territory. The Surveyor General was later merged with the United States General Land Office, which later became a part of the U.S. Bureau of Land Management (BLM). Today, the BLM controls the survey, sale, and settling of lands acquired by the United States.
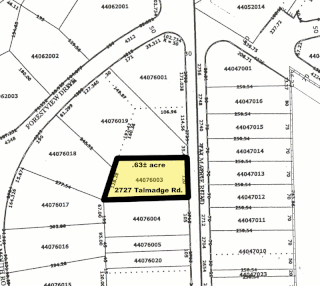
In the United States, a plat (plan) is a cadastral map, drawn to scale, showing the divisions of a piece of land. United States General Land Office surveyors drafted township plats of Public Lands Surveys to show the distance and bearing between section corners, sometimes including topographic or vegetation information. City, town or village plats show subdivisions broken into blocks with streets and alleys. Further refinement often splits blocks into individual lots, usually for the purpose of selling the described lots; this has become known as subdivision.
Torrens title is a land registration and land transfer system, in which a state creates and maintains a register of land holdings, which serves as the conclusive evidence of title of the person recorded on the register as the proprietor (owner), and of all other interests recorded on the register.
Land registration is any of various systems by which matters concerning ownership, possession, or other rights in land are formally recorded to provide evidence of title, facilitate transactions, and prevent unlawful disposal. The information recorded and the protection provided by land registration varies widely by jurisdiction.

In real estate, a land lot or plot of land is a tract or parcel of land owned or meant to be owned by some owner(s). A plot is essentially considered a parcel of real property in some countries or immovable property in other countries. Possible owners of a plot can be one or more persons or another legal entity, such as a company, corporation, organization, government, or trust. A common form of ownership of a plot is called fee simple in some countries.
A cadastral community is a cadastral subdivision of municipalities in the nations of Austria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, the Netherlands, and the Italian provinces of South Tyrol, Trentino, Gorizia and Trieste. A cadastral community records property ownership in a cadastre, which is a register describing property ownership by boundary lines of the real estate.

The Integrated Cadastral Information Society is a not-for-profit organization, created as a partnership between local government, provincial government, and major utility companies in British Columbia, Canada to share and integrate spatial data.
The Land Title and Survey Authority of British Columbia (LTSA) is a publicly accountable, statutory corporation which operates and administers the land title and survey systems in British Columbia, Canada. The LTSA delivers secure land titles through timely, efficient registration of land title interests and survey records; these services are an essential underpinning to BC’s private property market and the civil justice system, and to BC’s civic governance, taxation and Crown land management frameworks.
A Land Information System (LIS) is a geographic information system for cadastral and land-use mapping, typically used by local governments.

A unit of real estate or immovable property is limited by a legal boundary. The boundary may appear as a discontinuation in the terrain: a ditch, a bank, a hedge, a wall, or similar, but essentially, a legal boundary is a conceptual entity, a social construct, adjunct to the likewise abstract entity of property rights.
Survey of Israel - SOI is the survey and mapping department of the Israeli Ministry of Housing and Construction. It is the successor of the Survey Department of Palestine, which existed in Mandatory Palestine between 1920 and 1948.
Jordi Guimet is an Industrial Engineer. He is an expert on Information Technologies applied to land management, specially related with the Cadastre, Land Use and Urban Plan, and more recently in the fields of GIS, maps in Internet, GeoWeb and interoperability technologies.
The Association of Canada Lands Surveyors (ACLS) is the national licensing body for professionals surveying in the three Canadian territories, in the Federal parks, on Aboriginal reserves, as well as on and under the surface of Canada's oceans. It is a self-governing, non-profit, non-governmental organization that manages the activities of its members across Canada in the field of cadastral surveying.
Land administration is the way in which the rules of land tenure are applied and made operational. Land administration, whether formal or informal, comprises an extensive range of systems and processes to administer. The processes of land administration include the transfer of rights in land from one party to another through sale, lease, loan, gift and inheritance; the regulating of land and property development; the use and conservation of the land; the gathering of revenues from the land through sales, leasing, and taxation; and the resolving of conflicts concerning the ownership and the use of land. Land administration functions may be divided into four components: Juridical, regulatory, fiscal, and information management. These functions of land administration may be organized in terms of agencies responsible for surveying and mapping, land registration, land valuation and land revenue generation. The purpose and scope of this knowledge domain appear from the following introducing notes:
Cadastral surveying is the sub-field of cadastre and surveying that specialises in the establishment and re-establishment of real property boundaries. It involves the physical delineation of property boundaries and determination of dimensions, areas and certain rights associated with properties. This is regardless of whether they are on land, water or defined by natural or artificial features. It is an important component of the legal creation of properties. A cadastral surveyor must apply both the spatial-measurement principles of general surveying and legal principles such as respect of neighboring titles.

The Lantmäteriet is a government agency in Sweden acting as the national mapping, cadastral and land registration authority. It provides information on Swedish geography and property. Its main seat is in Gävle. Susanne Ås Sivborg is currently the Director General of the organisation.

The Association of British Columbia Land Surveyors (ABCLS) is a self-governing, non-profit, non-governmental organization which sets educational requirements, examines for admission, and regulates professional land surveyors within British Columbia, Canada. The ABCLS is responsible for developing bylaws and guidelines for the conduct of its members, establishing and administering entry requirements for the profession, and liaising with governmental bodies and other associations to improve the quality of the profession's service to the public.

Surveying in Australia is triangulation-based and shares many similarities with the United Kingdom, including the title deed system. However, a distinctive feature of surveying in Australia is the Torrens System, where real estate records are held in a central deposit and guaranteed by the state.
The Survey of Palestine was the government department responsible for the survey and mapping of Palestine during the British mandate period.
![Cadastral map from 1827 in Austria (Franziszeischer Kataster [de]) FR schloss kinsky.jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8b/FR_schloss_kinsky.jpg/220px-FR_schloss_kinsky.jpg)