A riding is an administrative jurisdiction or electoral district, particularly in several current or former Commonwealth countries.
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions of municipalities, school district, or political district.

The administrative geography of the United Kingdom is complex, multi-layered and non-uniform. The United Kingdom, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe, consists of England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales. For local government in the United Kingdom, England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales each have their own system of administrative and geographic demarcation. Consequently, there is "no common stratum of administrative unit encompassing the United Kingdom".

Local government in Scotland comprises thirty-two local authorities, commonly referred to as councils. Each council provides public services, including education, social care, waste management, libraries and planning. Councils receive the majority of their funding from the Scottish Government, but operate independently and are accountable to their local electorates. Councils raise additional income via the Council Tax, a locally variable domestic property tax, and Business rates, a non-domestic property tax.

The Local Government Act 1972 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Government of 1970–74.
A precinct or voting district, polling district or polling division, is a subdivision of an electoral district, typically a contiguous area within which all electors go to a single polling place to cast their ballots.

Hexham is a constituency in Northumberland represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 2024 by Joe Morris of the Labour Party. As with all constituencies, the constituency elects one Member of Parliament (MP) by the first past the post system of election at least every five years.

In the United Kingdom (UK), each of the electoral areas or divisions called constituencies elects one member to the House of Commons.

Wokingham is a constituency of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, located in the English county of Berkshire. From its creation in 1950 until 2024, it was represented solely by Conservatives, most notably, John Redwood, who held his position from 1987 until 2024 when he stepped down after the dissolution of parliament.
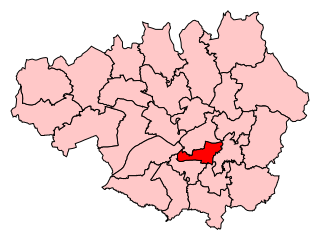
Manchester Gorton was a constituency represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament. It was the safest Labour seat in Greater Manchester by numerical majority and one of the safest in the country.

Sketty is the name of an electoral ward in the City and County of Swansea, Wales, UK. The electoral ward is coterminous with the community.
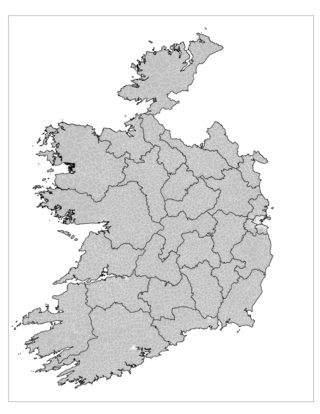
An electoral division is a legally defined administrative area in the Republic of Ireland, generally comprising multiple townlands, and formerly a subdivision of urban and rural districts. Until 1996, EDs were known as district electoral divisions in the 29 county council areas and wards in the five county boroughs. Until 1972, DEDs also existed in Northern Ireland. The predecessor poor law electoral divisions were introduced throughout the island of Ireland in the 1830s. The divisions were used as local-government electoral areas until 1919 in what is now the Republic and until 1972 in Northern Ireland.
A ward is a local authority area, typically used for electoral purposes. In some countries, wards are usually named after neighbourhoods, thoroughfares, parishes, landmarks, geographical features and in some cases historical figures connected to the area. It is common in the United States for wards to simply be numbered.
The wards and electoral divisions in the United Kingdom are electoral districts at sub-national level, represented by one or more councillors. The ward is the primary unit of English electoral geography for civil parishes and borough and district councils, the electoral ward is the unit used by Welsh principal councils, while the electoral division is the unit used by English county councils and some unitary authorities. Each ward/division has an average electorate of about 5,500 people, but ward population counts can vary substantially. As of 2021 there are 8,694 electoral wards/divisions in the UK. An average area of wards or electoral divisions in the United Kingdom is 28.109 km2 (10.853 sq mi).
The subdivisions of Belfast are a series of divisions of Belfast, Northern Ireland that are used for a variety of cultural, electoral, planning and residential purposes.

Elections to Wiltshire Council, a new unitary authority, were held on 4 June 2009.

The City of London is divided into 25 wards. The city is the historic core of the much wider metropolis of Greater London, with an ancient and sui generis form of local government, which avoided the many local government reforms elsewhere in the country in the 19th and 20th centuries. Unlike other modern English local authorities, the City of London Corporation has two council bodies: the now largely ceremonial Court of Aldermen, and the Court of Common Council.

An election to Leicestershire County Council took place on 2 May 2013 as part of the 2013 United Kingdom local elections. 55 councillors were elected from 52 electoral divisions, which returned either one or two county councillors each by first-past-the-post voting for a four-year term of office. The Conservatives held control of the council with a reduced majority of 5 seats. Despite a strong challenge from UKIP, the party only gained 2 seats whilst the Liberal Democrats lost one seat and Labour recouped some of their 2009 losses, gaining 6 seats.

The 2017 Hampshire County Council election took place on 4 May 2017 as part of the 2017 local elections in the United Kingdom. All councillors were elected from electoral divisions by first-past-the-post voting for a four-year term of office. The electoral divisions were somewhat changed from the previous election, with some being split, merged or with boundary changes. No elections were held in Portsmouth and Southampton, which are unitary authorities and hold their elections in other years. Similarly the districts within Hampshire did also not hold elections this year.
Local government in Dublin, the capital city of Ireland, is currently administered through the local authorities of four local government areas. The historical development of these councils dates back to medieval times.












