
China proper, Inner China, or the Eighteen Provinces is a term used by some Western writers in reference to the "core" regions of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China. This term is used to express a distinction between the "core" regions populated by the dominant Han population and the "frontier" regions of China, sometimes known as "Outer China". There is no fixed extent for China proper, as many administrative, cultural, and linguistic shifts have occurred in Chinese history. One definition refers to the original area of Chinese civilization, the Central Plain ; another to the Eighteen Provinces of the Qing dynasty. There is no direct translation for "China proper" in the Chinese language due to differences in terminology used by the Qing to refer to the regions. The expression is controversial among scholars, particularly in China, due to issues pertaining to territorial integrity.

Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (IMAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a small section of China's border with Russia. Its capital is Hohhot; other major cities include Baotou, Chifeng, Tongliao, and Ordos.
The Manchus are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and Qing (1636–1912) dynasties of China were established and ruled by the Manchus, who are descended from the Jurchen people who earlier established the Jin dynasty (1115–1234) in northern China. Manchus form the largest branch of the Tungusic peoples and are distributed throughout China, forming the fourth largest ethnic group in the country. They can be found in 31 Chinese provincial regions. Among them, Liaoning has the largest population and Hebei, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Inner Mongolia and Beijing have over 100,000 Manchu residents. About half of the population live in Liaoning and one-fifth in Hebei. There are a number of Manchu autonomous counties in China, such as Xinbin, Xiuyan, Qinglong, Fengning, Yitong, Qingyuan, Weichang, Kuancheng, Benxi, Kuandian, Huanren, Fengcheng, Beizhen and over 300 Manchu towns and townships. Manchus are the largest minority group in China without an autonomous region.
The Eight Banners were administrative and military divisions under the Later Jin and Qing dynasties of China into which all Manchu households were placed. In war, the Eight Banners functioned as armies, but the banner system was also the basic organizational framework of all of Manchu society. Created in the early 17th century by Nurhaci, the banner armies played an instrumental role in his unification of the fragmented Jurchen people and in the Qing dynasty's conquest of the Ming dynasty.

Mengjiang, also known as Mengkiang or the Mongol Border Land, officially referred to as the Mengjiang United Autonomous Government, was an autonomous area in Inner Mongolia, formed in 1939 as a puppet state of the Empire of Japan, then from 1940 being under the nominal sovereignty of the Reorganized National Government of the Republic of China. It consisted of the previously Chinese provinces of Chahar and Suiyuan, corresponding to the central part of modern Inner Mongolia. It has also been called Mongukuo or Mengguguo. The capital was Kalgan, from where it was under the nominal rule of Mongol nobleman Demchugdongrub. The territory returned to Chinese control after the defeat of the Japanese Empire in 1945.

Demchugdongrub, also known as Prince De, courtesy name Xixian, was a Qing dynasty Mongol prince descended from the Borjigin imperial clan who lived during the 20th century and became the leader of an independence movement in Inner Mongolia. He was most notable for being the chairman of the pro-Japanese Mongol Military Government (1938–39) and later of the puppet state of Mengjiang (1939–45), during the Second Sino-Japanese War. In the modern day, some see Demchugdongrub as a Mongol nationalist promoting Pan-Mongolism, while others view him as a traitor and a pawn of the Japanese during World War II.

Oirats or Oirds, also formerly Eluts and Eleuths, are the westernmost group of the Mongols whose ancestral home is in the Altai region of Siberia, Xinjiang and western Mongolia.
A banner is an administrative division of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region in China, equivalent to a county-level administrative division.

Hulunbuir or Hulun Buir is a region that is governed as a prefecture-level city in northeastern Inner Mongolia, China. Its administrative center is located at Hailar District, its largest urban area. Major scenic features are the high steppes of the Hulun Buir grasslands, the Hulun and Buir lakes, and the Khingan range. Hulun Buir borders Russia to the north and west, Mongolia to the south and west, Heilongjiang province to the east and Hinggan League to the direct south. Hulunbuir is a linguistically diverse area: next to Mandarin Chinese, Mongolian dialects such as Khorchin and Buryat, the Mongolic language Daur, and some Tungusic languages, including Oroqen and Solon, are spoken there.

Five Races Under One Union was one of the major principles upon which the Republic of China was founded in 1911 at the time of the Xinhai Revolution. Its central tenet was the harmonious existence under one nation of what were considered the five major ethnic groups in China: the Han, the Manchu, the Mongols, the Hui, and the Tibetans.
Chinese Mongolians can be subdivided into three groups: Mongolian citizens of ethnic Chinese background, temporary residents with Chinese citizenship, and permanent residents with Chinese citizenship. Mongolia's 1956 census counted ethnic Chinese as 1.9% of the population; the United States government estimated their proportion to be 2% in 1987, or roughly 40,000 people. The 2000 census showed 1,323 permanent residents of Chinese descent; this figure does not include naturalised citizens, temporary residents, nor illegal immigrants. Illegal immigrants from China were estimated at 10,000 in the 1990s; some use Mongolia as a transit point into Russia.

Ewenki Autonomous Banner is an autonomous banner that lies on the border between northwestern Greater Khingan and Hulun Buir grasslands and directly south of the urban district of Hailar in the prefecture-level city of Hulunbuir, People's Republic of China. The autonomous banner has an area of 19,111 km2 (7,379 sq mi), and a population of 136,832 as of 2019. The banner's seat of government is the town of Bayan Tohoi. The most populous town in the banner is Dayan, which was once Dayan Mining Area as an administrative division and is now the main part of an industrial district also named Dayan Mining Area, has an area of 443 square kilometres (171 sq mi) and a population of about 73,000.

Mongols in China or Mongolian Chinese are ethnic Mongols who were integrated into the nation-building of the Republic of China (1912–1949) after the fall of Qing Empire (1636–1911). Those not integrated broke away in the Mongolian Revolution of 1911 and again in 1921. The Republic of China recognized Mongols to be part of the Five Races Under One Union. Its successor, the People's Republic of China (1949—present), recognized Mongols to be one of the 55 ethnic minorities in China.

Mongolia under Qing rule was the rule of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China over the Mongolian Plateau, including the four Outer Mongolian aimags and the six Inner Mongolian aimags from the 17th century to the end of the dynasty. The term "Mongolia" is used here in the broader historical sense, and includes an area much larger than the modern-day state of Mongolia. Ligdan saw much of his power weakened due to the disunity of the Mongol tribes. He was subsequently defeated by the Later Jin dynasty and died soon afterwards. His son Ejei handed the Yuan imperial seal over to Hong Taiji in 1635, thus ending the rule of the Northern Yuan dynasty in Inner Mongolia. However, the Khalkha Mongols in Outer Mongolia continued to rule until they were overrun by the Dzungar Khanate in 1690, and they submitted to the Qing dynasty in 1691.
De-Sinicization is a process of eliminating or reducing Chinese cultural elements, identity, or consciousness from a society or nation. In modern contexts, it is often used in tandem with decolonization and contrasted to the assimilation process of Sinicization.

The Dzungar people were the many Mongol Oirat tribes who formed and maintained the Dzungar Khanate in the 17th and 18th centuries. Historically, they were one of the major tribes of the Four Oirat confederation. They were also known as the Eleuths or Ööled, from the Qing dynasty euphemism for the hated word "Dzungar", and as the "Kalmyks". In 2010, 15,520 people claimed "Ööled" ancestry in Mongolia. An unknown number also live in China, Russia and Kazakhstan.

Zhonghua minzu is a political term in modern Chinese nationalism related to the concepts of nation-building, ethnicity, and race in the Chinese nationality.

Manchurian nationalism or Manchu nationalism refers to the ethnic nationalism of the Manchu people or the territorial nationalism of the inhabitants of Manchuria, regardless of ethnic origin.
Anti-Mongol sentiment has been prevalent throughout history, often perceiving the Mongols to be barbaric and uncivilized people with a lack of intelligence or civilized culture.
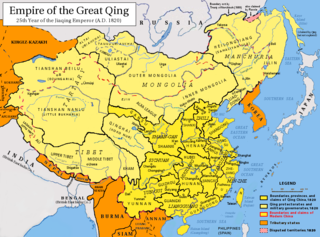
The Qing dynasty in Inner Asia was the expansion of the Qing dynasty's realm in Inner Asia in the 17th and the 18th century AD, including both Inner Mongolia and Outer Mongolia, both Inner Manchuria and Outer Manchuria, Tibet, Qinghai and Xinjiang.













