Type of human-geographic territorial entity
Development region is a designation for a territorial entity.
It is used for:
| | This article about geography terminology is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Development region is a designation for a territorial entity.
It is used for:

France is divided into eighteen administrative regions, of which thirteen are located in metropolitan France, while the other five are overseas regions.

In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry typically are described as rural. Different countries have varying definitions of rural for statistical and administrative purposes.

In the Philippines, regions are administrative divisions that primarily serve to coordinate planning and organize national government services across multiple local government units (LGUs). Most national government offices provide services through their regional branches instead of having direct provincial or city offices. Regional offices are usually but not necessarily located in the city designated as the regional center.

The regions of Greece are the country's thirteen first-level administrative entities, each comprising several second-level units, originally known as prefectures and, since 2011, as regional units.

The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical composite index of life expectancy, education, and per capita income indicators, which is used to rank countries into four tiers of human development. A country scores a higher level of HDI when the lifespan is higher, the education level is higher, and the gross national income GNI (PPP) per capita is higher. It was developed by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul-Haq and was further used to measure a country's development by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)'s Human Development Report Office.
Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 69 districts and 11 cities that are subordinate to the Republic. Out of these, 7 districts and 1 city is located within the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The districts are further divided into municipalities.

Regions of the Czech Republic are higher-level territorial self-governing units of the Czech Republic. Every region is governed by a regional council, headed by a governor (hejtman). Elections to regional councils take place every four years.

Tanzania is administratively divided into thirty-one regions.

The regional policy of the European Union (EU), also referred as Cohesion Policy, is a policy with the stated aim of improving the economic well-being of regions in the European Union and also to avoid regional disparities. More than one third of the EU's budget is devoted to this policy, which aims to remove economic, social and territorial disparities across the EU, restructure declining industrial areas and diversify rural areas which have declining agriculture. In doing so, EU regional policy is geared towards making regions more competitive, fostering economic growth and creating new jobs. The policy also has a role to play in wider challenges for the future, including climate change, energy supply and globalisation.

Togo is divided into five regions :

Per Law No.40/98/AN in 1998, Burkina Faso adhered to decentralization to provide administrative and financial autonomy to local communities. Most of these, according to their individual articles, were implemented on 2 July 2001.
Thailand is variably divided into different sets of regions, the most notable of which are the six-region grouping used in geographic studies, and the four-region grouping consistent with the Monthon administrative regional grouping system formerly used by the Ministry of Interior. These regions are the largest subdivisions of the country.

North Macedonia is divided into eight statistical regions.

The regions, formerly known as the government office regions, are the highest tier of sub-national division in England. They were established in 1994 and follow the 1974–96 county borders. They are a continuation of the former 1940s standard regions which followed the 1889–1974 administrative county borders. Between 1994 and 2011, all nine regions had partly devolved functions; they no longer fulfil this role, continuing to be used for limited statistical purposes.

The statistical regions of Slovenia are 12 administrative entities created in 2000 for legal and statistical purposes.
This article includes several ranked indicators for Chile's regions.
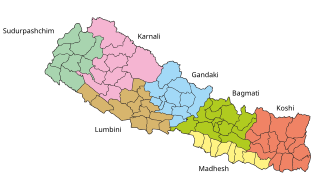
The Autonomous Nepalese Provinces were formed on 20 September 2015 in accordance with Schedule 4 of the Constitution of Nepal. The seven provinces were formed by grouping the existing districts. The current system of seven provinces replaced an earlier system where Nepal was divided into 14 administrative zones which were grouped into five development regions.