
Chocolate is a food product made from roasted and ground cacao seed kernels, that is available as a liquid, solid or paste, on its own or as a flavoring agent in other foods. Cacao has been consumed in some form since at least the Olmec civilization, and the majority of Mesoamerican people - including the Maya and Aztecs - made chocolate beverages.

Cocoa butter, also called theobroma oil, is a pale-yellow, edible fat extracted from the cocoa bean. It is used to make chocolate, as well as some ointments, toiletries, and pharmaceuticals. Cocoa butter has a cocoa flavor and aroma. Its melting point is just below human body temperature.

White chocolate is a chocolate confection, pale ivory in color, made from cocoa butter, sugar, milk solids and sometimes vanilla. White chocolate does not contain cocoa solids, which are found in other types of chocolate, such as milk chocolate and dark chocolate. It is solid at room temperature 25 °C (77 °F) because the melting point of cocoa butter, the only cocoa bean component of white chocolate, is 35 °C (95 °F).

The Dangerous Substances Directive was one of the main European Union laws concerning chemical safety, until its full replacement by the new regulation CLP Regulation (2008), starting in 2016. It was made under Article 100 of the Treaty of Rome. By agreement, it is also applicable in the EEA, and compliance with the directive will ensure compliance with the relevant Swiss laws. The Directive ceased to be in force on 31 May 2015 and was repealed by Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006.
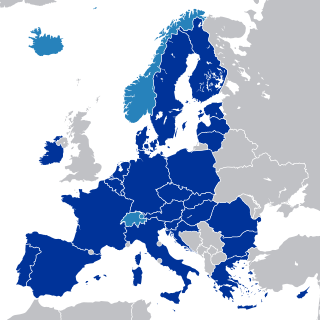
The European Single Market, Internal Market or Common Market is a single market comprising the 27 member states of the European Union (EU) as well as – with certain exceptions – Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway through the Agreement on the European Economic Area, and Switzerland through bilateral treaties. The single market seeks to guarantee the free movement of goods, capital, services, and people, known collectively as the "four freedoms".
"Big Chocolate" is a business term assigned to multi-national chocolate food producers, akin to the terms "Big Oil," "Big Pharma," and "Big Tobacco".
In the experimental (non-clinical) research arena, good laboratory practice or GLP is a quality system of management controls for research laboratories and organizations to ensure the uniformity, consistency, reliability, reproducibility, quality, and integrity of products in development for human or animal health through non-clinical safety tests; from physio-chemical properties through acute to chronic toxicity tests.

Couverture chocolate is a chocolate that contains a higher percentage of cocoa butter (32–39%) than baking or eating chocolate. This additional cocoa butter, combined with proper tempering, gives the chocolate more sheen, a firmer "snap" when broken, and a creamy mellow flavor.

Ibarra is a brand of Mexican chocolate para mesa, produced since 1925, and since 1954 produced by the company Chocolatera de Jalisco of Guadalajara, Jalisco, Mexico. The company manufactures other chocolate products, but Ibarra table chocolate is its best-known product, with presence throughout Mexico as well as international markets, mainly in the Americas, but also in parts of Europe. It is often found in gourmet shops.

Compound chocolate is a product made from a combination of cocoa, vegetable fat and sweeteners. It is used as a lower-cost alternative to true chocolate, as it uses less-expensive hard vegetable fats such as coconut oil or palm kernel oil in place of the more expensive cocoa butter. It may also be known as "compound coating" or "chocolatey coating" when used as a coating for candy. It is often used in less expensive chocolate bars to replace enrobed chocolate on a product.

Polyglycerol polyricinoleate (PGPR), E476, is an emulsifier made from glycerol and fatty acids. In chocolate, compound chocolate and similar coatings, PGPR is mainly used with another substance like lecithin to reduce viscosity. It is used at low levels, and works by decreasing the friction between the solid particles in molten chocolate, reducing the yield stress so that it flows more easily, approaching the behaviour of a Newtonian fluid. It can also be used as an emulsifier in spreads and in salad dressings, or to improve the texture of baked goods. It is made up of a short chain of glycerol molecules connected by ether bonds, with ricinoleic acid side chains connected by ester bonds.

Chocolate is a food product made from roasted and ground cocoa pods mixed with fat and powdered sugar to produce a solid confectionery. There are several types of chocolate, classified primarily according to the proportion of cocoa and fat content used in a particular formulation.
The Waste Incineration Directive, more formally Directive 2000/76/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 4 December 2000 on the incineration of waste, was a Directive issued by the European Union and relates to standards and methodologies required by Europe for the practice and technology of incineration. The aim of this Directive is to minimise the impact of negative environmental effects on the environment and human health resulting from emissions to air, soil, surface and ground water from the incineration and co-incineration of waste. The requirements of the Directive were developed to reflect the ability of modern incineration plants to achieve high standards of emission control more effectively. The Directive was replaced by the Industrial Emissions Directive with effect from 7 January 2014
Hershey Kissables were a chocolate candy sold by The Hershey Company from 2005 to 2009. Comparable to M&M's, Hershey Kissables were shaped like miniature Hershey's Kisses and were coated in a thick sugar shell.

As of 2009, the European Union had issued two units of measurement directives: In 1971 it issued Directive 71/354/EEC which required EU member states to standardise on the International System of Units (SI) rather than use a variety of CGS and MKS units then in use. The second, which replaced the first, was Directive 80/181/EEC made in 1979 and amended in 1984, 1989, 2000 and 2009. It issued a number of derogations to the United Kingdom and Ireland based on the former directive.

The CLP Regulation is a European Union regulation from 2008, which aligns the European Union system of classification, labelling and packaging of chemical substances and mixtures to the Globally Harmonised System (GHS). It is expected to facilitate global trade and the harmonised communication of hazard information of chemicals and to promote regulatory efficiency. It complements the 2006 Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) Regulation and replaces the current system contained in the Dangerous Substances Directive (67/548/EEC) and the Dangerous Preparations Directive (1999/45/EC).
AMBAO is a certification mark for chocolate created by the Belgian Ministry of Economic Affairs.

Commission v Italy (2003) C-14/00 is an EU law case, concerning the free movement of goods in the European Union.











