Jerdon's day gecko is a species of gecko, a lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is endemic to India and Sri Lanka.
The minor snake-eyed skink is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is native to Asia.

Riopa guentheri, commonly known as Günther's supple skink and Günther's writhing skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to India.
Eutropis beddomei, commonly known as Beddome's mabuya or Beddome's skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is native to India and Sri Lanka.

Eutropis bibronii, also known commonly as Bibron's mabuya, Bibron's skink, and the seashore skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is native to India and Sri Lanka.

Eutropis multifasciata, commonly known as the East Indian brown mabuya, many-lined sun skink, many-striped skink, common sun skink or (ambiguously) as golden skink, is a species of skink.
Ristella beddomii, commonly known as Beddome's cat skink and Beddome's ristella, is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is native to southwestern India.
Ristella guentheri, commonly known as Günther's ristella and Gunther's cat skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to India.

Ristella rurkii, commonly known as Rurk's ristella, is a species of skink endemic to the Western Ghats of southern India. It is a small, insectivorous, diurnal skink found in shola grasslands and rainforests of hills ranges in parts of Tamil Nadu and Kerala states of India.

Ristella travancorica, commonly known as the Travancore cat skink or the Travancore ristella, is a species of skink endemic to the Western Ghats in India.

Wright's skink, also known commonly as Wright's mabuya, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Seychelles. There are two recognized subspecies.

Eutropis is a genus of skinks belonging to the subfamily Mabuyinae. For long, this genus was included in the "wastebin taxon" Mabuya; it contains the Asian mabuyas. They often share their habitat with the related common skinks (Sphenomorphus), but they do not compete significantly as their ecological niches differ. This genus also contains the only member of the subfamily to occur in Australasia, the many-lined sun skink, whose wide range includes New Guinea.

Trachylepis boettgeri, commonly known as Boettger's mabuya, is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Madagascar.

Chioninia vaillantii, also known commonly as Vaillant's mabuya or Vaillant's skink, is a species of skink in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to the Cape Verde Islands. There are two recognized subspecies.

Trachylepis bocagii, also known commonly as Bocage's skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is native to southern Africa.
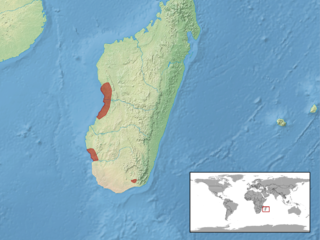
Trachylepis dumasi is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Madagascar.

Trachylepis gravenhorstii, also known commonly as Gravenhorst's mabuya, is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Madagascar.

Kaestlea beddomii, also known as Beddome's ground skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to the Western Ghats of India.
Ophiomorus blanfordii, also known commonly as Blanford's snake skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is native to Western Asia and South Asia.















