
The Stereaceae are a family of corticioid fungi in the Russulales order. Species in the family have a widespread distribution, are lignicolous or terrestrial, and typically saprobic. According to the Dictionary of the Fungi, the family contains 22 genera and 125 species.

Exobasidium is a genus of fungi in the family Exobasidiaceae. The genus has a widespread distribution, especially in northern temperate regions, and contains about 50 species. Many of the species in this genus are plant pathogens that grow on Ericaceae. The comprising fungi are parasitic in nature, especially on various heath plants where they cause galls.

Rhizopogonaceae are a family of fungi in the order Boletales. The family, first named and described by botanists Ernst Albert Gäumann and Carroll William Dodge in 1928, contains 2 genera and 151 species. The genus Fevansia, formerly thought to belong in the Rhizopogonaceae, was found to belong in the Albatrellaceae in a molecular phylogenetics study.

Schizoporaceae are a family of fungi in the order Hymenochaetales. These are saprobic, and cause white rots of standing and fallen wood of coniferous and broadleaved trees. According to one 2008 estimate, the family contains 14 genera and 109 species.

The Phacidiaceae are a family of fungi in the order Helotiales. According to a 2008 estimate, the family contained seven genera and 148 species.

The Leotiaceae are a family of fungi in the order Leotiales. Species in this family are saprobic, and have a wide distribution, especially in temperate regions. The family contains 7 genera and 34 species.

The Cenangiaceae are a family of fungi in the order Helotiales.

The Helotiaceae are a family of fungi in the order Helotiales. The distribution of species in the family are widespread, and typically found in tropical areas. There are 117 genera and 826 species in the family.

The Bulgariaceae are a family of fungi in the order Helotiales. Species are found in northern and southern temperate regions. The family contains four genera and seven species.

The Peniophoraceae are a family of fungi in the order Russulales. Species of this family have a cosmopolitan distribution and are mostly saprobic, causing rots of standing and fallen wood. According to a 2008 estimate, the family contains 7 genera and 88 species.
The Pyxidiophorales are an order of fungi in the class Laboulbeniomycetes. The order was created in 2001 to contain the single family Pyxidiophoraceae, circumscribed in 1971. The Pyxidiophoraceae are mostly coprophilous fungi that associate with mites and other arthropods. The type genus, Pyxidiophora, the largest genus of the family, has about 20 species.

The Choanephoraceae are a family of fungi in the order Mucorales. Members of this family are found mostly in the tropics or subtropics, and only rarely in temperate zones. The family currently includes species formerly classified in the family Gilbertellaceae.
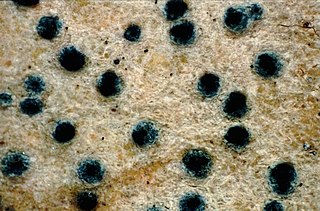
The Pyrenulaceae are a family of fungi in the order Pyrenulales. The family was first named by German botanist Gottlob Ludwig Rabenhorst in 1870. Species in the family have a widespread distribution, but are especially prevalent in the tropics, where they grow lichenized with green algae on bark.
The Cryptobasidiaceae are a family of fungi in the Basidiomycota, Exobasidiales order. Species in the family have a widespread distribution, especially in neotropical areas. Members of the Cryptobasidiaceae are plant pathogens that grow parasitically on the leaves, stems and fruits of plants, especially those in the family Lauraceae.

The Graphiolaceae are a family of fungi in the Basidiomycota, Exobasidiales order. Species in the family have a widespread distribution, especially in warm temperate and tropical areas. Members of the Graphiolaceae are plant pathogens that grow biotrophically on the leaves of plants in the Palmae family.
Endobasidium is a genus of fungi in the Exobasidiaceae family. The genus is monotypic and contains the single species Endobasidium clandestinum, found in Samarkand and named by Nikolay Nikolayevich Speshnev in 1901.
Muribasidiospora is a genus of fungi in the Exobasidiaceae family. The genus contains four species that are found in India and Taiwan.

The Chaconiaceae are a family of rust fungi in the order Pucciniales. The family contained 8 genera and 75 species in 2008. By 2020, there were 8 genera and 84 species.

The Leptosphaeriaceae are a family of fungi in the order Pleosporales. The family was circumscribed by mycologist Margaret E. Barr in 1987. According to the Dictionary of the Fungi, the family contained 8 genera and 302 species. The family has a widespread distribution, but is especially prevalent in temperate regions. Species are either saprobic or grow as nectrotrophs on the stems or leaves of plants.
The Microthyriales are an order of sac fungi. According to a 2008 estimate, the order contains 3 families, 62 genera and 323 species. Species in the Microthyriales have small, flattened fruit bodies with one of more central slits, and are saprobic or epiphytic on the leaves and stems of plants.















